Kubeseal VSCode Extension






📚 Table of Contents
🚀 Installation
Install from VS Code Marketplace:
- Open VS Code
- Go to Extensions (Ctrl+Shift+X)
- Search for "Kubeseal VSCode"
- Click Install
Or install directly:
Recommended Extensions:
For the best Kubernetes development experience, we recommend installing:
- Kubernetes - Provides Kubernetes cluster management, syntax highlighting, and IntelliSense for Kubernetes YAML files.
✨ Features
- 🔐 Encrypt Secrets: Right-click on YAML files containing Kubernetes secrets to encrypt them using kubeseal
- 🔓 Decrypt Secrets: Retrieve the original content of sealed secrets from your Kubernetes cluster
- 📝 Base64 Encoding/Decoding: Encode and decode base64 values in Kubernetes secret data fields
- 📂 Certificate Folder Management: Configure a folder containing multiple kubeseal certificates and easily switch between them
- 🔄 Active Certificate Selection: Click on the status bar to select which certificate to use for encryption
- 🎯 Context Menu Integration: Access kubeseal operations directly from the file explorer and editor context menus
🔄 How It Works
This extension integrates with the Bitnami Sealed Secrets workflow for securing Kubernetes secrets:
Encryption Workflow
┌─────────────────────┐
│ Plain Secret YAML │ (your-secret.yaml)
│ kind: Secret │
└──────────┬──────────┘
│
│ Right-click → "Encrypt with Kubeseal"
│
▼
┌─────────────────────┐
│ kubeseal CLI │ Uses selected certificate
│ Encryption │ from configured folder
└──────────┬──────────┘
│
▼
┌─────────────────────┐
│ SealedSecret YAML │ (your-secret-sealed.yaml)
│ kind: SealedSecret │ ✓ Safe to commit to Git
└─────────────────────┘
Key Points:
- Requires
kubeseal binary in PATH
- Uses certificate from your configured folder
- Original secret remains unchanged
- Creates new file with
-sealed suffix
- Encrypted secrets are safe to store in version control
Decryption Workflow
┌─────────────────────┐
│ SealedSecret YAML │ (deployed to cluster)
│ kind: SealedSecret │
└──────────┬──────────┘
│
│ Right-click → "Decrypt Secret"
│
▼
┌─────────────────────┐
│ kubectl CLI │ Fetches from cluster using
│ Get Secret │ namespace and name from YAML
└──────────┬──────────┘
│
▼
┌─────────────────────┐
│ Plain Secret YAML │ (your-secret-unsealed.yaml)
│ kind: Secret │ Retrieved from cluster
└─────────────────────┘
Key Points:
- Requires
kubectl binary in PATH
- Requires cluster access with proper permissions
- SealedSecret must be deployed to the cluster first
- Extension extracts namespace/name from SealedSecret YAML
- Creates new file with
-unsealed suffix
Base64 Encoding/Decoding Workflow
Before Encoding: After Encoding:
┌──────────────────┐ ┌──────────────────┐
│ kind: Secret │ │ kind: Secret │
│ data: │ Encode │ data: │
│ username: admin│ ──────▶ │ username: YWRt │
│ password: 123 │ │ password: MTIz │
└──────────────────┘ └──────────────────┘
Decoding reverses the process ◀──────
Key Points:
- Works on local YAML files (no cluster needed)
- Automatically detects already-encoded values
- Preserves binary data when decoding
- Useful before encrypting secrets
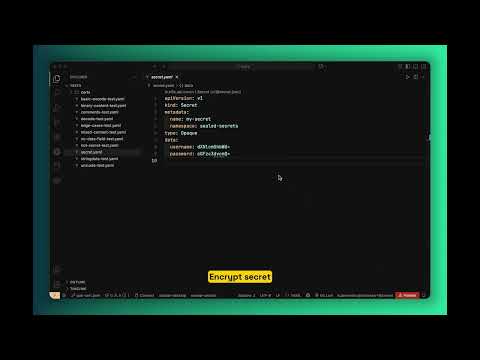
🎥 Video Demonstration
Watch how to use the Kubeseal VS Code extension in action:
📋 Requirements
Important: You must have access to your Kubernetes cluster before using this extension, especially for decryption.
Development Requirements:
- Node.js 20+ (for development and building)
Runtime Requirements:
kubeseal binary must be installed and accessible in your PATHkubectl binary must be installed and configured for cluster access- For encryption: A kubeseal certificate folder containing certificate files (
.pem, .crt, or .cert)
- For decryption: Access to the Kubernetes cluster where the secret is deployed
🛠️ Setup
- Install the
kubeseal binary from sealed-secrets releases
- Install this extension from the VS Code marketplace
- Configure your certificate folder using the command palette: "Set Kubeseal Certificate Folder"
- Select an active certificate by clicking on the status bar item
📖 Usage
Note: You must have access to your Kubernetes cluster before using the extension. Decryption will not work unless your kubectl is configured and you have the necessary permissions.
Typical Workflow
Here's a typical workflow for managing secrets with this extension:
- Prepare your secret - Create a Kubernetes Secret YAML file with plain text values
- Encode values (optional) - Use "Encode Base64 Values" if your values are in plain text
- Set up certificate - Configure your certificate folder and select an active certificate
- Encrypt - Use "Encrypt with Kubeseal" to create a SealedSecret
- Commit safely - The encrypted SealedSecret can be safely committed to Git
- Deploy - Apply the SealedSecret to your Kubernetes cluster
- Decrypt (if needed) - Use "Decrypt Secret" to retrieve the original secret from the cluster
🔐 Encrypting Secrets
- Create a Kubernetes secret YAML file
- Right-click on the file in the explorer or editor
- Select "Encrypt with Kubeseal"
- The encrypted file will be saved with
-sealed suffix
Example:
# input: my-secret.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: my-secret
namespace: default
data:
username: YWRtaW4=
password: cGFzc3dvcmQ=
# output: my-secret-sealed.yaml
apiVersion: bitnami.com/v1alpha1
kind: SealedSecret
metadata:
name: my-secret
namespace: default
spec:
encryptedData:
username: AgBy3i4OJSWK+PiTySYZ...
password: AgAKqjbxK9...
🔓 Decrypting Secrets
- Right-click on a sealed secret YAML file
- Select "Decrypt Secret"
- The extension will retrieve the actual secret from your Kubernetes cluster using
kubectl
- The decrypted secret will be saved with
-unsealed suffix
Example:
# input: my-secret-sealed.yaml (must be deployed to cluster)
apiVersion: bitnami.com/v1alpha1
kind: SealedSecret
metadata:
name: my-secret
namespace: default
spec:
encryptedData:
username: AgBy3i4OJSWK+PiTySYZ...
password: AgAKqjbxK9...
# Extension extracts: namespace="default", name="my-secret"
# Runs: kubectl get secret my-secret -n default -o yaml
# output: my-secret-unsealed.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: my-secret
namespace: default
data:
username: YWRtaW4=
password: cGFzc3dvcmQ=
Requirements:
- The sealed secret has been deployed to your cluster
- Your
kubectl is configured to access the correct cluster
- You have permissions to read secrets in the target namespace
🔧 Managing Certificates
Setting Certificate Folder
- Use Command Palette:
Ctrl+Shift+P → "Set Kubeseal Certificate Folder"
- Or configure in VS Code settings:
kubeseal.certsFolder
Selecting Active Certificate
- Look at the status bar at the bottom of VS Code
- Click on the certificate name (or "(not selected)" if none is active)
- Choose from the list of available certificates in your configured folder
- The selected certificate will be used for all encryption operations
Note: If no certificate folder is configured, clicking the status bar will prompt you to set one up.
📝 Base64 Encoding/Decoding
The extension provides utilities for working with base64 encoded values in Kubernetes secrets:
Encode Base64 Values
- Right-click on a Kubernetes secret YAML file
- Select "Encode Base64 Values"
- All plain text values in the
data field will be base64 encoded
Example:
# Before encoding:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: my-secret
data:
username: admin # plain text
password: password123 # plain text
# After encoding:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: my-secret
data:
username: YWRtaW4= # base64 encoded
password: cGFzc3dvcmQxMjM= # base64 encoded
Decode Base64 Values
- Right-click on a Kubernetes secret YAML file
- Select "Decode Base64 Values"
- All base64 encoded values in the
data field will be decoded to plain text
Note: The extension automatically detects which values are already encoded/decoded and skips them to prevent double encoding/decoding.
⚙️ Configuration
The extension provides the following settings:
kubeseal.certsFolder: Path to the folder containing kubeseal certificate files (*.pem, *.crt, *.cert)kubeseal.activeCertFile: Filename of the currently active certificate in the certs folder
🎮 Commands
kubeseal.encrypt: Encrypt with Kubesealkubeseal.decrypt: Decrypt Secretkubeseal.setCertFolder: Set Kubeseal Certificate Folderkubeseal.selectCertificate: Select Certificatekubeseal.encodeBase64: Encode Base64 Valueskubeseal.decodeBase64: Decode Base64 Values
🛠️ Getting Help
If you encounter any issues or have questions, feel free to:
⚠️ Known Issues
- Decryption may fail if the
kubectl context is not properly configured.
- Ensure the
kubeseal binary is compatible with your Kubernetes cluster version.
For a complete list of changes, see the Changelog.
🤝 Contributing
Contributions are welcome! Please feel free to submit a Pull Request.
📄 License
This project is licensed under the MIT License - see the LICENSE file for details.
🔗 Links







