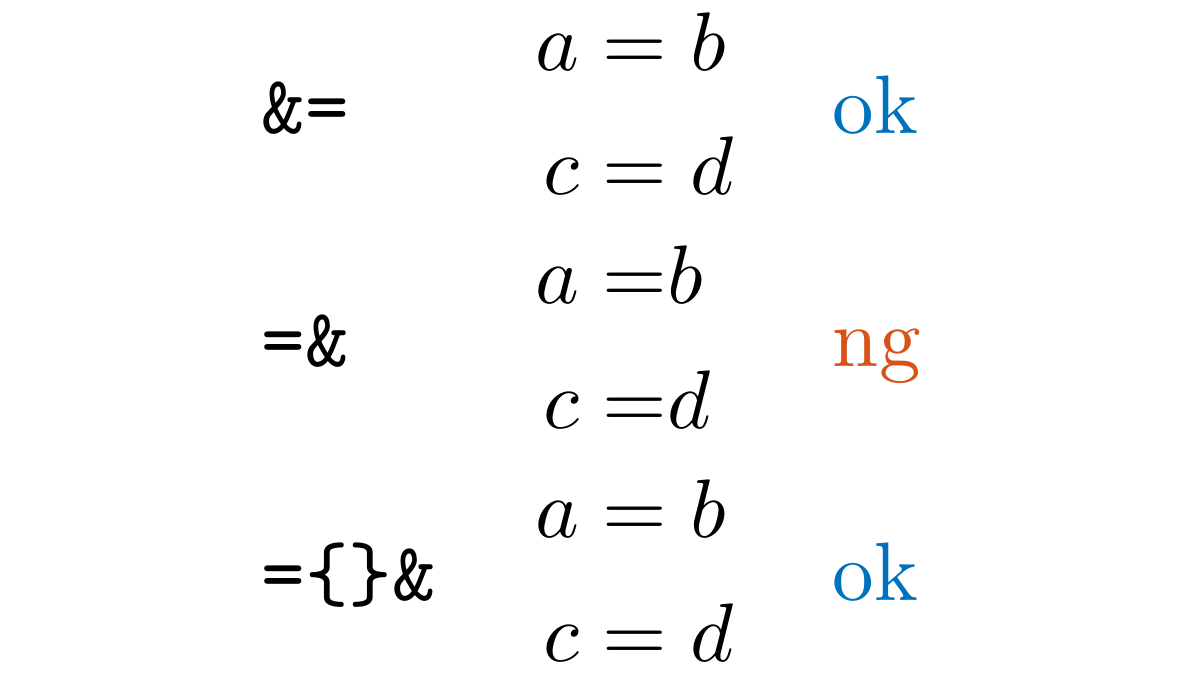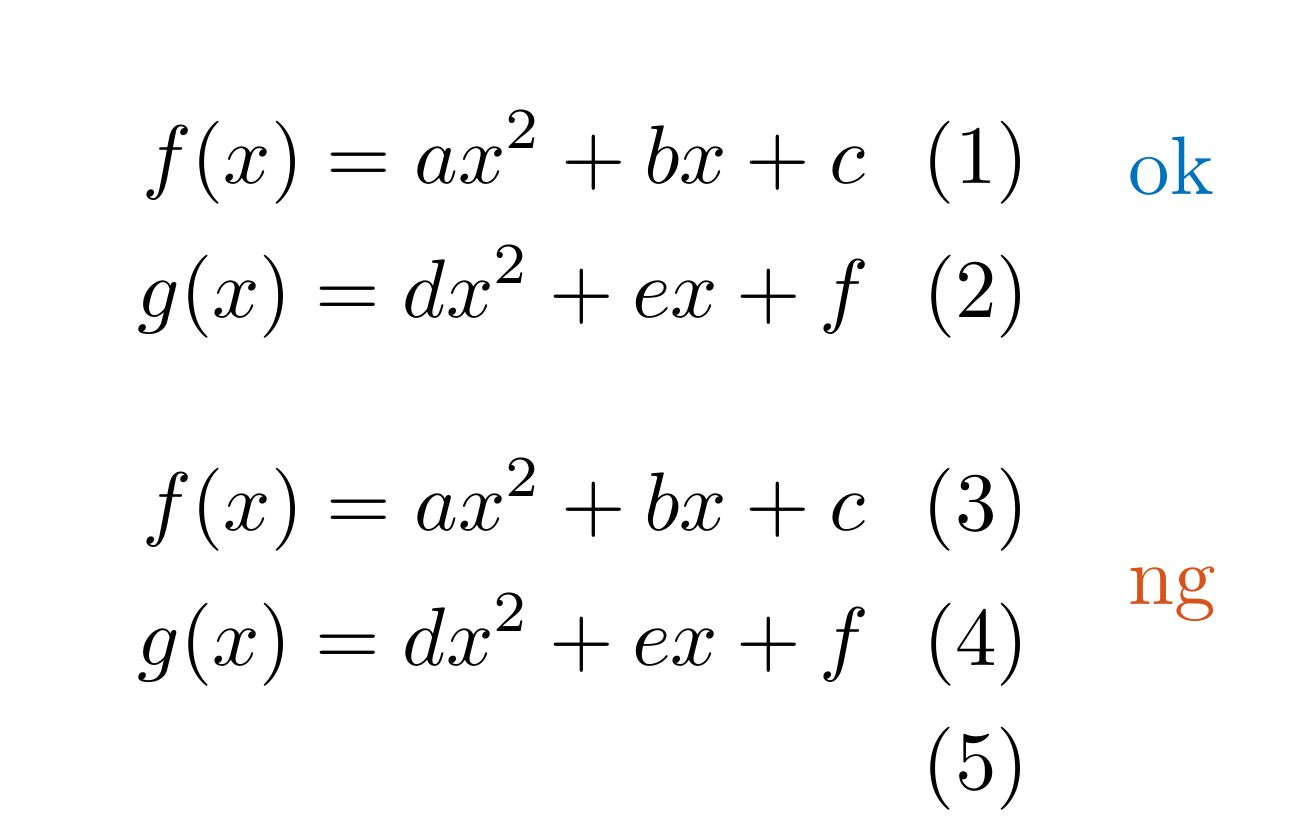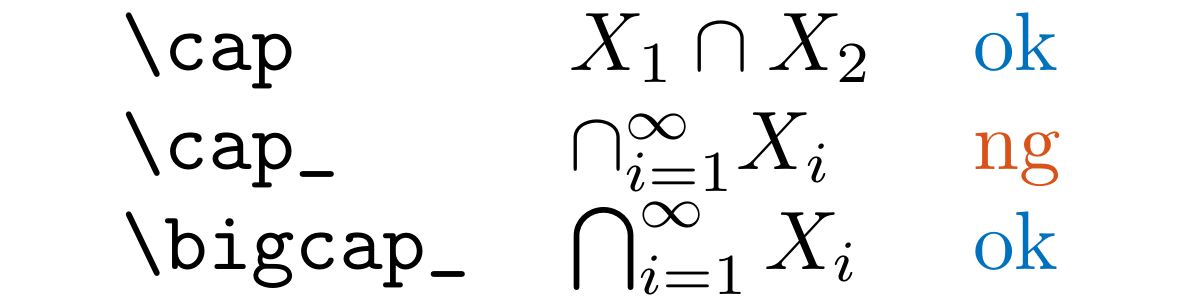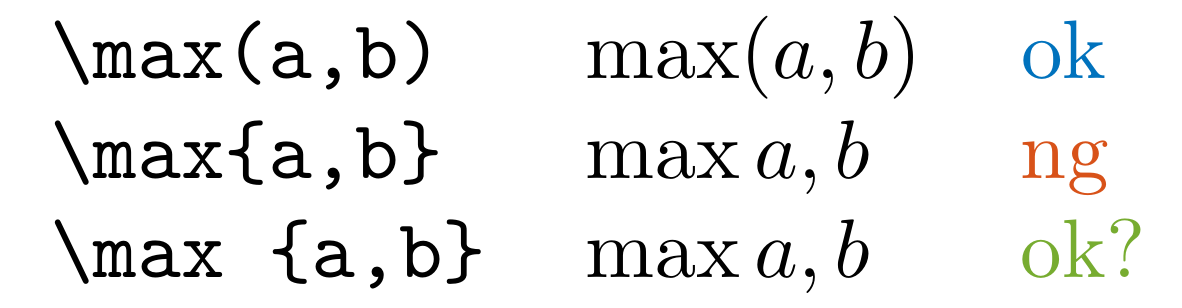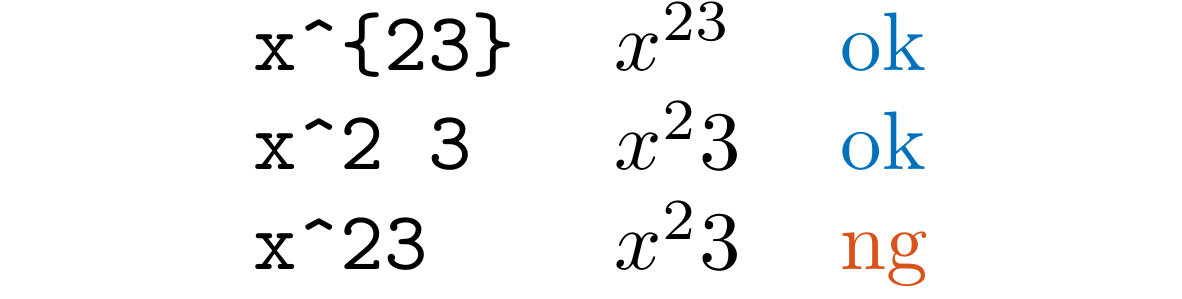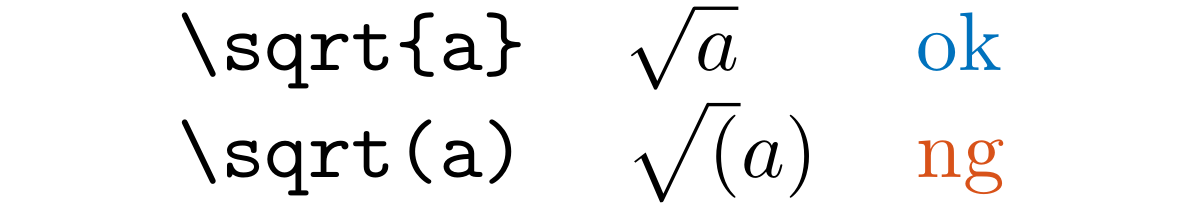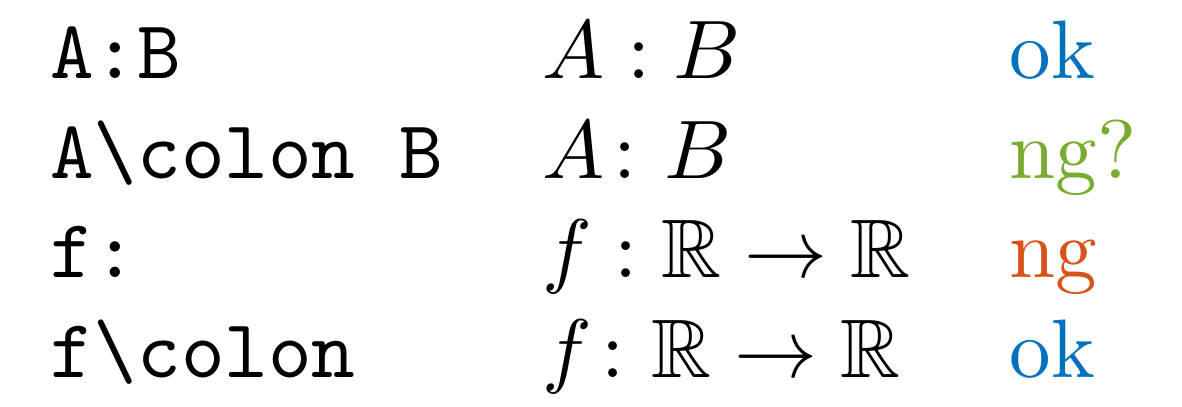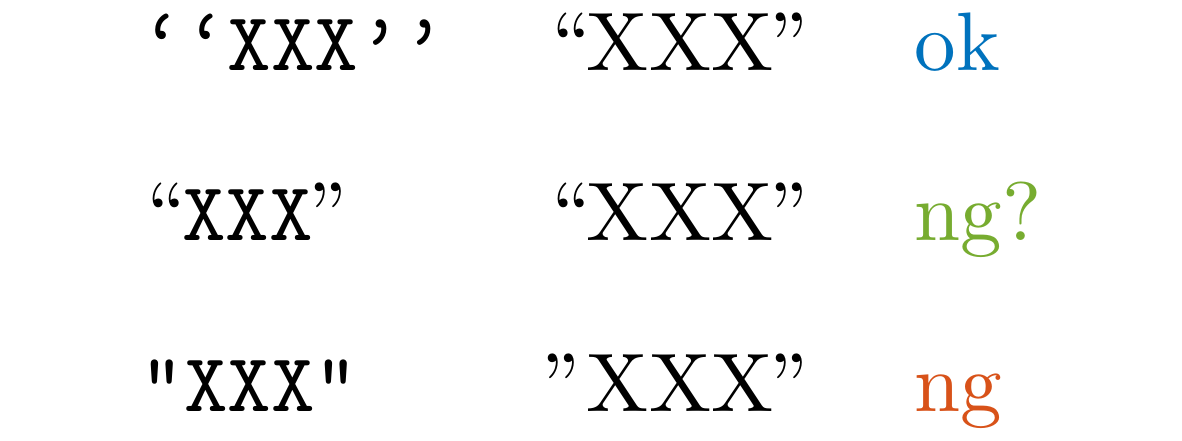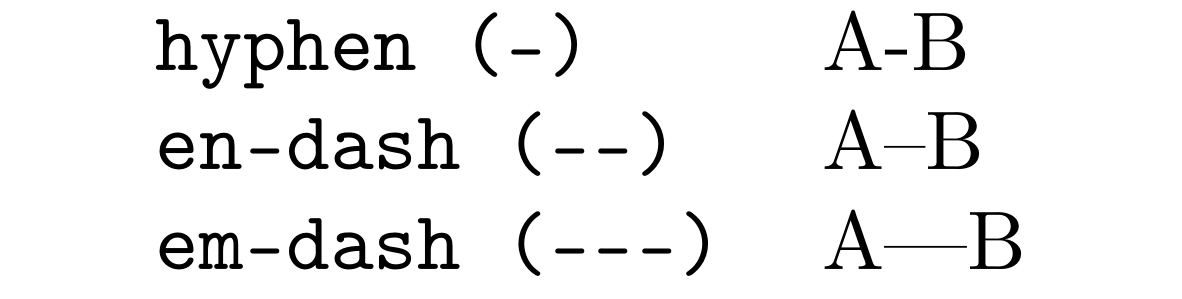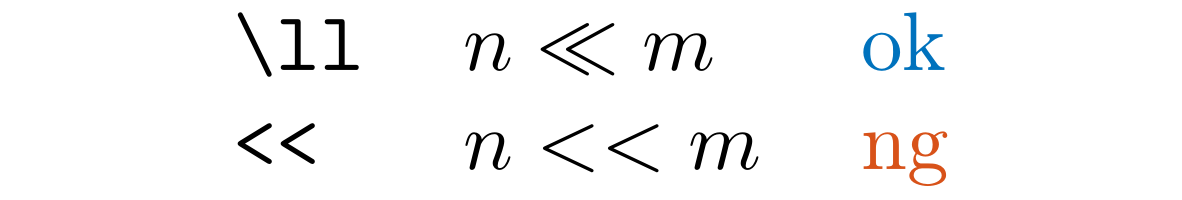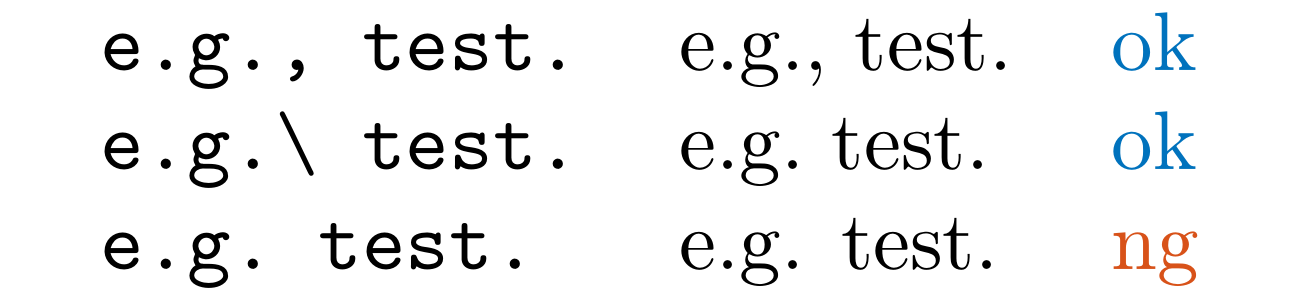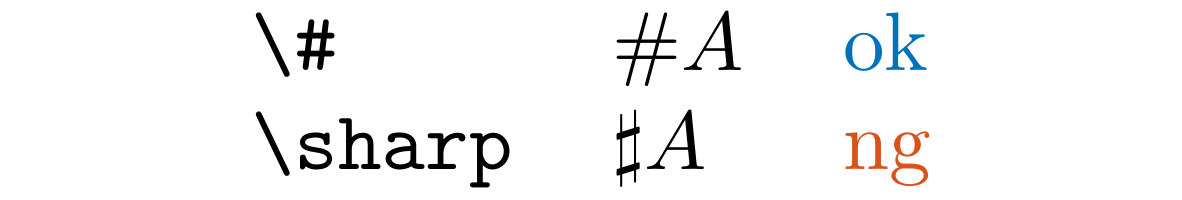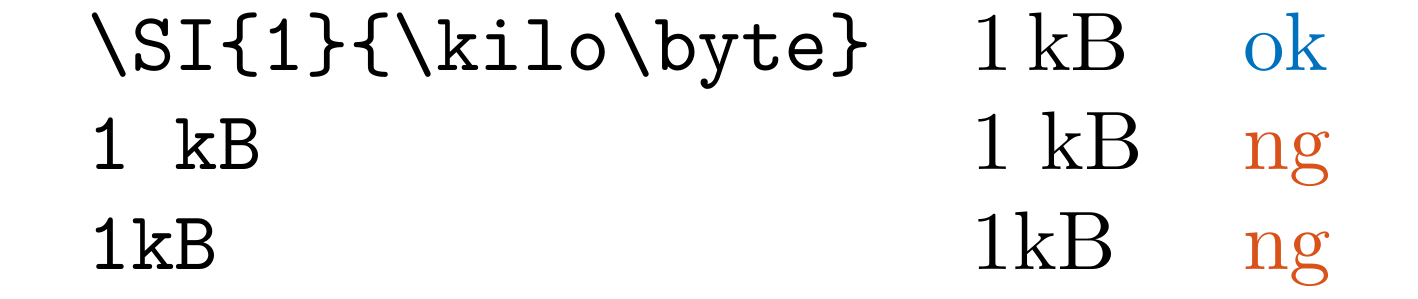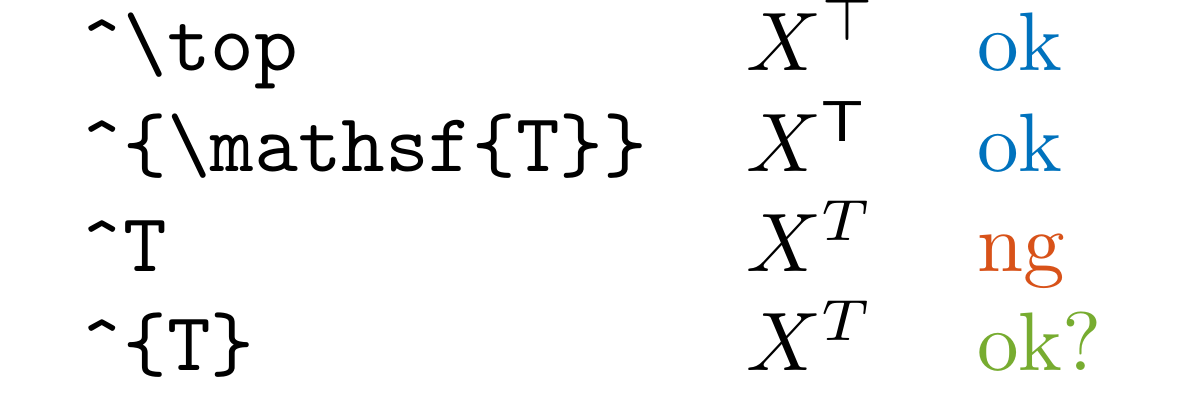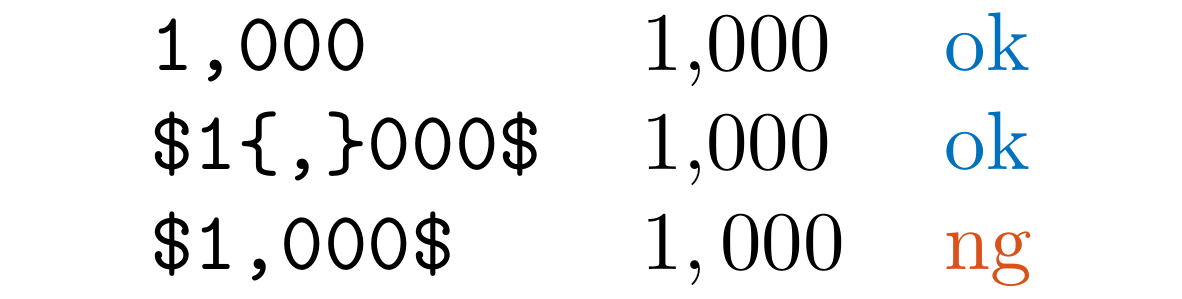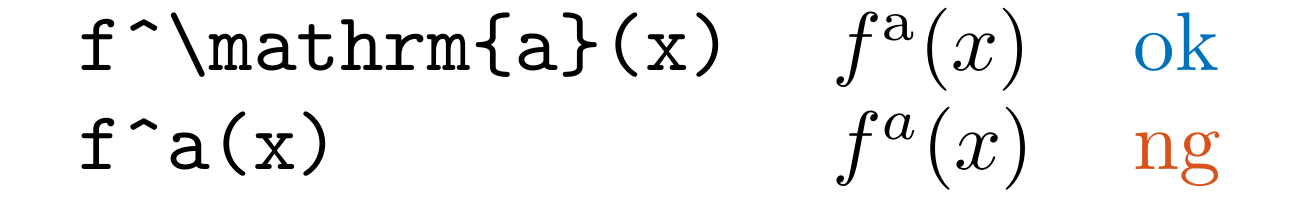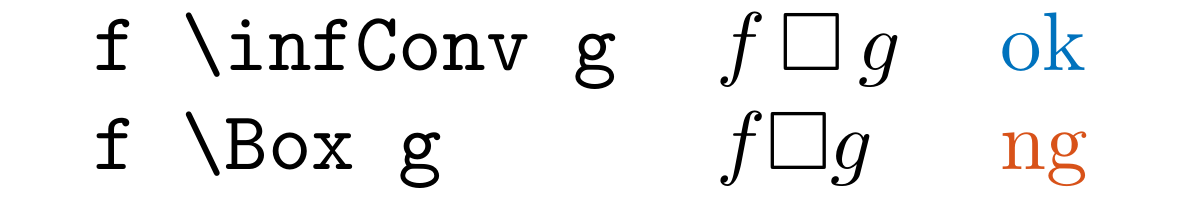LaTeX Lint
Abstract
LaTex Lint is a LaTeX Linter for .tex and .md files.
VS Code Extension Version is available.
Web Version is also available.
We welcome any kind of feedback, suggestions, and pull requests!
Rules
Here is the list of rules we detect.
- LLAlignAnd (detect
=&, \leq&, \geq&, etc.)
- LLAlignEnd (detect
align environment ends with \\)
- LLAlignSingleLine (detect
align environment without \\)
- LLArticle (detect wrong article usage)
- LLBig (detect
\cap_, \cup_, etc.)
- LLBracketCurly (detect
\max{ and \min{)
- LLBracketMissing (detect
^23, _23, disabled by default)
- LLBracketRound (detect
\sqrt(, ^(, and _()
- LLColonEqq (detect
:=, =:,::=, and =::)
- LLColonForMapping (detect
: for mapping)
- LLCref (detect
\ref, disabled by default)
- LLDoubleQuotes (detect
“, ” and ")
- LLENDash (detect the dubious use of
-(hyphen))
- LLEqnarray (detect
eqnarray environment)
- LLFootnote (detect space before
\footnote)
- LLHeading (detect heading level jumps)
- LLLlGg (detect
<< and >>)
- LLNonASCII (detect fullwidth ASCII characters)
- LLNonstandard (detect nonstandard mathematical notations)
- LLPeriod (detect
e.g.)
- LLRefEq (detect
\ref{eq:)
- LLSharp (detect
\sharp likely to be a misuse of \#)
- LLSI (detect
KB, MB, GB, etc. without \SI)
- LLSortedCites (detect unsorted cites)
- LLSpaceEnglish (detect the lack of space for English)
- LLSpaceJapanese (detect the lack of space for Japanese, disabled by default)
- LLT (detect
^T, disabled by default)
- LLTextLint (part of textlint features)
- LLThousands (detect
1,000 etc.)
- LLTitle (detect dubious title case in
\title{}, \section{}, etc.)
- LLUnRef (detect unreferenced figure and table labels)
- LLURL (detect unnecessary info in URLs)
- LLUserDefined (detect Regexes in
latexlint.userDefinedRules)
Please also refer to sample/lint.pdf and our Japanese article (日本語解説記事) if needed.
LLAlignAnd
Detect =& of align environments in .tex and .md files.
Use &= or ={}& to avoid extra spaces.
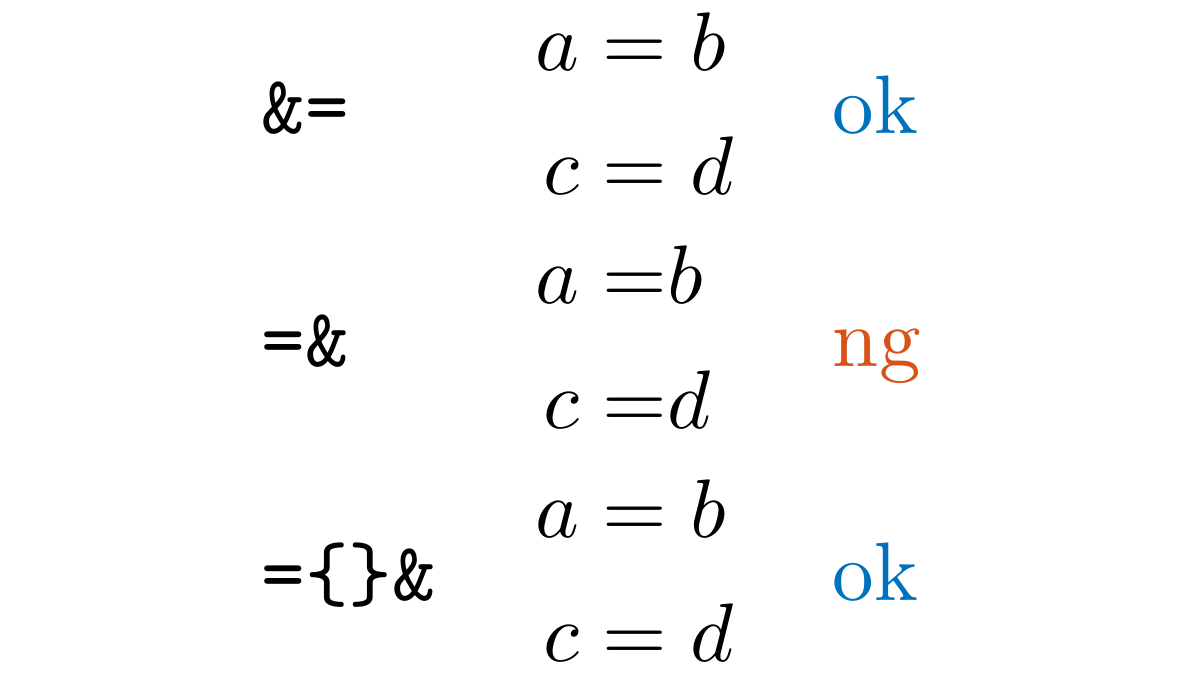
We also detect \neq&, \leq&, \geq&, etc.
References:
Relation spacing error using =& in aligned equations (Stack Exchange)
LLAlignEnd
Detect align, gather, and other environments end with \\ in .tex and .md files.
This \\ would be unnecessary.
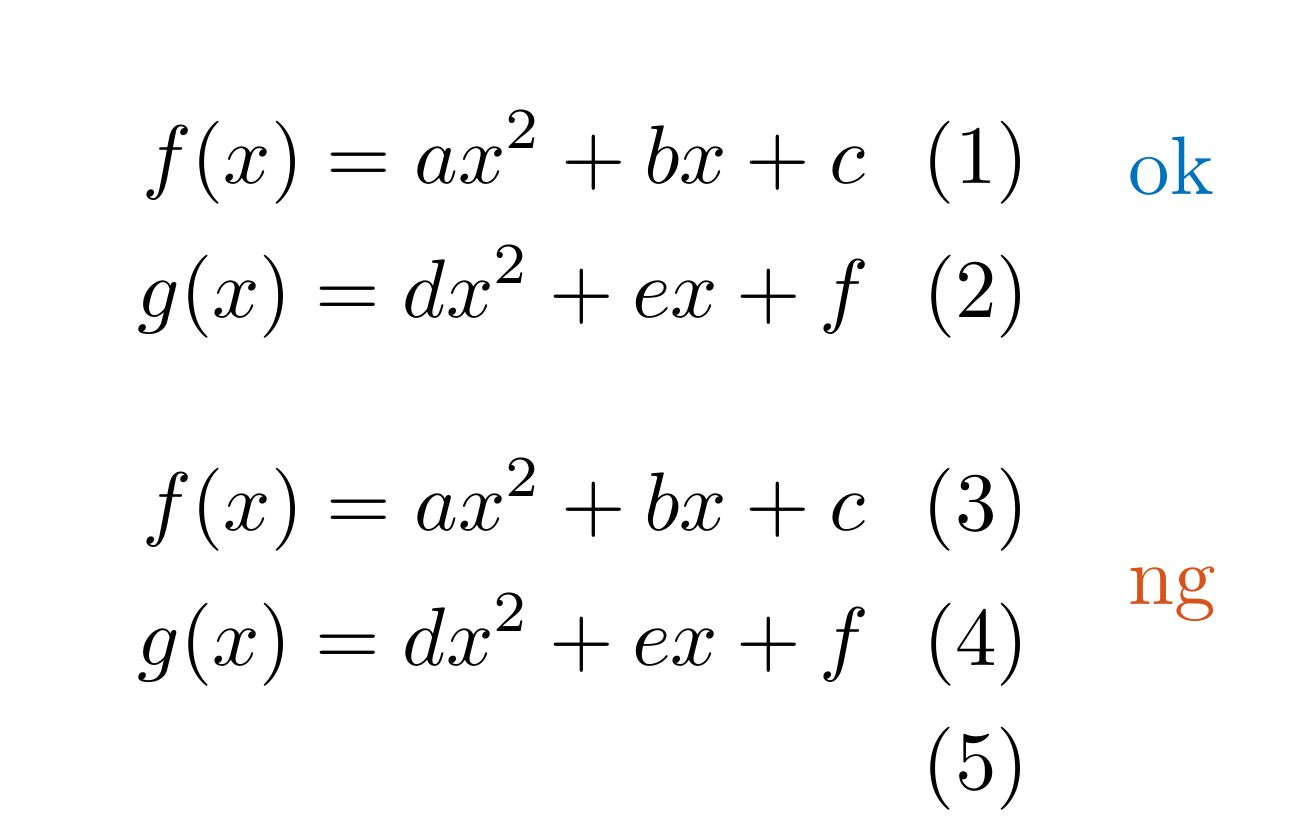
LLAlignSingleLine
Detect align environment without \\ in .tex and .md files.
Single-line equations are recommended to use the equation environment.

The spacing of the align environment is different from the equation environment with only one equation. Official documentation of amsmath package suggests using the equation environment for only one equation.
To rewrite \begin{align} ... \end{align} to \begin{equation} ... \end{equation}, you can rename the command by LaTeX Lint: Rename Command or Label.
References:
What is the difference between align and equation environment when I only want to display one line of equation? (Stack Exchange)
LLArticle
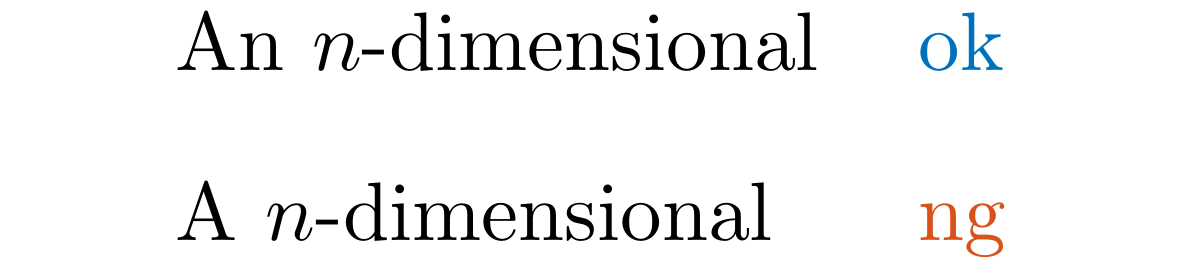
Detect wrong article usage in .tex and .md files.
For example, A $n$-dimensional should be An $n$-dimensional (We might add more patterns in the future).
LLBig
Detect \cap_, \cup_, \odot_, \oplus_, \otimes_, \sqcup_, uplus_, \vee_, and \wedge_ in .tex and .md files.
You should likely use \bigcap, \bigcup, \bigodot, \bigoplus, \bigotimes, \bigsqcup, \biguplus, \bigvee, and \bigwedge instead.
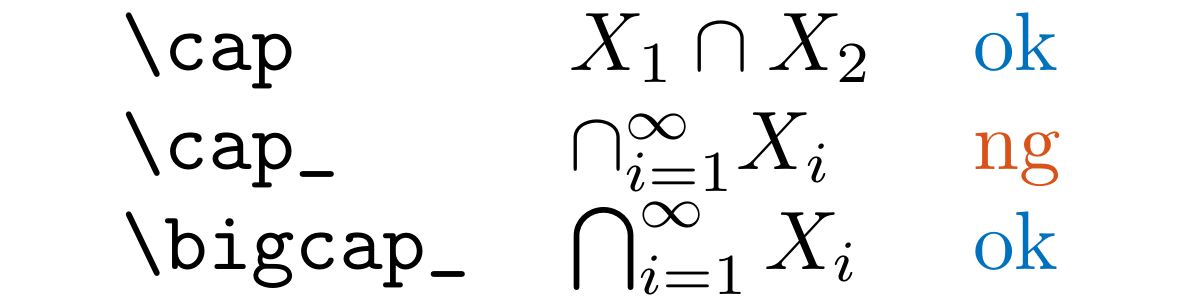
References:
Formatting the union of sets (Stack Exchange)
LLBracketCurly
Detect \max{ and \min{ in .tex and .md files.
You should likely use \max( and \min( instead, or add a space like \max { or \min { to make it clear.
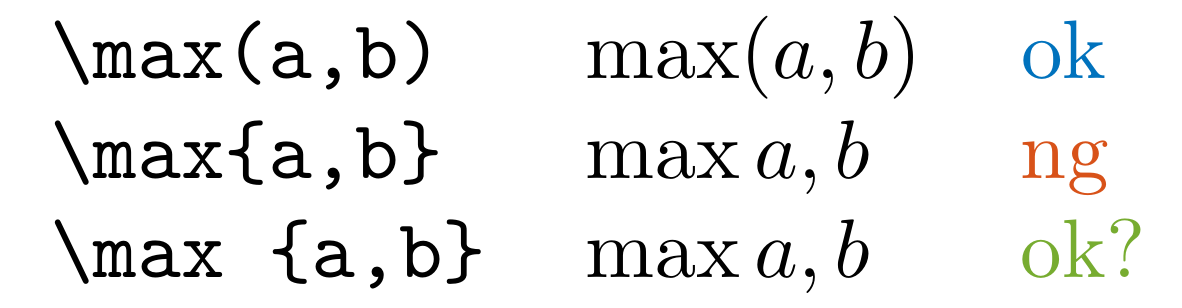
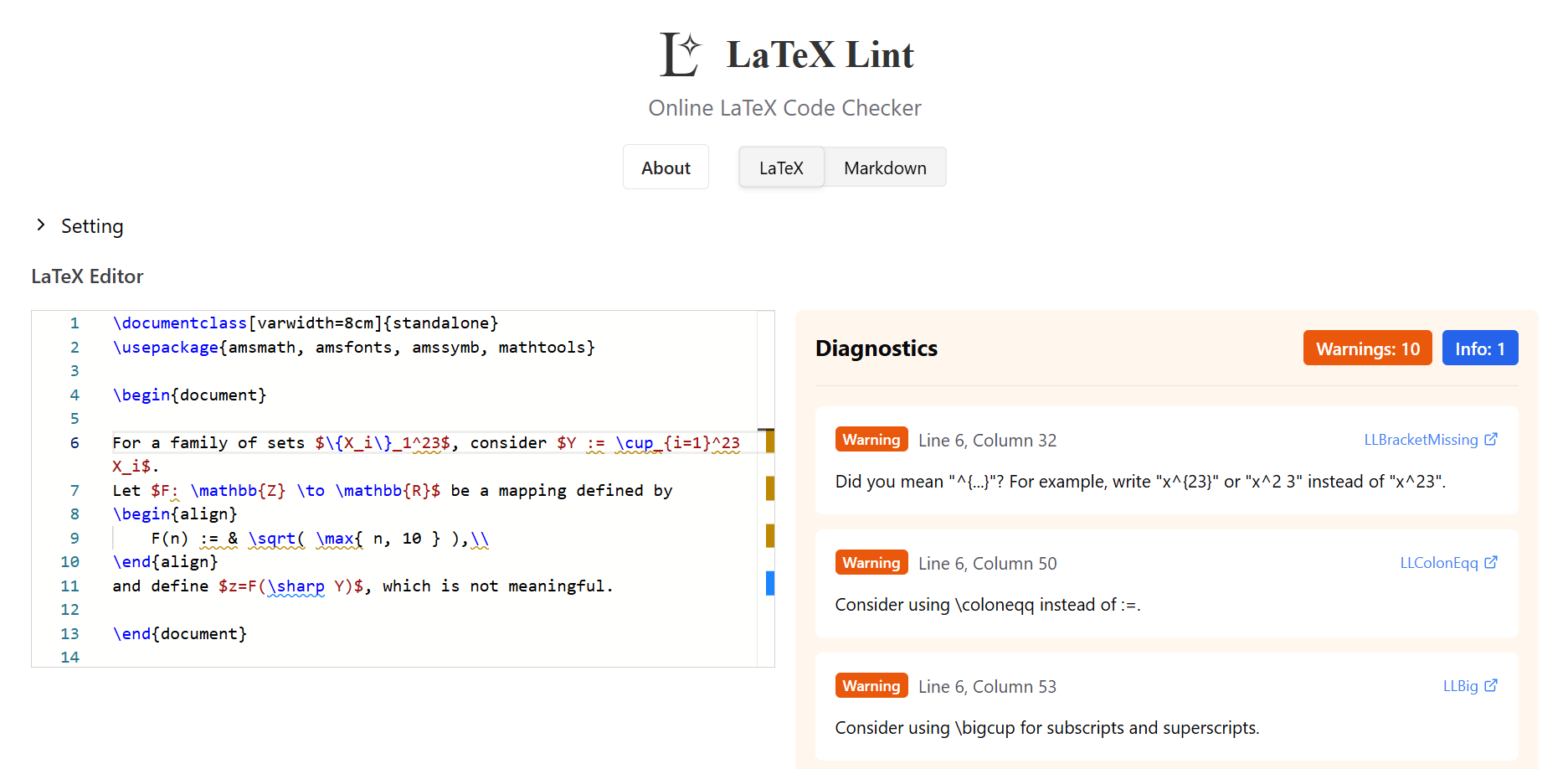
LLBracketMissing
Detect cases such as ^23, _23, ^ab, and _ab in .tex files. Clarify the scope of the superscript and subscript by adding {} or a space.
This rule is disabled by default.
Filenames / URLs / labels are ignored, such as in \includegraphics{figure_23} or \url{http://example.com/abc_123}.
This rule is disabled in the preamble (only if \begin{document} exists, before that).
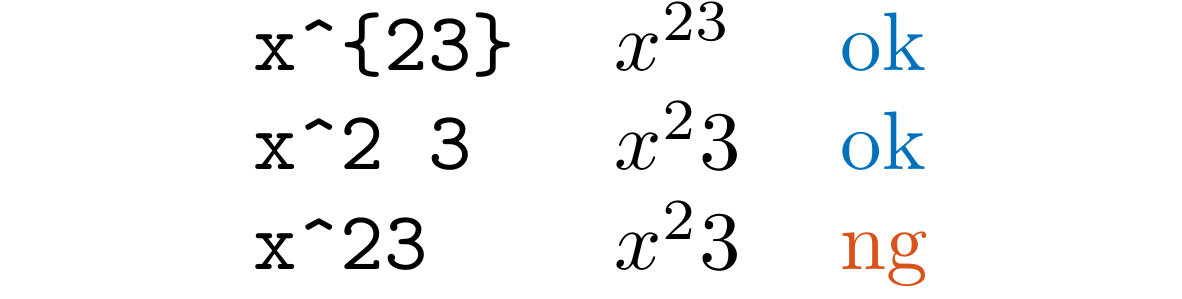
LLBracketRound
Detect \sqrt(, ^(, and _( in .tex and .md files.
You should likely use \sqrt{, ^{, and _{ instead.
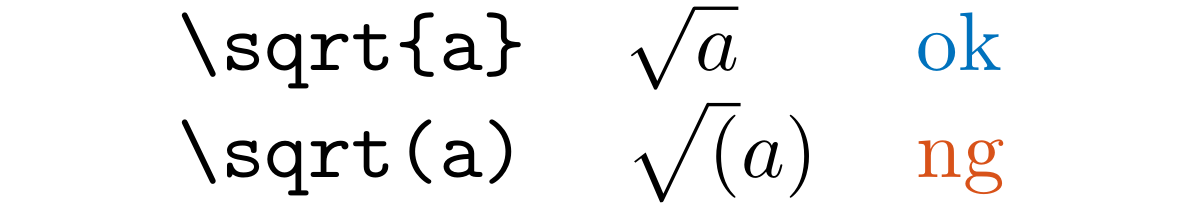
LLColonEqq
Detect :=, =:, ::=, and =:: in .tex and .md files.
You should likely use \coloneqq, \eqqcolon, \Coloneqq, and \Eqqcolon in the mathtools package instead.

The colon is slightly too low in :=, but vertically centered in \coloneqq.
References:
How to typeset $:=$ correctly? (Stack Exchange)
What is the latex code for the symbol "two colons and equals sign"? (Stack Exchange)
Detect : which seems to be used for mapping in .tex and .md files.
You likely want to use \colon instead.
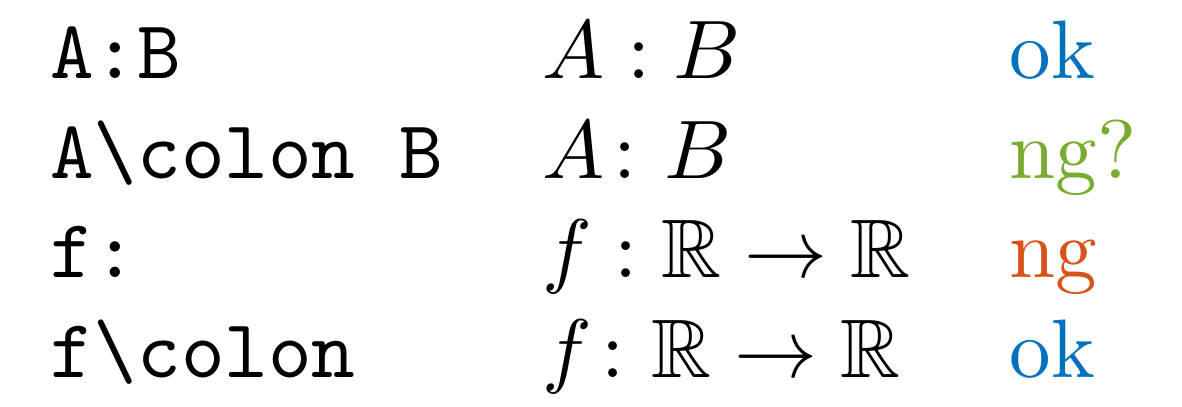
\colon is recommended for the mapping symbol. : is used for ratios, such as 1:2.
When \to, \mapsto, or \rightarrow appear, the rule looks back up to 10 words to find the nearest :, using some heuristics to suppress false positives.
References:
Using \colon or : in formulas? (Stack Exchange)
LLCref
Detect \ref in .tex files.
You should likely use \cref or \Cref in the cleveref package instead.
This rule is disabled by default.
We prefer this package because it can automatically add prefixes like "Sec." or "Fig.". We can keep the consistency of the reference format.
This rule is disabled in the preamble (only if \begin{document} exists, before that).
LLDoubleQuotes
Detect “, ” and " in .tex files.
Use ``XXX'' instead for double quotation.
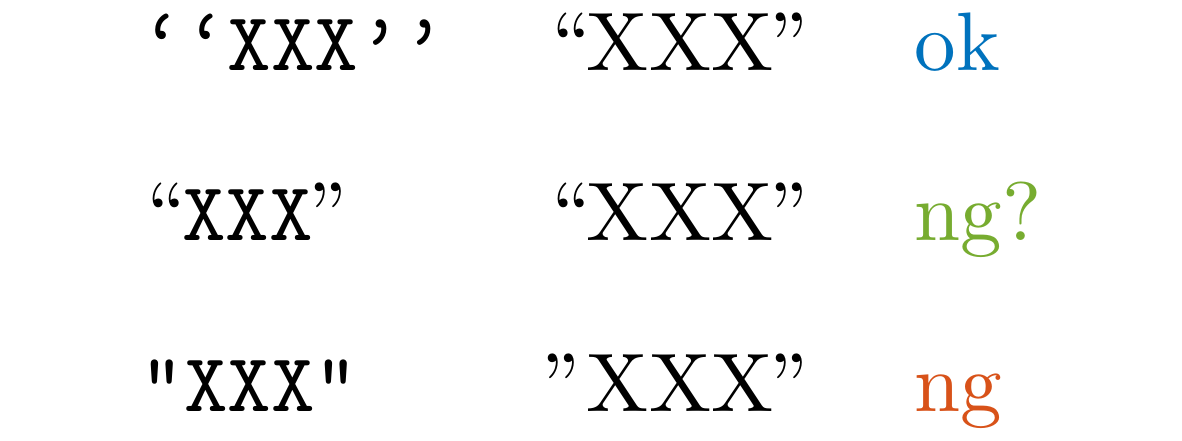
As for “XXX”, there is no problem in most cases. We prefer to use ``XXX'' for consistency.
You can also use \enquote{XXX} with the csquotes package.
References:
What is the best way to use quotation mark glyphs? (Stack Exchange)
LLENDash
Detect the dubious use of hyphens in .tex and .md files.
You should likely use -- for en-dash and --- for em-dash.
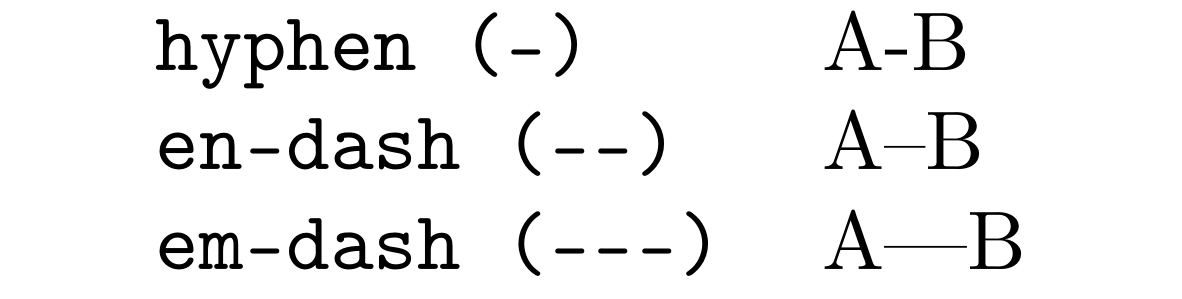
Although this rule is not inherent orthographic "correctness", in a lot of cases, the use of an en dash is preferred.
For example, we detect the following.
Erdos-Renyi (random graph, Erd\H{o}s--R\'enyi)Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen (quantum physics, Einstein--Podolsky--Rosen)Fruchterman-Reingold (graph drawing, Fruchterman--Reingold)Gauss-Legendre (numerical integration, Gauss--Legendre)Gibbs-Helmholtz (thermodynamics, Gibbs--Helmholtz)Karush-Kuhn-Tucker (optimization, Karush--Kuhn--Tucker)
However, we do not detect the following as an exception.
- Common word pairs such as
Real-Valued / Two-Dimensional are skipped when both words are recognized general vocabulary.
Fritz-John (optimization, name of a person)- (We might add more exceptions later.)
We also should use -- instead of - to indicate a range of pages, e.g., 123--456 instead of 123-456. A lot of BibTeX files follow this rule. We do not detect this because it might be just a subtraction.
LLEqnarray
Detect eqnarray environment in .tex and .md files.
You should likely use the align environment instead.
It is known that the eqnarray environment is not recommended because it has some spacing issues.
References:
Why not use eqnarray? (TeX FAQ)
Detect unnecessary space before \footnote command in .tex files.
You should likely remove the space before \footnote, or add a percentage sign % at the end of the previous line to avoid unwanted space in the output.

Whether putting footnote markers before or after punctuation marks is a style choice, and thus we do not enforce a specific style.
References:
Where do I place a note number in relation to punctuation? (MLA Style Center)
Best practice for source editing of footnotes (Stack Exchange)
How to properly typeset footnotes/superscripts after punctuation marks? (Stack Exchange)
LLHeading
Detect improper heading hierarchy in .tex files.
This rule warns when there are jumps in heading levels, such as going directly from \section to \subsubsection without an intermediate \subsection.
The rule checks the following heading levels:
\chapter\section\subsection\subsubsection
LLLlGg
Detect << and >> in .tex and .md files.
You should likely use \ll and \gg instead.
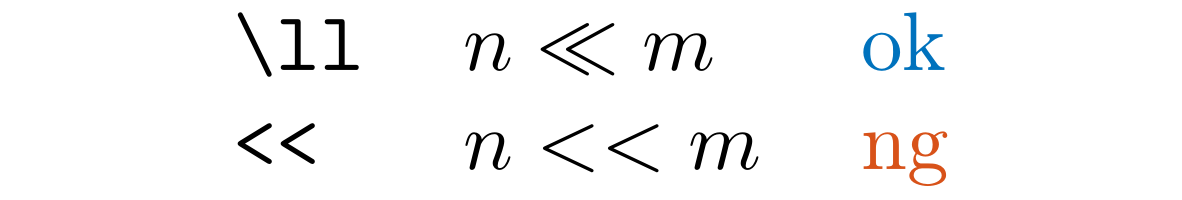
We do not detect << like this one.
I like human $<<<$ cat $<<<<<<<$ dog.
LLNonASCII
Detect all fullwidth ASCII characters in .tex and .md files.
We detect the following characters.
!"#$%&'*+-/0123456789:;
<=>?@ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRS
TUVWXYZ[\]^_`abcdefghijk
lmnopqrstuvwxyz{|}~
We use the following Regex.
[\u3000\uFF01-\uFF07\uFF0A-\uFF0B\uFF0D\uFF0F-\uFF5E]
Range U+FF01–FF5E reproduces the characters of ASCII 21 to 7E as fullwidth forms. U+FF00 does not correspond to a fullwidth ASCII 20 (space character), since that role is already fulfilled by U+3000 "ideographic space".
Wikipedia
Plus, U+3000 is used for a fullwidth space.
We do not detect the following characters because they are often used in Japanese documents.
- U+FF08
(
- U+FF09
)
- U+FF0C
,
- U+FF0E
.
LLNonstandard
Detect nonstandard mathematical notations in .tex and .md files that are not commonly used in formal academic writing.
This rule detects the following notations:
\therefore and \because commands
These symbols are not generally used in formal writing.
The word "iff"
While commonly used in informal mathematical writing, "iff" (if and only if) is preferred to be written out fully in formal academic writing.
\fallingdotseq and \risingdotseq commands
These are nonstandard notation symbols. \approx is preferred in formal writing.
{}_n C_k notation for combinations
The notation {}_n C_k for combinations is often used in Japan, but not standard in international academic writing. We recommend the standard binomial notation $\binom{n}{k}$ instead.
This rule only detects exact matches to avoid false positives.
References:
Therefore sign (Wikipedia):
While it is not generally used in formal writing, it is used in mathematics and shorthand.
数学英語 (河東泰之, Japanese article):
また ∀ や ∃ の記号は数理論理学でない限り,黒板などに書く時の略記法なので論文では使わないとされている.実は私の論文で ∀ が使われている例がいくつかあるのだが,それは共著者が書いたものを直し切れなかったのだ.これと同様のものとして,if and only if の意味の iff も略記法であって論文には不適切とされているが,私の論文中には共著者が書いたものが残っている例がある.
∵という記号は今ここに書いている通り JIS コードにもあるし,TeX でも \because という名前がついているのだが,私の知っている限り欧米ではほとんど使わない.(∴のほうはこれよりは使われている.) これを日本人が黒板に書いて,「それは何か」と聞かれているところを見たことが何度もある.同じく欧米で使わない数学記号として≒がある.「大体等しい」ことを表すのによく使われる記号は≈である.
組合せ (数学) (Japanese Wikipedia):
ピエール・エリゴン(フランス語版)が1634年の『実用算術』で ${}_n C_k$ の記号を定義した。ただし、この数は数学のあらゆる分野に頻繁に現れ、大抵の場合 $\binom{n}{k}$ と書かれる。
(Pierre Hérigone defined the ${}_n C_k$ notation in his 1634 work "Practical Arithmetic". However, this number appears frequently in all areas of mathematics and is usually written as $\binom{n}{k}$.)
LLPeriod
Detect e.g. in .tex and .md files.
You should likely add a comma like e.g., or use e.g.\ to avoid spacing issues. i.e. is treated similarly.
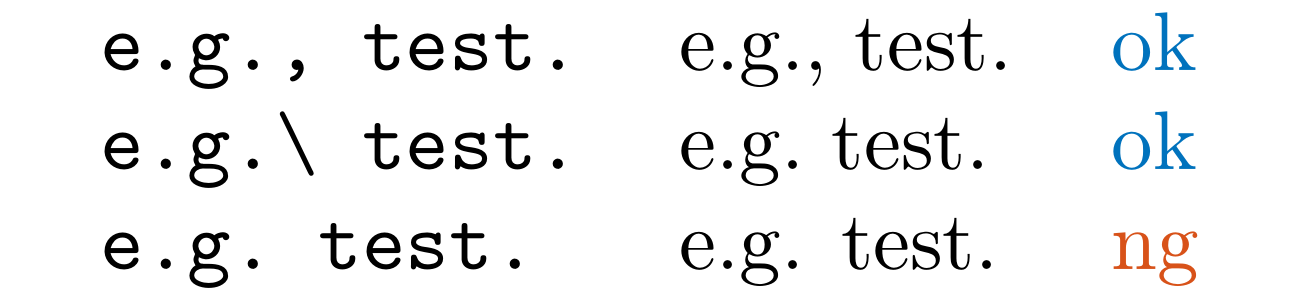
References:
Is a period after an abbreviation the same as an end of sentence period? (Stack Exchange)
LLRefEq
Detect \ref{eq: in .tex files.
You should likely use \eqref{eq: instead.
This command automatically adds parentheses around the reference.
LLSharp
Detect \sharp in .tex and .md files.
You should likely use \# instead for the number sign.
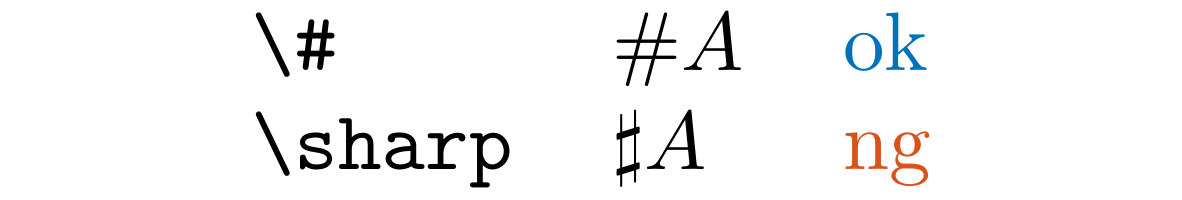
\sharp is used for the musical symbol. We only report it when some heuristic conditions are met.
LLSI
Detect KB, MB, GB, TB, PB, EB, ZB, YB, KiB, MiB, GiB, TiB, PiB, EiB, ZiB, and YiB without \SI in .tex files.
You should likely use \SI instead, like \SI{1}{\kilo\byte}(10^3 byte) and \SI{1}{\kibi\byte}(2^{10} byte) in the siunitx package.
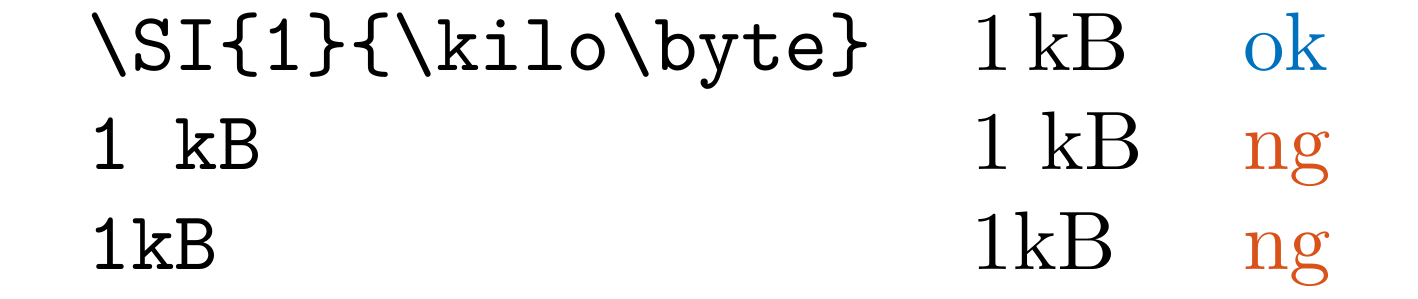
| Prefix |
Command |
Symbol |
Power |
| kilo |
\kilo |
k |
3 |
| mega |
\mega |
M |
6 |
| giga |
\giga |
G |
9 |
| tera |
\tera |
T |
12 |
| peta |
\peta |
P |
15 |
| exa |
\exa |
E |
18 |
| zetta |
\zetta |
Z |
21 |
| yotta |
\yotta |
Y |
24 |
It would be better to use \SI for units such as m, s, kg, A, K, mol, and rad.
LLSortedCites
Detect unsorted multiple citations in .tex files.
Multiple citations like \cite{b,a} can be displayed as [2,1] instead of the sorted order [1,2]. This rule detects such cases and suggests adding the sort option to natbib or using \usepackage{cite}.
This rule only applies when:
- The document uses
\usepackage[numbers]{natbib} without sort option, and
- The document does NOT use
\usepackage{cite} or \usepackage{biblatex}
(This rule might not be accurate.)
LLSpaceEnglish
Detect the lack of space between English text and inline math in .tex and .md files.

LLSpaceJapanese
Detect the lack of space between Japanese characters and math equations in .tex and .md files.
This rule is disabled by default.
LLT
Detect ^T in .tex and .md files.
You likely want to use ^\top or ^\mathsf{T} instead to represent the transpose of a matrix or a vector.
This rule is disabled by default.
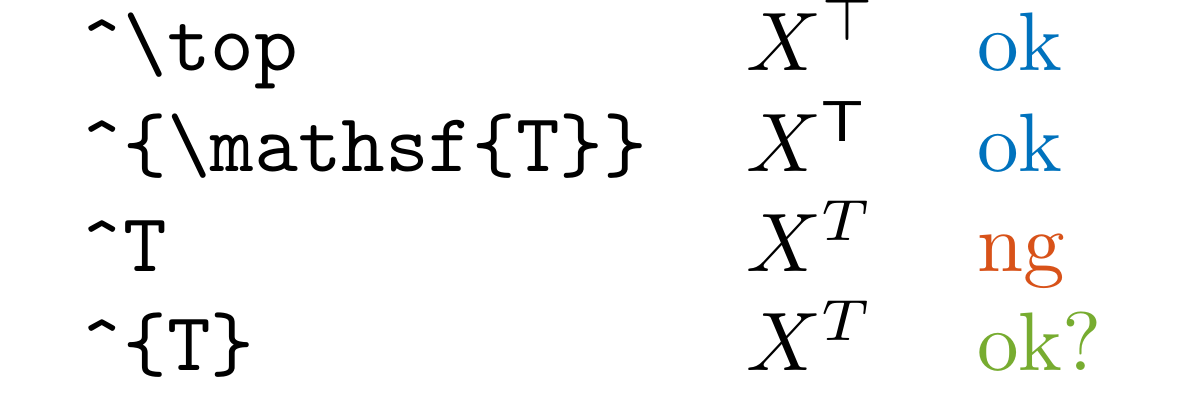
Otherwise, we cannot distinguish between the transpose and the power by a variable T (you can use ^{T} for the power).
References:
What is the best symbol for vector/matrix transpose? (Stack Exchange)
LLTextLint
Detect dubious text in .tex and .md files.
Currently, it only checks japanese texts, and full features are available only in web version.
LLThousands
Detect wrongly used commas as thousands separators, such as 1,000 in .tex files.
You should likely use 1{,}000 or use the package icomma.
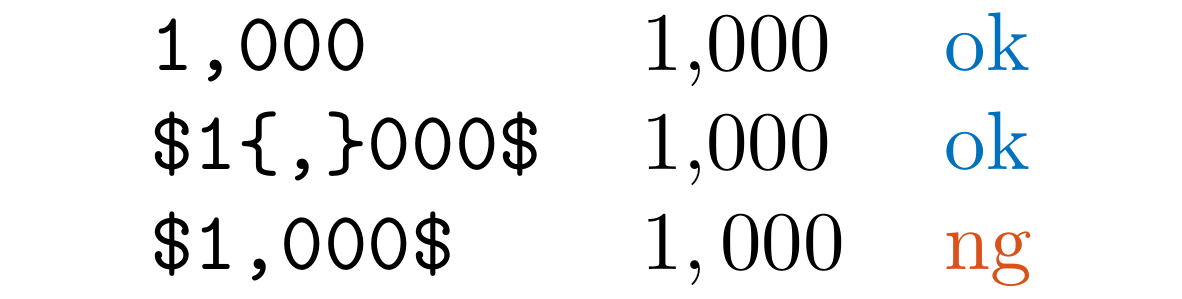
References:
avoid space after commas used as thousands separator in math mode (Stack Exchange)
LLTitle
Detect dubious title cases in \title{}, \section{}, \subsection{}, \subsubsection{}, \paragraph{}, and \subparagraph{} in .tex files.
For example,
The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog
should be
The Quick Brown Fox Jumps Over the Lazy Dog
in the title case. We detect such cases.
It is very difficult to detect all non-title cases because of the many exceptions and styles. We highly recommend using Title Case Converter or Capitalize My Title to convert the title in your preferred style.
We test the string inside the {} is invariant by the function toTitleCase implemented based on to-title-case, JavaScript library. There might be some false positives and negatives.
References:
Title Case Capitalization (APA Style)
LLUnRef
Detect \label{...} in figure and table environments that are never referenced by \ref{...} or \cref{...} in .tex files.
Reference all the figures and tables you label to ensure there are no unused labels in your document.
LLURL
Detect URLs containing query strings in .tex and .md files.
The following query strings are considered unnecessary:
The other query strings are allowed:
?user=... (e.g., Google Scholar profile URLs)?q=... (e.g., search queries)?page=...?lang=...
LLUserDefined
You can define your own regular expressions to detect in .tex and .md files.
Check LaTex Lint: Add Custom Detection Rule for more details.
We listed some examples in the following.
Example 1: Use mathrm for English letters
When you use English letters in math mode for an explanation, you should use \mathrm.
For example, if the character a is not a variable and represents something like atractive force, f^a(x) should be written as f^{\mathrm{a}}(x).
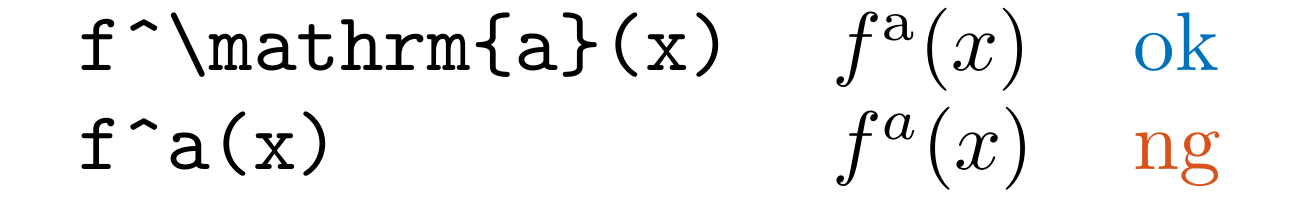
However, it is difficult to detect without context. You can define the rule f\^a to detect this pattern.
Example 2: Use appropriately defined operators
When you use operators, you should use \DeclareMathOperator.
For example, if you use \Box as a infimal convolution, you should define it as an operator.
\DeclareMathOperator{\infConv}{\Box}
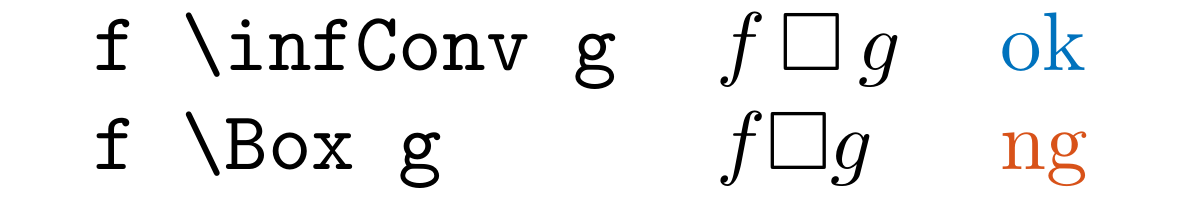
Then, you can use \infConv instead of \Box, and you can define \\Box as a regular expression to detect this pattern.
Other Features
You can also use the following features in VS Code. These commands are available by clicking the icon on the editor toolbar.
LaTeX Lint: Add Custom Detection Rule
Add your own rule to detect.
For example, we can detect f^a by the following steps.
1. Select the string you want to detect (optional)
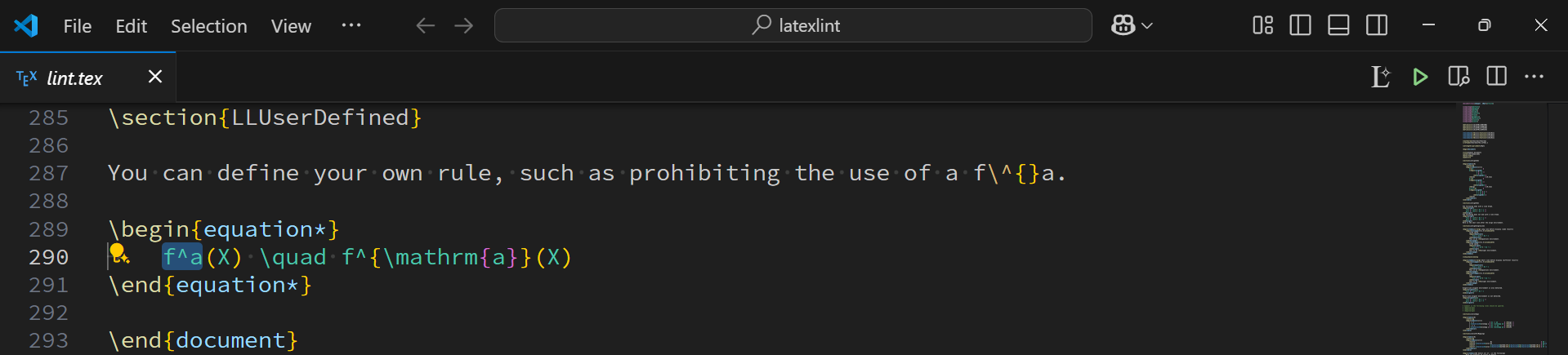
2. Run the command (Add Custom Detection Rule)
Run the commands by clicking the icon or opening the command palette (Ctrl+Shift+P) and type LaTeX Lint: Add Custom Detection Rule.
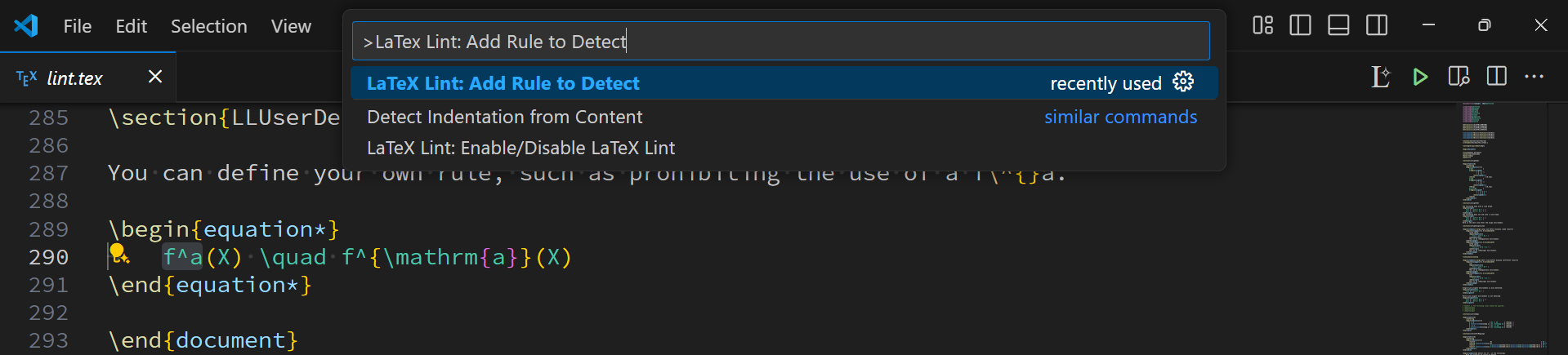
3. Follow the instructions
If you choose string, we detect the input itself.
If you choose Regex, we detect the pattern using Regex.
Then, you can define your own rule.
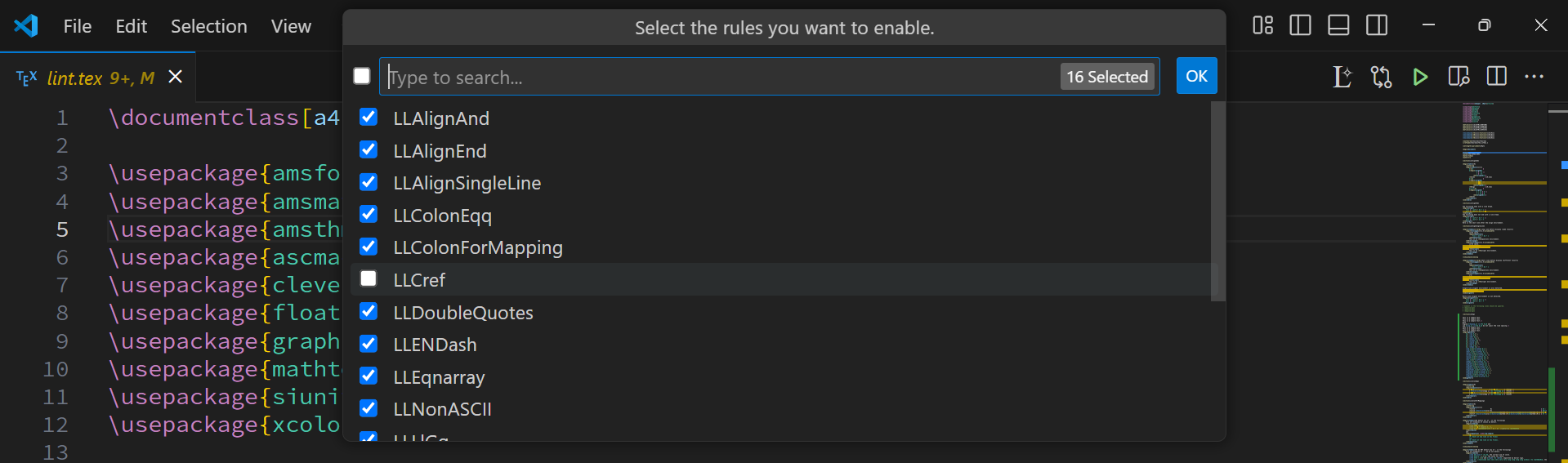
LaTeX Lint: Choose Detection Rules
Select which rules to detect. Check the rules you want to detect.
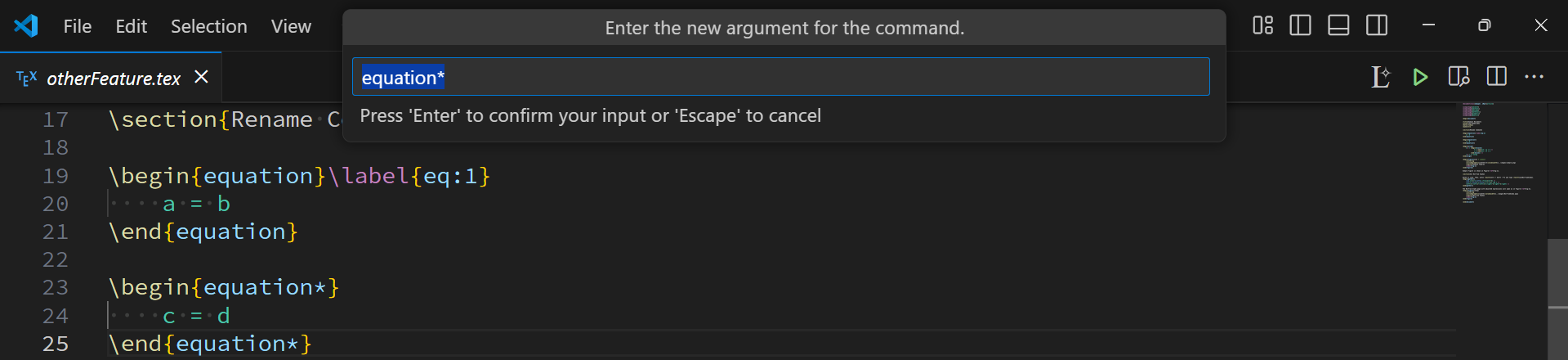
LaTeX Lint: Rename Command or Label
Rename by pressing F2 on the \begin{name}, \end{name} or \label{name}.
Go to Label Definition
Jump to the corresponding \label{xxx} definition by pressing F12 on \ref{xxx}, \cref{xxx}, or \Cref{xxx}.
This feature searches for the matching \label{xxx} in the current file and jumps to the first non-commented occurrence
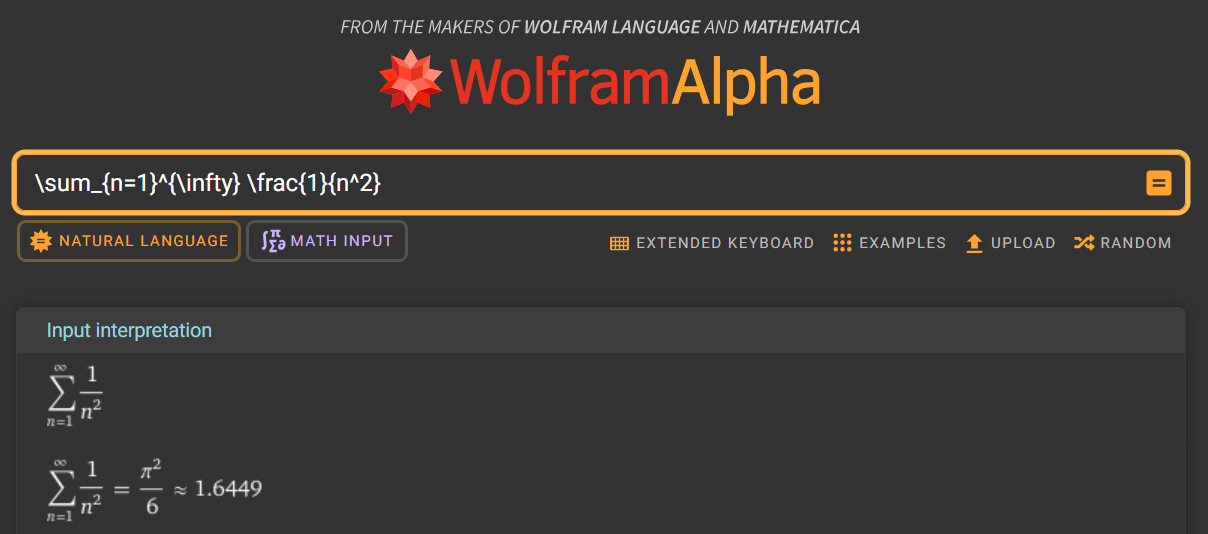
LaTeX Lint: Query Wolfram Alpha
Query Wolfram Alpha to solve the equation.
1. Select the equation you want to solve
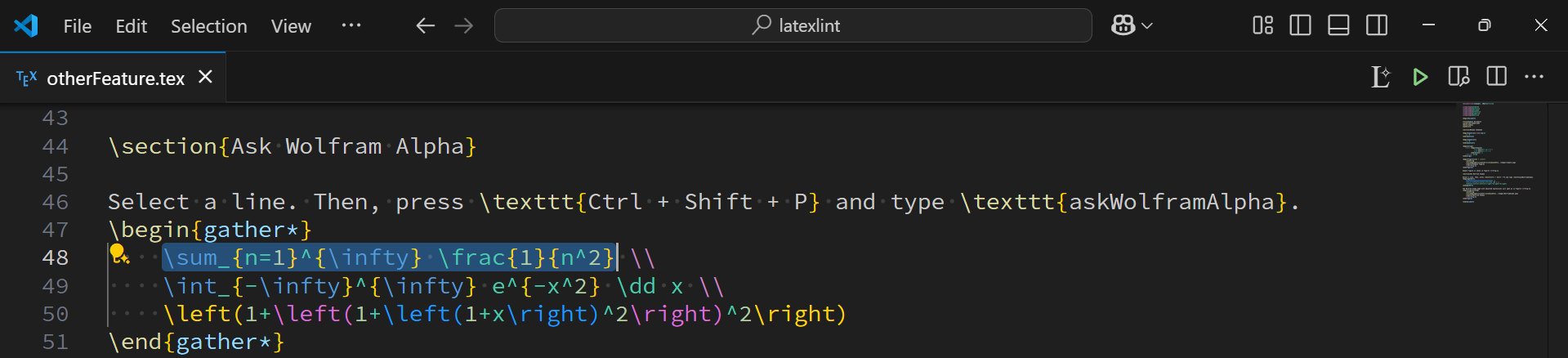
2. Run the command (Query Wolfram Alpha)
Run the commands by clicking the icon or opening the command palette (Ctrl+Shift+P) and type LaTeX Lint: Query Wolfram Alpha.
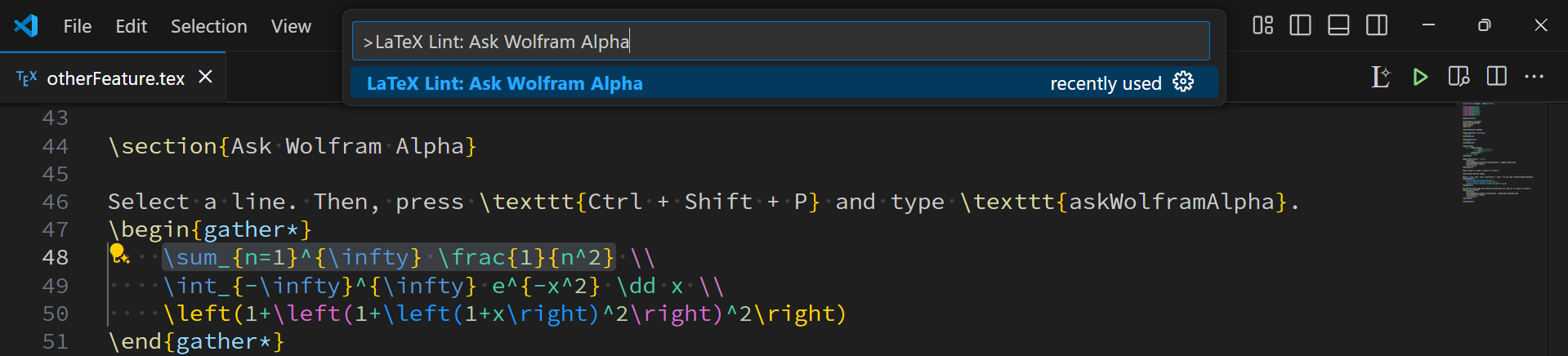
3. Check the Wolfram Alpha page
You can see the result on the Wolfram Alpha page. We remove some unnecessary commands when sending the equation.
Note
As stated in the Rules, false positives and false negatives may occur. We apologize for the inconvenience. If you find any errors, please report them via GitHub Issues.
When writing papers, please ensure you follow the style specified by the academic society or publisher.
We hope our extension would be helpful for your academic writing.
License
This project consists of multiple components with different licenses:
Main Extension (Root Directory)
Licensed under the MIT License.
See LICENSE file for details.
(The library to-title-case is also under MIT License.)
Web Component (web/ directory)
Licensed under the Apache License 2.0.
See web/LICENSE file for details.
The web component includes code from:
- textlint (MIT License)
- kuromoji.js (Apache License 2.0)
Acknowledgement
In some aspects, our extension resembles
We sincerely appreciate the developers of these tools.