AIConfig Extension for Visual Studio Code
Overview
AIConfig Editor turns VS Code into a generative AI prompt IDE, allowing you to run models from any provider (OpenAI, Google, Hugging Face, your local computer...) or any modality (text, image, audio) in a single universal playground.
The prompts and model settings get saved in a .aiconfig.yaml or .aiconfig.json file, which can be source controlled and used in your application code via the AIConfig SDK.
Read the full documentation for more details

Demo Video
Getting Started
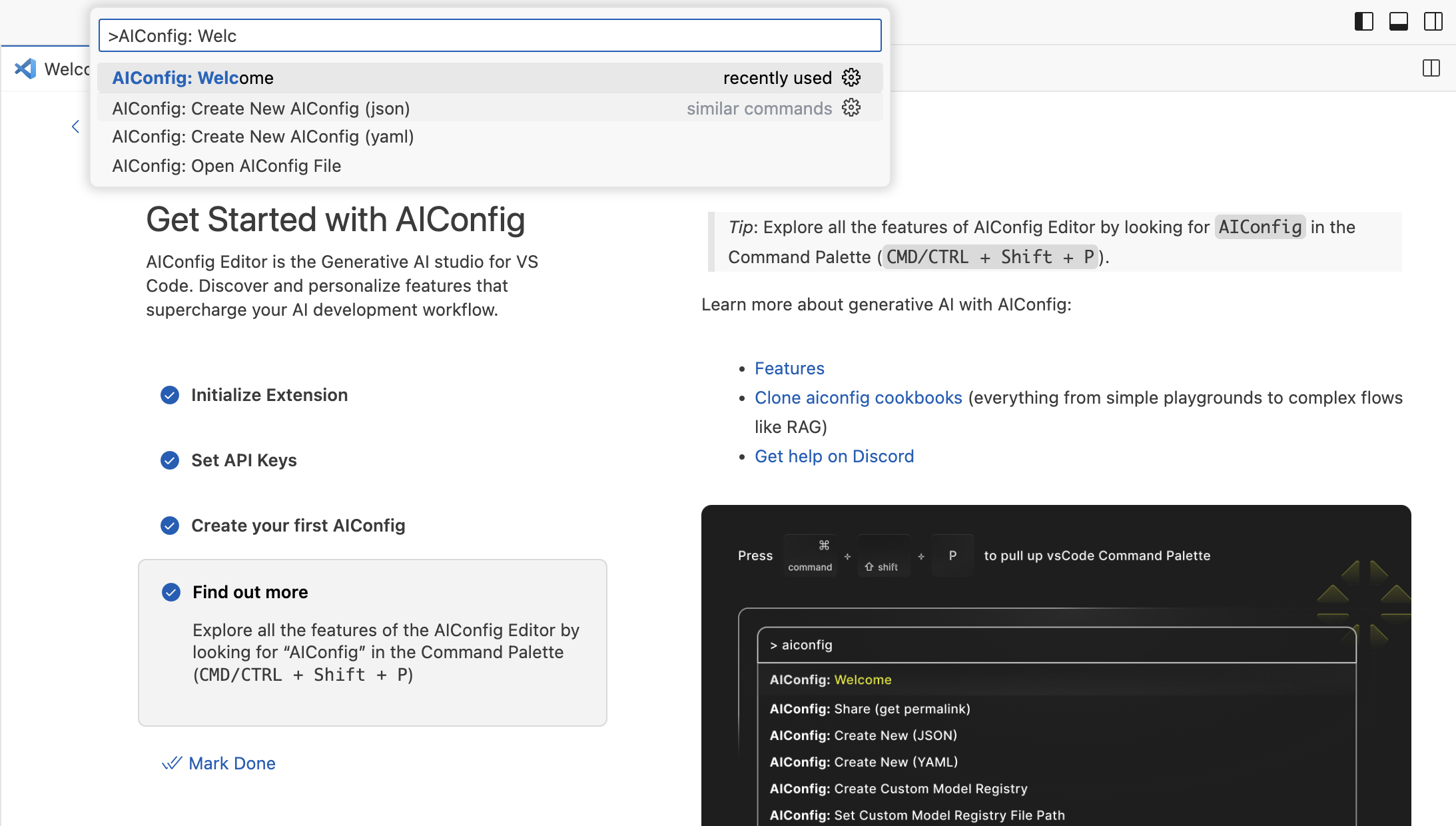
First use
- Install the AIConfig Editor extension.
- Run the AIConfig: Welcome command (
CMD+SHIFT+P -> AIConfig: Welcome), and follow the steps.
- Check out some of our cookbook templates for inspiration!
Next use
- Create an untitled aiconfig using the AIConfig: Create New command (
CMD+SHIFT+P -> AIConfig: Create New) to launch an Untitled aiconfig.
Key Features
- Access local and remote models in one place. Access all generative AI models in a single place, directly in your IDE. Out-of-the-box support for text, image, and audio models.
- Universal prompt engineering playground. Swap between models, chain prompts together, and create prompt templates. Use these prompts in code using the AIConfig SDK.
- Version control prompts. Manage prompts and model settings in config files that you can put in source control, right beside your code.
- Connect to your own models and endpoints. Extend AIConfig to work with any model and endpoint. See custom models section for more details.
Supported Models
This extension supports all major foundation models from major model providers.
For more details, please see https://aiconfig.lastmileai.dev/docs/overview/model-parsers/.
| Provider |
Model |
Language |
Support |
| OpenAI |
GPT3.5 |
Python |
✅ Built-in |
| OpenAI |
GPT4 |
Python |
✅ Built-in |
| OpenAI |
Dall-E 3 |
Python |
✅ Built-in |
| Azure OpenAI |
GPT3.5, GPT4 |
Python |
✅ Built-in |
| AWS Bedrock |
Claude |
Python |
✅ Built-in |
| HuggingFace Inference Endpoints |
Text Generation, Text-to-image, Text-to-speech, Summarization, Translation, Automatic Speech Recognition |
Python |
✅ Built-in |
| Google |
PaLM 2 |
Python |
✅ Built-in |
| Google |
Gemini |
Python |
✅ Built-in |
| Meta |
Llama 2 |
Python |
🤝 Extension |
| Meta |
Llama Guard |
Python |
🤝 Extension |
| HuggingFace Transformer Pipelines |
Text Generation |
Python |
🤝 Extension |
How it works
AIConfig Editor is the UI for AIConfig, which is a JSON/YAML schema for storing generative AI prompts, models and model settings as a config file.
For example, check out this sample aiconfig that handles function calling and prompt chaining.
On install, the extension installs the python-aiconfig pip package in your Python environment.
On open, when you open a *.aiconfig.yaml file in VS Code, this extension launches a Python server which is running the AIConfig SDK.
As you edit and run prompts in the editor, the server uses the AIConfig SDK to run those prompts. This provides you with a lot of flexibility, because you can install additional AIConfig Extensions in your Python environment, and use them in the editor.
Extensibility and Customization
Read How it works for some additional context.
When you use the AIConfig Editor, the extension installs python-aiconfig in your Python env. You can install additional extensions and dependencies in the same Python env, and then use them in the AIConfig Editor.
Instructions
pip3 install <extension_package> in your python env (e.g. pip3 install aiconfig-extension-hugging-face for Hugging Face models via Transformers, Diffusers and Inference endpoints)- Run AIConfig: Create Custom Model Registry command (
CMD+SHIFT+P -> AIConfig: Create Custom Model Registry)
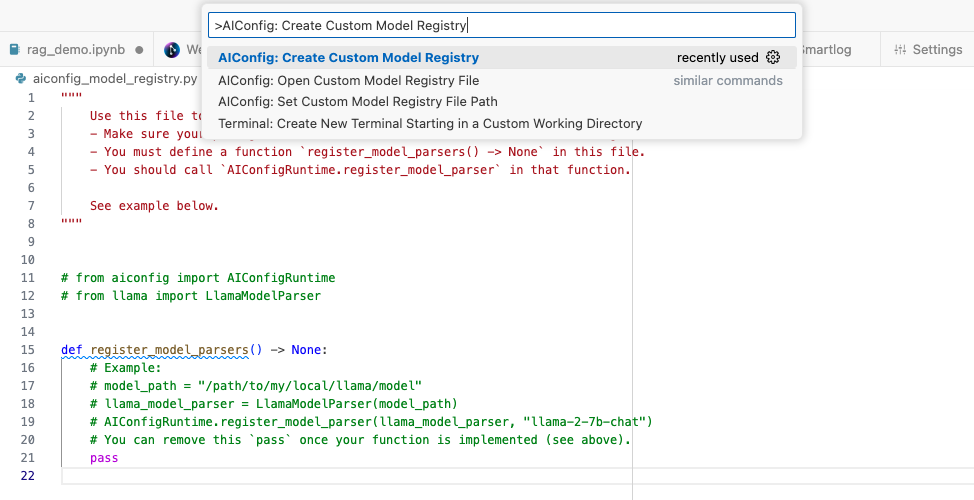
- Register the additional models from the package imported in Step 1. e.g.
Copy the full sample
from aiconfig_extension_hugging_face import (
HuggingFaceText2ImageDiffusor,
HuggingFaceTextGenerationTransformer,
HuggingFaceTextSummarizationTransformer,
)
from aiconfig import AIConfigRuntime
def register_model_parsers() -> None:
"""Register model parsers for HuggingFace models."""
text_to_image = HuggingFaceText2ImageDiffusor()
AIConfigRuntime.register_model_parser(text_to_image, text_to_image.id())
text_generation = HuggingFaceTextGenerationTransformer()
AIConfigRuntime.register_model_parser(
text_generation, text_generation.id()
)
text_summarization = HuggingFaceTextSummarizationTransformer()
AIConfigRuntime.register_model_parser(
text_summarization, text_summarization.id()
)
- Open an
*.aiconfig.yaml (e.g. CMD+SHIFT+P -> AIConfig: Create New), and now you can use the custom extension in the editor!
To define you own extensions, please see Extensibility docs.

