


VSTosc
General commands to boost productivity:
Specialized commands for R development:
- knitRmd – Render current file via
rmarkdown::render
- updateRDocstring – Generate roxygen2 docs for currently
selected R function
- testRFunction – Run
testthat file of currently selected R
function
Installation
Open the Extensions Tab in VSCode's activity bar and search for vstosc. Then
click install.

Usage
Hit F1 or Ctrl+Shift+P to open the Command Palette and then choose a
command.
For often used commands you might want to define a shortcut as shown below:
Commands
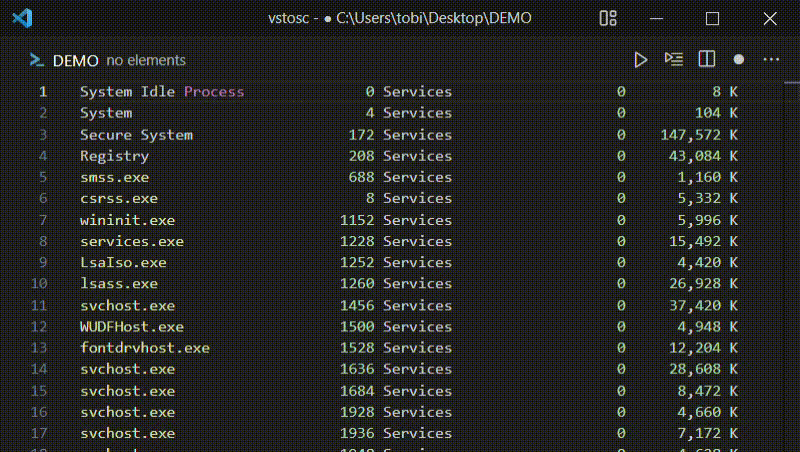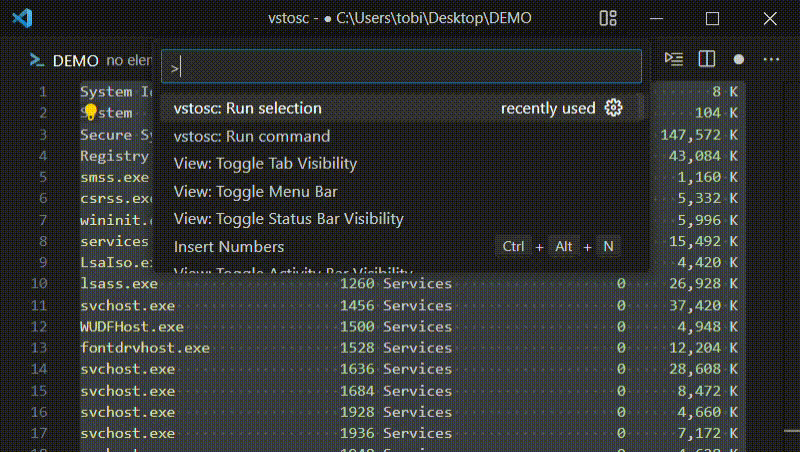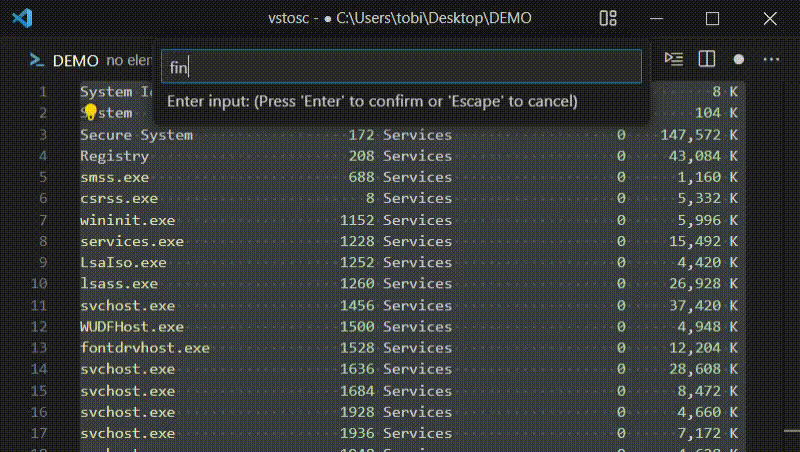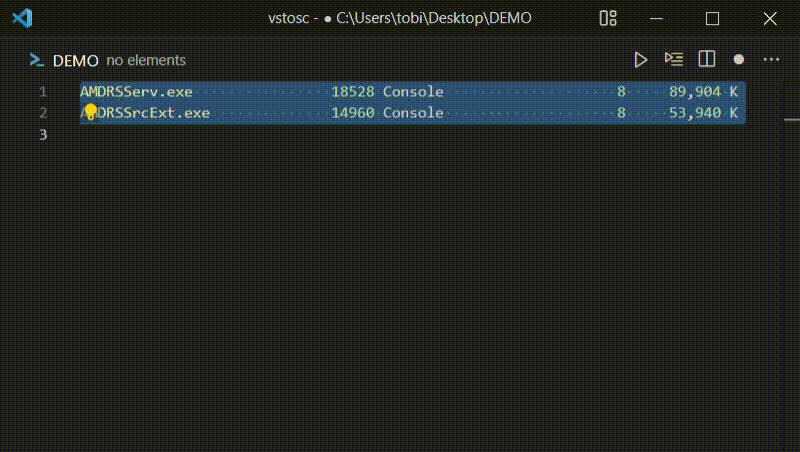
runCommand
Opens an input box asking the user for a command. The entered command runs
inside a configurable shell and the output (with trailing whitespace removed) is
inserted at the current cursor position. If text is selected, it is passed as
stdin to the command and replaced with the output (with trailing whitespace
removed).
The following settings can be used to customize the shell used for command
execution:
vstosc.shell.windows – default cmd.exe /q /cvstosc.shell.mac – default /bin/sh -evstosc.shell.linux – default /bin/sh -e
Each command is written to a temporary file, which is then executed using the
configured shell. When customizing the shell command, make sure it accepts the
pattern <shell-command> <script-file>, where <script-file> is the temporary
file created by the extension. For example, to run everything through Git Bash
on Windows, set vstosc.shell.windows to "C:/Program Files/Git/bin/bash.exe" -lc.
runSelection
Executes the current selection using the same shell configuration described
under runCommand (defaults: /bin/sh -e on macOS/Linux, cmd.exe /q /c on Windows) and replaces the selection with the command output (with
trailing whitespace removed).

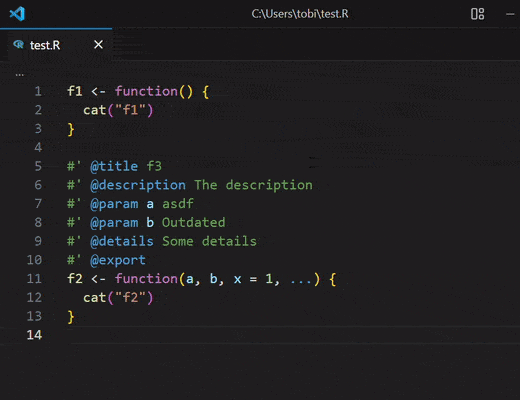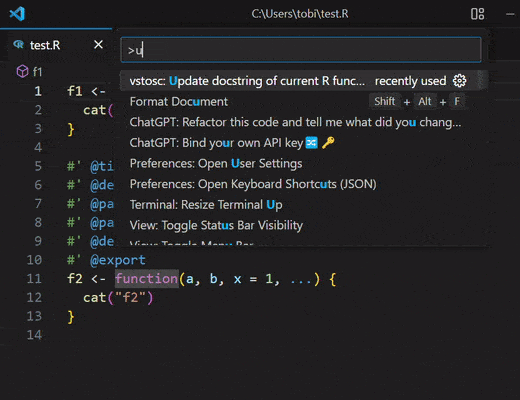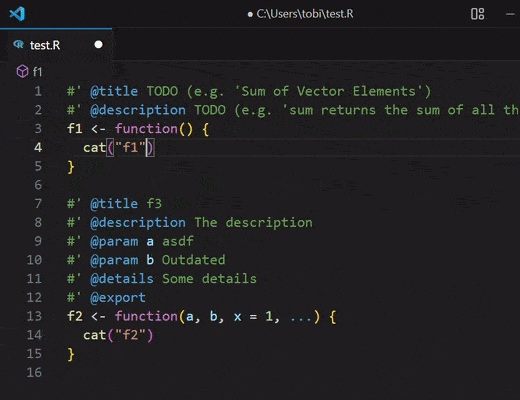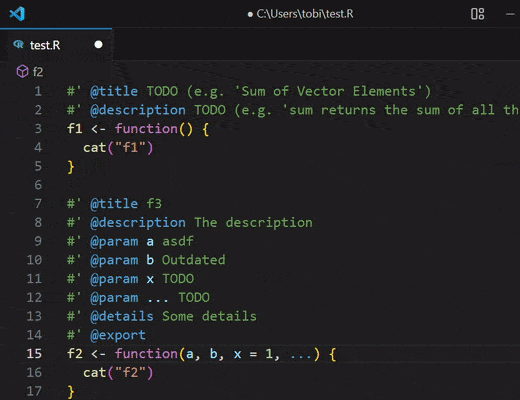
updateRDocstring
Updates the roxygen2 docstring of the R function
the cursor currently is in.
⚠️WARNING: This command requires the R package
toscutil (version 2.7.1 or greater). For
now you have to install it by hand using command: install.packages("toscutil")
from within a running R session.
🗒️NOTE: In case a function is defined multiple times in the same file. The
generated roxygen2 docstring will always be based on the last definition of the
function.
testRFunction
Execute test cases for the R function where the cursor is currently positioned.
- If the file path of the currently edited file matches glob pattern
{package_dir}/tests/testthat/test[-_]*.R, command
testthat::test_file("${currentFilePath}") is sent to the currently active
terminal.
- If the currently edited file matches glob pattern
{package_dir}/**/*.R, the
name of the currently edited function is determined and command
testthat::test_file("{package_dir}/tests/testthat/test-{currentFunctionName}.R")
is sent instead.
- If the current editor matches neither of the above glob patterns or no
terminal is active, nothing happens (except for an info message explaining
why).
To speed up the develop-test-cycle even more, you might want to define a
shortcut for this command. For instance, I have set up the following binding in
my keybindings.json file:
{
"key": "ctrl+shift+t",
"command": "vstosc.testRFunction",
"when": "editorTextFocus && editorLangId == 'r'"
}
knitRmd
Sends the following text to the currently active console:
rmarkdown::render("<path-of-currently-active-file")
mathMode
Inserts ~$$ at the current position and places the cursor in between $$. A
potential leading space is removed.
toggleEditorTerminalFocus
Smart focus switching between terminal and editor with Ctrl+ `
This command replaces the default VS Code Ctrl+ ` behavior with intelligent
bidirectional focus switching. Instead of just opening the terminal, it toggles
between your terminal and editor based on what was previously focused, creating
a seamless workflow for rapid switching during development.
The command uses focus tracking to remember whether you were last working in the
terminal or editor, ensuring the toggle behavior works correctly even when
accessed through the Command Palette.
goToAnything
Allows keyboard-based navigation to any document position (line[:column]) or
VS Code UI area. UI targets jump instantly, while line/column entries follow the
classic Go to Line/Column flow (press Enter to confirm).
Default shortcut: Alt+G (Option+G on macOS).
Letters map to the following locations:
| Key |
Destination |
a |
Active editor group |
b |
Sidebar |
c |
Secondary sidebar |
d |
Debug console |
e |
Explorer |
f |
Search |
g |
Source control |
i |
AI Chat |
j |
Settings |
J |
Settings (JSON) |
k |
Keyboard shortcuts |
K |
Keyboard shortcuts (JSON) |
o |
Outline |
p |
Panel |
s |
Status bar |
t |
Terminal |
x |
Extensions |
Numbers behave like VS Code's built-in Go to Line/Column feature, e.g. 120
jumps to line 120 and 42:15 jumps to line 42, column 15 (1-based). The options
list is displayed beneath the input so you can keep the key hints visible while
typing.
insertNumbers
Generates and inserts number sequences at the current cursor position based on a
specification. The command opens an input dialog where you can specify the
number range and step size.
Supported formats:
a:b - Creates integers from a to b (inclusive)
- Example:
3:7 generates: 3, 4, 5, 6, 7
- Example:
7:3 generates: 7, 6, 5, 4, 3 (descending)
- Example:
-2:2 generates: -2, -1, 0, 1, 2
a:b:s - Creates numbers from a to b with step size s (inclusive)
- Example:
2:10:2 generates: 2, 4, 6, 8, 10
- Example:
0:1:0.25 generates: 0, 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, 1
- Example:
10:2:-2 generates: 10, 8, 6, 4, 2 (descending with negative
step)
The numbers are inserted one per line at the cursor position. If text is
selected, it will be replaced with the generated numbers.
Contribute
- Clone this repo and open the folder in VSCode
- Run
npm install to install all dependencies
- Modify package.json and
src/extensions.ts as required (ChatGPT is your friend).
- Hit F5 to run the extension in a new Extension Development Host window.
- See Debugging the
extension
in case something isn't working as expected.
- Increase the version in package.json according to the rules
of Semantic versioning
- Push your changes and tag the commit (see section publish for
details about the publishing process triggered by tagging a commit from the
main branch)
Testing
To run the tests locally, execute the following commands in the extension root
folder:
npm install
npm test
Some background: automated tests run through VS Code's integration harness:
src/test/runTest.ts boots a disposable VS Code instance via
@vscode/test-electron, loads this extension from the workspace root, and
executes the Mocha suite defined in src/test/suite/extension.test.ts (compiled
into out/test/suite). The suite can rely on helper fixtures such as
test_data/functions.R when exercising R-specific
behavior. To run everything locally, execute npm test, which first compiles
the sources and runs ESLint (pretest), then launches the integration tests.
The downloaded VS Code binaries are cached in .vscode-test/ so subsequent runs
re-use them.
Publish
Whenever a commit from the main branch receives a tag, the
publish action is triggered, which uploads the
extension vsce to the VSCode
Marketplace. In
case the pipeline fails and you want to do the publishing manually, the
following steps would be required:
- Run
npm install -g @vscode/vsce to install the Visual Studio Code Extension
Tool.
- Run
vsce package to build the new package in VSCode package format .vsix
- Login to the VSCode
Marketplace
using a valid access token for the Azure DevOps Organization
toscm using command
vsce login toscm
- Publish the extension using command
vsce publish
For further guidelines see VSCode Extension
API and VSCode Publishing
Extensions.



