vs-rest-api



A Visual Studio Code (VS Code) extension that provides a REST API to control your editor.

Table of contents
- Install
- How to use
- Documentation
Install [↑]
Launch VS Code Quick Open (Ctrl+P), paste the following command, and press enter:
ext install vs-rest-api
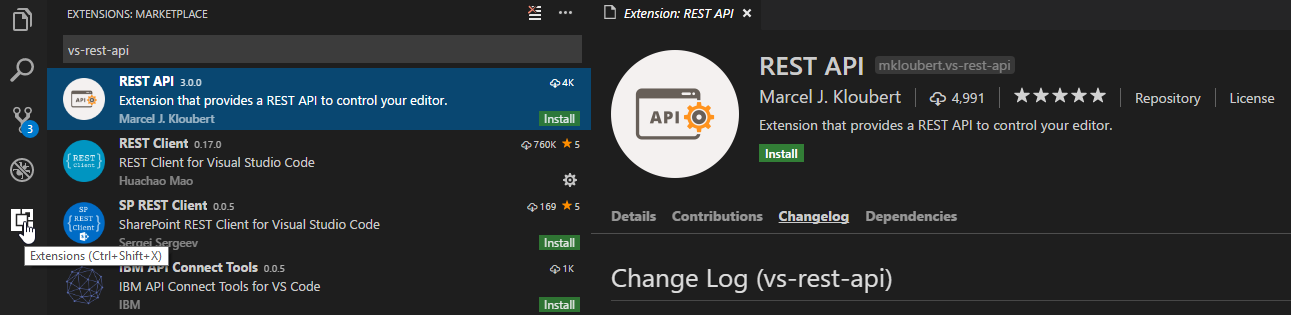
Or search for things like vs-rest-api in your editor:
How to use [↑]
Settings [↑]
Open (or create) your settings.json in your .vscode subfolder of your workspace.
Add a deploy section:
{
"rest.api": {
"autoStart": true,
"openInBrowser": true,
"port": 1781
}
}
This example will run the host on port 1781 on startup and opens the URL https://localhost:1781/ in your default application, like your browser.
Users [↑]
By default anyone can access the API with read-only access.
You can define one or more users, that can access the API via Basic Authentification:
{
"rest.api": {
// ...
"guest": false,
"users": [
{
"name": "mkloubert",
"password": "P@sswort123!"
},
{
"name": "jlpicard",
"password": "NCC-1701-D"
},
{
"name": "neo",
"password": "Follow_the_white_rabbit"
}
]
}
}
By default any user (and guest) have read-only access.
HTTPs [↑]
For secure access, you can define a SSL certificate:
{
"rest.api": {
// ...
"ssl": {
"cert": "./api-host.crt",
"key": "./api-host.key"
}
}
}
Build-in endpoints [↑]
Visit the wiki to get more information about build-in endpoints.
| Name |
Description |
| /api/appglobals |
Accesses permanent data for all users outside the current workspace. |
| /api/appstate |
Accesses permanent data for the current user / guest outside the current workspace. |
| /api/commands |
Accesses commands. |
| /api/cron |
Accesses cron jobs. |
| /api/deploy |
Accesses features to deploy files. |
| /api/editor |
Accesses resources of the active editor (tab). |
| /api/editors |
Accesses resources of all opened editors. |
| /api/extensions |
Accesses resources of all known extensions. |
| /api/files |
Accesses resources for handling file operations. |
| /api/globals |
Accesses permanent data for all users. |
| /api/html |
Accesses resources for handling HTML documents. |
| /api/languages |
Accesses resources of all known languages. |
| /api/outputs |
Accesses resources of output channels handled by the extension. |
| /api/popups |
Accesses resources for handling popup messages. |
| /api/state |
Accesses permanent data for the current user / guest. |
| /api/whiteboard |
Accesses resources for handling a virtual whiteboard. |
| /api/workspace |
Accesses or manipulates resources, like files or folders, inside the current workspace. |
Custom endpoints [↑]
Detailed information can be found at the wiki. Otherwise...
You can define custom endpoints that are executed via script.
Define one ore more regular expressions in your settings and the scripts that should be executed, if a pattern matches:
{
"rest.api": {
// ...
"endpoints": {
"myendpoint": {
"script": "./my-endpoint.js",
"options": "Hello!"
}
}
}
}
The ./my-endpoint.js must contain a public function with the name of the current HTTP request method (upper case).
For example if you want to make a simple GET request
GET /api/myendpoint
your script should look like this:
exports.GET = function(args) {
// access VS Code API (s. https://code.visualstudio.com/Docs/extensionAPI/vscode-api)
var vscode = require('vscode');
// access Node.js API provided by VS Code
// s. (s. https://nodejs.org/api/)
var fs = require('fs');
// access an own module
var myModule = require('./my-module.js');
// access a module used by the extension:
// s. https://mkloubert.github.io/vs-rest-api/modules/_helpers_.html
var helpers = args.require('./helpers');
// s. https://mkloubert.github.io/vs-rest-api/modules/_host_helpers_.html
var hostHelpers = args.require('./host/helpers');
// access a module that is part of the extentsion
// s. https://github.com/mkloubert/vs-rest-api/blob/master/package.json
var glob = args.require('glob');
// access the data from the settings
// from the example above this is: "Hello!"
var opts = args.options;
// share / store data (while current session)...
// ... for this script
var myState = args.state;
args.state = new Date();
// ... with other scripts of this type
args.globalState['myEndpoint'] = new Date();
// ... with the whole workspace
args.workspaceState['myEndpoint'] = new Date();
// if you want to return an AJAX response object:
// s. https://mkloubert.github.io/vs-rest-api/interfaces/_contracts_.apiresponse.html
{
args.response.code = 666; // the response code (not the HTTP response code!)
args.response.msg = 'Result of the evil!'; // a custom message for more information
args.response.data = {
'mk': 23979,
'TM': '5979'
};
}
// if you want to return custom content
// instead of the object in 'args.response'
// s. https://mkloubert.github.io/vs-rest-api/interfaces/_contracts_.apimethodarguments.html#setcontent
{
var html = fs.readFileSync('/path/to/my/file.html');
// open HTML document in new tab (for reports e.g.)
args.openHtml(html.toString('utf8'), 'My HTML document from "file.html"').then(function() {
// HTML opened
}, function(err) {
// opening HTML document failed
});
args.setContent(html, 'text/html');
}
// deploys 'index.html' to 'My SFTP server'
// s. https://github.com/mkloubert/vs-deploy
args.deploy(['./index.html'], ['My SFTP server']).then(function() {
// file deployed
}, function(err) {
// deployment failed
});
// custom HTTP status code
args.statusCode = 202;
// ...
}
The args parameter of the function uses the ApiMethodArguments interface.
You can return a Promise for async executions or nothing for sync executions (as in this example).
You are also able to define functions for other request methods, like POST or DELETE, which are supported by http / https modules of Node.js:
// [DELETE] /api/myendpoint
exports.DELETE = function(args) {
return new Promise(function(resolve, reject) {
// for async executions
try {
// ...
resolve(); // MUST be called at the end
// on SUCCESS
}
catch (e) {
reject(e); // MUST be called at the end
// on ERROR
}
});
}
// [POST] /api/myendpoint
exports.POST = function(args) {
// no (promise) result means: sync execution
}
HINT: Custom endpoints will always overwrite build-in ones!
Commands [↑]
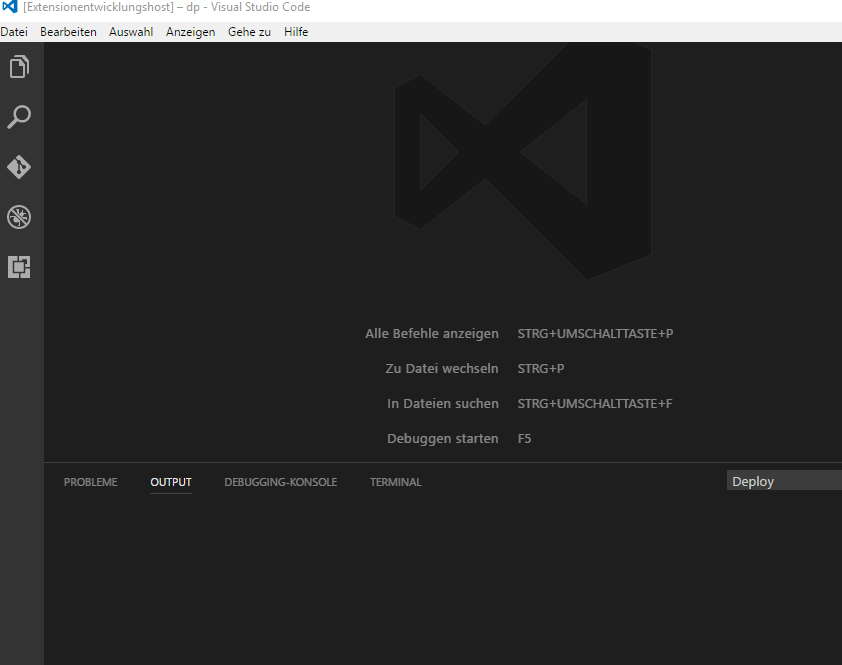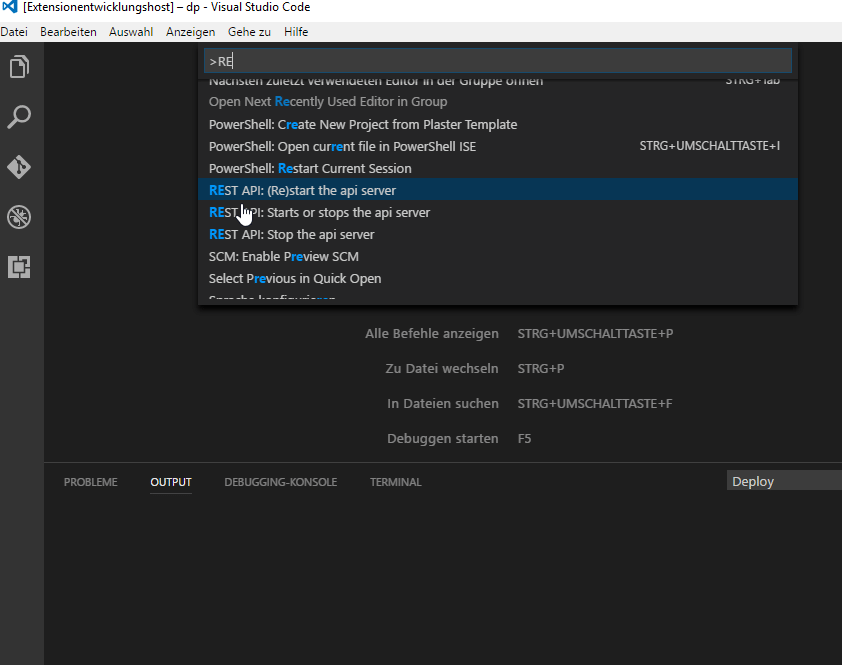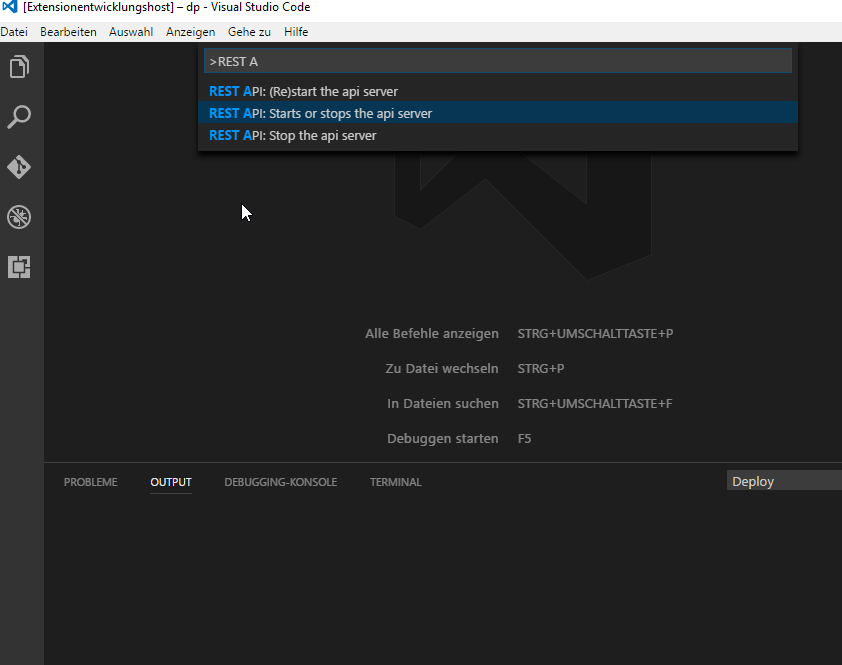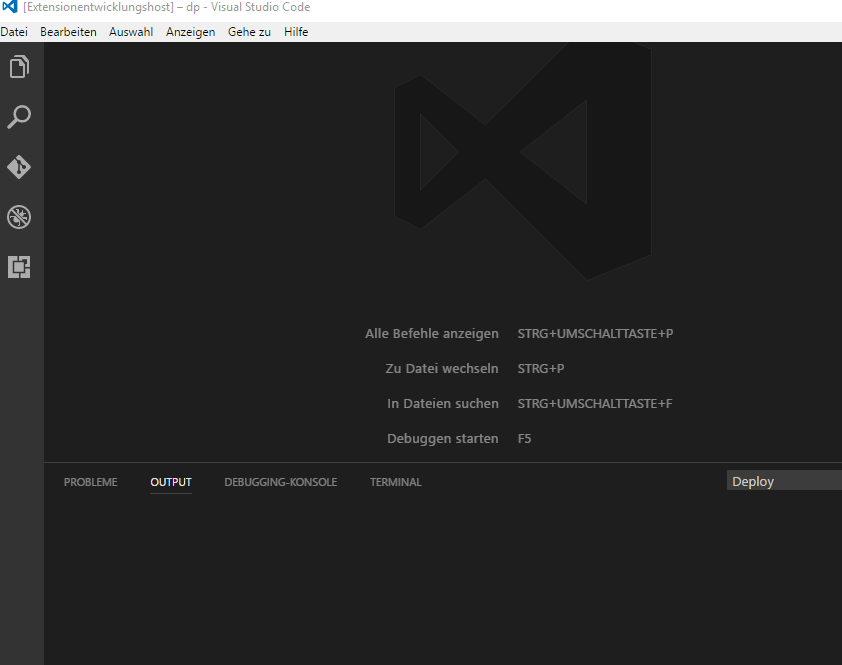
Press F1 to open the list of commands and select one of the following commands:
| Name |
Description |
ID |
REST API: Starts or stops the api server |
Toggles the state of the API's HTTP server. |
extension.restApi.toggleHostState |
REST API: (Re)start the api server |
(Re-)Starts the API's HTTP server. |
extension.restApi.startHost |
REST API: Stop the api server |
Stops the API. |
extension.restApi.stopHost |
Documentation [↑]
The full documentation of the extension's API can be found here.
Detailed information on how to use the extension, can be found at the wiki.




