Welcome to Connext Copilot
Connext Copilot brings the power of Connext AI to your IDE.
Requirements
To use Connext Copilot, you need the following:
- A Connext AI account
- RTI Chat Extension, which is automatically installed as a dependency when you install this extension
In addition, some chat commands may require additional extensions. For example,
the /createSystemDiagram command requires the Draw.io Integration.
Access
To use Connext Copilot, log in to your
Connext AI account by opening the command palette and selecting "Connext: Login".
You can log out of your Connext AI account by opening the command palette
and selecting "Connext: Logout".
If you do not log in, the extension will ask you to log in when you try to
ask a question.
Features
Chat View: To open the chat view, click the Connext AI avatar icon on the left sidebar, as shown below:
And then type your question:
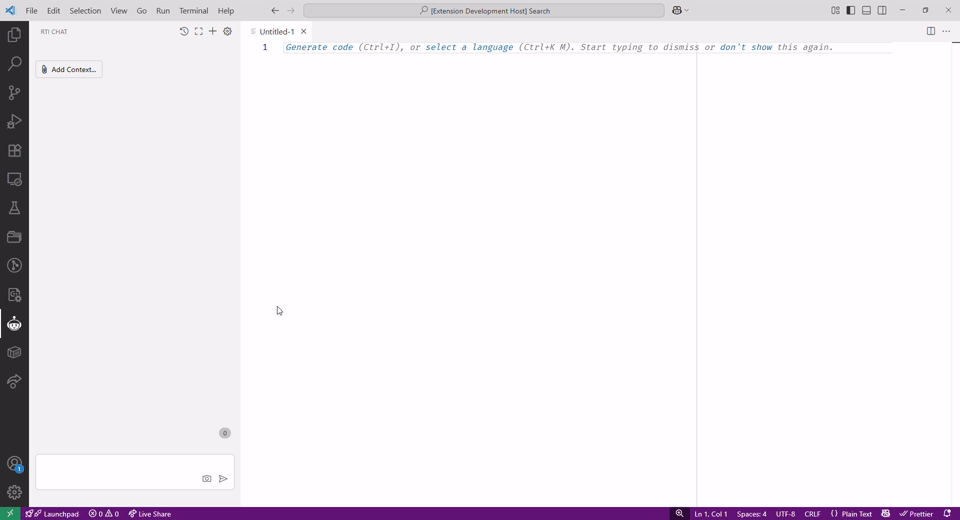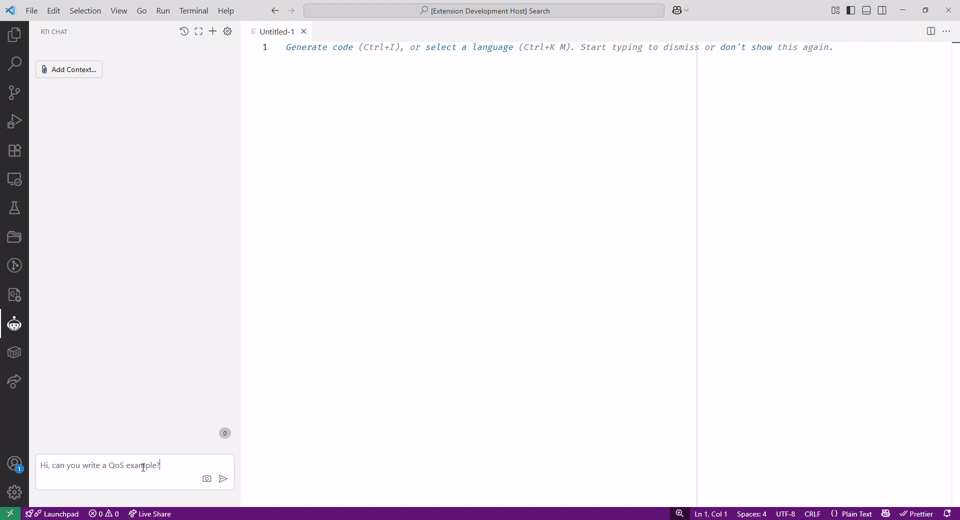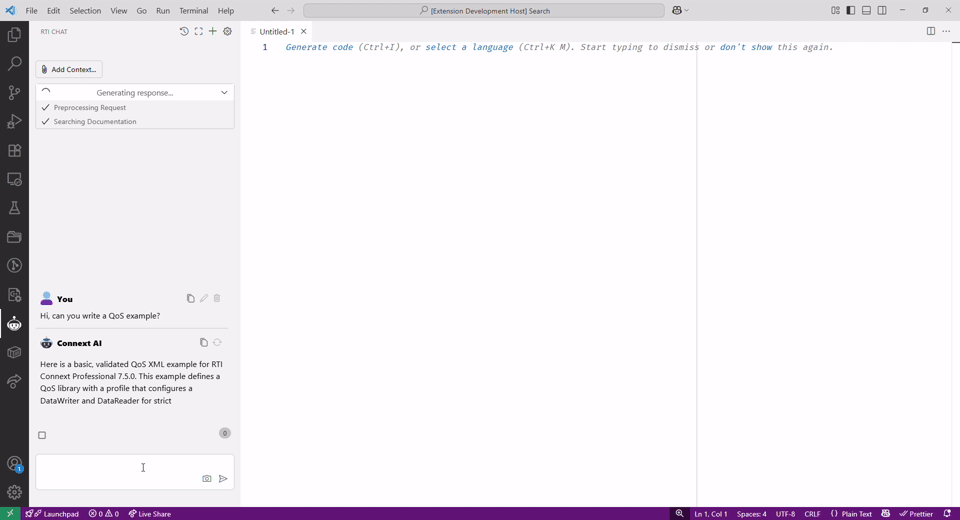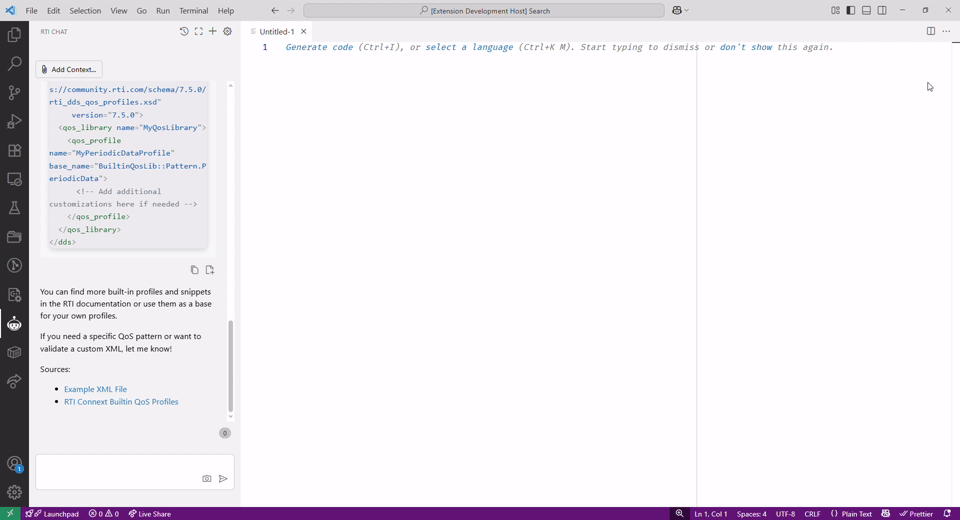
You can enrich your question by adding relevant files or images via the Add Context button:

Chat Commands
This extension allows invoking pre-defined commands from the chat window by
typing /<command>. Standalone Commands can be sent on their own, and Contextual
Commands require an argument or further input.
The available Standalone Commands are:
/showConnextInstallations: Displays information about the Connext installations (Micro,
Professional, or Drive) detected on your system. This command also allows you to
set the default Connext installation and architecture used by the extension./setConnextInstallation: Sets a Connext installation. The user will
be prompted to select the directory where Connext (Micro, Professional, or Drive)
is installed. This command does not select the installation as the default.
To do that, use the /showConnextInstallations command. By default, the extension will try
to detect the installation(s) directories automatically based on standard
locations. However, if an installation is not detected, you can use this
command to manually set the installation./startAdminConsole: Opens RTI Admin Console using the default installation./startSystemDesigner: Opens RTI System Designer using the default
installation./startMonitorUI: Opens the RTI Monitor UI using the default installation./startShapesDemo: Starts the RTI Shapes Demo using the default installation./createSystemDiagram: Opens the draw.io extension to create a diagram. From this
diagram, you can generate a Connext system XML model using the command
/generateSystemXmlModel. You can find an example diagram here./generateSystemXmlModel: Generates a Connext system XML model from a draw.io
diagram or an image (PNG, JPG, GIF, WebP). Open the file in your IDE and
enter /generateSystemXmlModel. Example image here. If there
are multiple files open, the command will use the first one.
The Contextual Commands are:
/includeOpenFiles <your prompt>: By adding this command alongside your question or prompt,
the extension will consider open files in the editor
as part of the question context. To not type the command every time, you can
toggle this setting on and off in the extension settings./includeWorkspace <your prompt>: By adding this command alongside your question or prompt,
the extension will consider all files in the
workspace as part of the question context. To not type the command every time,
you can toggle this setting on and off in the extension settings./quickStartExample <example description>: Generates a new example project using the default
installation for an example of your description. It is recommended to describe the DDS type
you want to use and programming language of your choice. See examples below in the New Example
Command section. It also allows you to modify the publisher and subscriber code. This command
uses the rtiddsgen tool to generate the example code. This command is designed to generate a
simple, self-contained Hello-World type application — ideal for learning and
experimentation, not for starting production projects.
The commands that start tools and generate new examples will fail if there is
no default Connext installation configured (either by using the default
installation directory or by setting the NDDSHOME environmental variable).
The commands that start tools may not work on Windows Subsystem Linux (WSL)
depending on the OS and WSL versions.
Using natural language to invoke commands
You can use natural language to invoke commands, for example:
- Can you tell me what version of Connext am I running?
- Please start shapes demo
- Can you create a simple example for a basic sensor type in python? I would like the example to use waitsets in the subscriber
To use this feature, you must enable the checkbox under User Settings ->
Connext -> Enable Command Detection.
includeOpenFiles and includeWorkspace commands
The /includeOpenFiles and /includeWorkspace commands allow you to include open
files and workspace files in the question context. Only files with the following
extensions are considered: .xml, .drawio, .idl, .c, .h, .cxx,
.cpp, .hpp, .py, .cs, .java, .txt, .md, .png, .jpg, .jpeg,
.gif, .webp
Additionally, the following files automatically generated by rtiddsgen are
ignored:
- For C:
<IDL file name>Support.h, <IDL file name>Support.c, <IDL file name>Plugin.h,
<IDL file name>Plugin.c, and <IDL file name>.c.
- Traditional C++:
<IDL file name>Support.h, <IDL file name>Support.cxx,
<IDL file name>Plugin.h, <IDL file name>Plugin.cxx, and <IDL file name>.cxx.
- Modern C++:
<IDL file name>Plugin.hpp, <IDL file name>Plugin.cpp, and
<IDL file name>.cpp.
- C#: Plugin.cs.
- Java:
<type name>TypeCode.java, <type name>Support.java,
<type name>DataReader.java, and <type name>DataWriter.java for each type in
the IDL file.
The /includeWorkspace command also excludes the following directories: .git,
.vscode, node_modules, CMakeFiles
New Example Command
The /quickStartExample command generates a new example project using the default
installation for a specified type and language.
For example:
/quickStartExample Temperature sensor in Python. The publisher should generate and publish temperature readings fluctuating between 60°F and 90°F.
/quickStartExample Car battery state in modern C++. The subscriber must use a listener to receive the battery state.
This command produces a fully functional example, including all necessary files
and code required for compilation and execution.
The command generates the example as follows:
- First, it generates the IDL file based on the type description you provide.
- Then, it generates the publisher and subscriber code based on the IDL file
using rtiddsgen.
- Then, it updates the publisher and subscriber code using the
instructions you provide.
- Finally, it generates the build system files and configuration files
required to build, run, and debug the example.
To compile and run the generated code, you may need different extensions such as
the CMake Tools
extension.
C, Traditional C++, and Modern C++
For C, traditional C++, and modern C++, the /quickStartExample command generates:
- A CMakeLists.txt file for building the example.
- A CMakePresets.json file for configuring the build system.
- A "launch.json" file for running and debugging the example.
By default, the generator variable in CMakePresets.json is set to:
- "Unix Makefiles" on macOS and Linux.
- A generator derived from the default Connext architecture you chose on Windows after
running the
/showConnextInstallations command.
You can override the generator by configuring the cmake.generator option if
the default generator is not suitable or available in your environment.
To list the available generators, run the following command in the terminal:
cmake --help
Java
For Java, the /quickStartExample command generates:
- A setting.json file for building the example.
- A "launch.json" file for running and debugging the example.
Python
For Python, the /quickStartExample command generates:
- A "launch.json" file for debugging the example.
The Python example requires installing the Connext Python API. For details on
how to install the Connext Python API, refer to the RTI Connext DDS Professional Installation Guide.
C# and .NET
For C# and .NET, the /quickStartExample command generates:
- A "launch.json" file for running and debugging the example.
AI Privacy
Connext Copilot uses the Active File as part of its context for answering questions. To disable this feature,
select "None" from the dropdown menu under User Settings -> Connext -> Context Files.
Visit our Privacy information page for more information.
[Optional] Using Connext Copilot with GitHub Copilot Chat
Connext Copilot can be optionally used with GitHub Copilot Chat. To do so,
enable the checkbox under User Settings -> Connext -> GitHub Copilot Compatibility.
To run Connext Copilot with GitHub Copilot, you need:
In the GitHub Copilot Chat interface, simply type @connext followed by your
question or command. Once you type @connext, the Connext expert
will stay active allowing you to ask multiple questions without having to type
@connext again. Using @connext is only necessary if you are using the GitHub Copilot Chat interface.
GitHub Copilot Compatibility must be enabled to use the "Connext" right-click
context menu (with options like, "Explain this") and VS Code's "Quick Chat" feature.
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Real-Time Innovations, Inc. All rights reserved.
RTI grants you the right to compile and use this software. You may not modify, create derivative works of, or distribute the software.
This software is an experimental (i.e., pre-production or beta) product. It is provided “as is”, with no warranty of any type, including any warranty for fitness for any purpose. RTI is under no obligation to maintain or support the Software. RTI shall not be liable for any incidental or consequential damages arising out of the use or inability to use the software.
This software integrates with AI services provided by RTI, and your use of those services is subject to RTI's Privacy Policy and these Terms of Use.
Please provide feedback via email to the Connext AI team at
connext-ai-feedback@rti.com.
For further assistance or inquiries, you can also reach out to RTI's support
team at support@rti.com.



