Codebraid Preview
Codebraid Preview provides a Pandoc-based document
preview within VS Code. All of
Pandoc's extensions to
Markdown syntax are fully supported—because the preview is generated by
Pandoc itself! The preview also includes built-in support for
LaTeX, Org,
reStructuredText, and
Textile. Codebraid Preview is compatible with
any text-based document format supported by Pandoc. Additional formats can
typically be enabled by defining a few settings.
There is scroll sync between the document source and the preview for Markdown,
LaTeX, Org, reStructuredText, and Textile. Scroll sync support can be
extended for additional formats. Documents can be exported via Pandoc.
Several export formats are predefined, including HTML, LaTeX, PDF, PowerPoint,
and Word. Additional formats can be defined in settings. There is optional
support for executing code blocks and inline code to embed their output in the
preview and in exported documents. This is performed by
Codebraid and is currently limited to
Markdown documents.
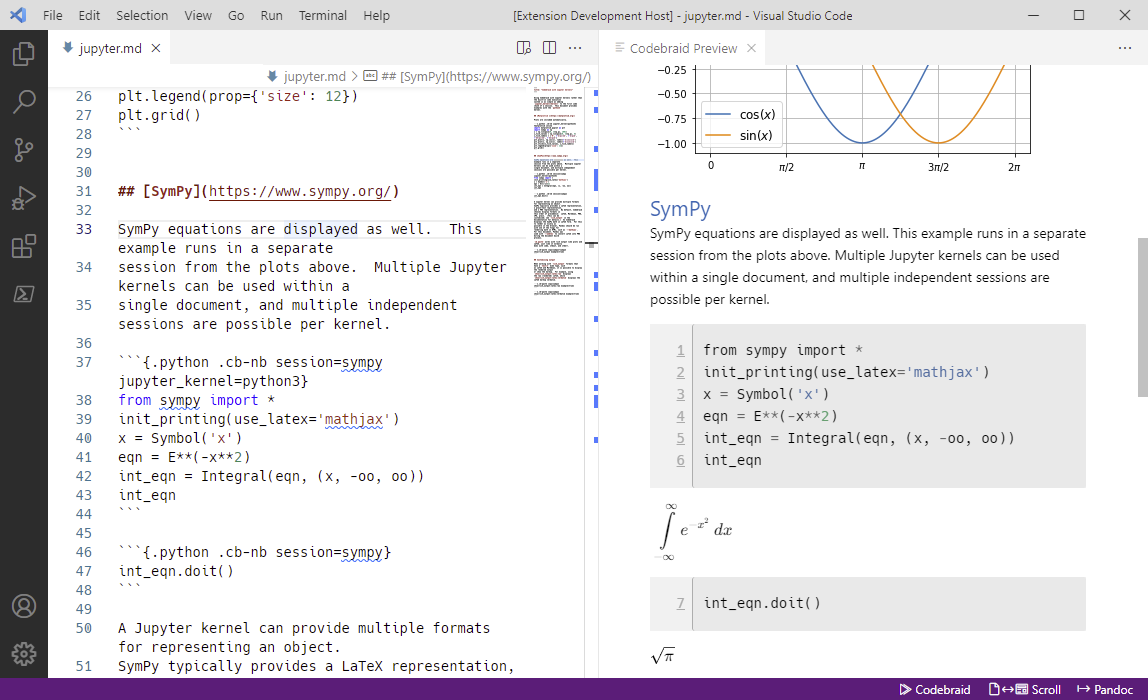
Features
HTML preview of Pandoc documents. Open the preview by running the "Open
Codebraid Preview" command (Ctrl+Shift+P, then type command). Or, for
document formats with built-in support, just click on the "Codebraid
Preview" button in the status bar (bottom right). When changes are
detected, the preview automatically refreshes.
Full bidirectional scroll sync. Scroll sync between the document source
and the preview is provided for Markdown, LaTeX, Org, reStructuredText, and
Textile. Scroll sync support can be extended for additional formats. For
formats with built-in Pandoc support, please open an issue on
GitHub to request
scroll sync. For custom formats, look in the Git repo under
pandoc/lib/readerlib.lua and pandoc/readers for details about adding
scroll sync using a short Lua wrapper script.
For best scroll sync results with Markdown, use a
CommonMark-based format (commonmark_x,
commonmark, or gfm). commonmark_x has
most of the features
in Pandoc's Markdown and continues to gain new features.
Math support with KaTeX. In Markdown documents,
surround LaTeX math with single dollar signs $ for inline math or double
dollar signs $$ for block math, following standard Pandoc conventions.
KaTeX is also used to display math for other document formats.
Adjustable scroll sync directions. Once a preview window is open, click
on the "Scroll" button in the status bar (bottom right) to toggle scroll
mode.
Double-click to jump to source. Double-click in the preview, and jump
to the start of the corresponding line in the document.
Jump to error. When a document is invalid, the preview displays the
Pandoc parse error with a link that jumps to the corresponding source
location. This is particularly useful for formats like LaTeX.
Export documents with Pandoc (including Codebraid output). Simply click
the "Pandoc" button in the status bar (bottom right), or use the "Export
document with Pandoc" command (Ctrl+Shift+P, then type command). Several
export formats are predefined, including HTML, LaTeX, PDF,
PowerPoint, and Word. Additional formats can be defined in settings,
under codebraid.preview.pandoc.build.
Scroll-sync support for multi-file documents. Pandoc allows you to
divide a document into multiple files that are combined into a single output
document at build time. Codebraid Preview can display such documents as
long as all document files are in the same directory (folder). For
multi-file documents, create a YAML file that lists the document files to be
combined. For example, suppose your document is divided into chapter_1.md
and chapter_2.md, both in the same directory. Simply create a file named
_codebraid_preview.yaml with this contents:
input-files:
- chapter_1.md
- chapter_2.md
Now, when you launch a preview in either chapter_1.md or chapter_2.md,
both files will be combined in the preview. When you scroll the preview,
the editor will automatically switch between chapter_1.md and
chapter_2.md depending on which part of the document you are viewing.
That is, scroll sync works across multiple input files!
Execute code. Codebraid allows
code blocks or inline code in Pandoc Markdown documents to be executed, with
output embedded in the document. Code execution is performed using Jupyter
kernels or Codebraid's own built-in code execution system. Simply add
Codebraid attributes to your code, then click the "Codebraid" button in the
status bar (bottom right) or use the "Run code with Codebraid" command
(Ctrl+Shift+P, then type command).
For example, to execute a Python fenced code block, simply add the
attributes {.python .cb-run} immediately after the opening fence ```,
so that the code block begins with ```{.python .cb-run}. Then click the
Codebraid button. To use a Jupyter kernel for code execution, with a notebook-style display of output, use
```{.python .cb-nb jupyter_kernel=python3} in the first code block to be
executed and ```{.python .cb-nb} in subsequent code blocks.
When you first load a document that uses Codebraid, any cached code output
will automatically be loaded and displayed in the document. The preview
will automatically refresh when you make changes to the document outside of
executed code. However, code never runs automatically. Code execution
requires clicking the "Codebraid" button or using the "Run code with
Codebraid" command.
When code is running, the preview still updates whenever the document is
modified, displaying all code output that is currently available. The
preview always remains live.
Setup and requirements
Pandoc
Install Pandoc. The latest version is recommended.
Version 3.1.1+ is required for scroll sync for formats besides commonmark_x,
commonmark, and gfm. Versions before 2.17.1.1 may work but will have
reduced functionality, including scroll sync issues with YAML metadata.
Default Markdown reader
By default, Markdown documents are treated as Pandoc's commonmark_x format,
since this provides the best scroll sync experience while still supporting
most Pandoc extensions to Markdown syntax. If you need features that are only
available in Pandoc's Markdown (markdown), modify the extension setting
codebraid.preview.pandoc.build, under *.md, to change reader from
commonmark_x to markdown. This will cause scroll sync to be less accurate
in some circumstances, since scroll sync data must be reconstructed by
Codebraid Preview instead of being generated by Pandoc itself.
Codebraid
For code execution, install the latest version of
Codebraid. Codebraid currently only
supports code execution in Markdown documents.
Security
You may want to review the default security settings under
codebraid.preview.security. For example, if you are using remote images,
you will need to enable codebraid.preview.security.allowRemoteImages. If
you are using Codebraid with Jupyter output that involves scripts, then you
will need to enable inline scripts or local scripts.
To add basic support for an additional document format, simply create a
defaults file in the document directory that specifies from or reader.
See setting codebraid.preview.pandoc.defaultsFile. Or define an additional
file extension under codebraid.preview.pandoc.build.
For formats with built-in Pandoc support, please open an issue on
GitHub to request scroll
sync. For custom formats, look in the Git repo under
pandoc/lib/readerlib.lua and pandoc/readers for details about adding
scroll sync using a short Lua wrapper script.
Jupyter notebooks
The preview is compatible with Jupyter notebooks (ipynb). Simply add the
following to settings.json, under codebraid.preview.pandoc.build:
"*.ipynb": {
"reader": "ipynb",
"preview": {
"html": {
"defaults": {},
"options": []
}
},
"export": {}
},
Jupyter notebooks have some limitations compared to other formats. Scroll
sync is not currently supported. The preview currently only updates when the
notebook is saved; the preview does not update live as you type.
VS Code already provides a
built-in notebook editor.
A Pandoc-based preview for Jupyter notebooks will primarily be useful when
Pandoc filters or similar features are used to customize a notebook during
export.
By default, Markdown documents are treated as Pandoc's commonmark_x format,
which is different from Pandoc's default markdown format. Scroll sync data
is only generated by Pandoc for CommonMark-based formats, and commonmark_x
is the most powerful of these. For other formats, Codebraid Preview must
reconstruct scroll sync data, and this can be less accurate in some
circumstances.
The Pandoc Roadmap
provides details about commonmark_x features. commonmark_x currently
lacks some markdown features that are summarized below. If you need these
features, you can switch the input format to markdown by modifying the
extension setting codebraid.preview.pandoc.build, under *.md, to change
reader from commonmark_x to markdown. Or you can create a
defaults file _codebraid_preview.yaml in the document directory and set
from: markdown in it. Keep in mind that switching to markdown will
make scroll sync less accurate in some circumstances.
Summary of some key features not present in commonmark_x compared to
markdown:
Citations: Not currently supported, but planned.
Tables: Grid tables, multiline tables, simple tables, and table
captions are not supported but planned. Pipe tables are supported.
LaTeX math: Only $ and $$ are supported as delimiters. Variations
on \(...\) and \[...\] are not supported.
Raw LaTeX: LaTeX cannot just be mixed with Markdown text. Instead, raw
attributes must be used. So instead of text \command text use something
like text `\command`{=tex} text.
LaTeX macros: User-defined LaTeX macros are not expanded by Pandoc
itself before document conversion (the latex_macros extension is not
supported), so the output format must handle macro expansion. This is
primarily important for non-LaTeX formats.
In a document using LaTeX math but targeting a non-LaTeX format like HTML,
this can mean that macro definitions belong in a LaTeX math block and must
be made global. For example, the markdown document
\newcommand{\tuple}[1]{\langle [#1](https://github.com/gpoore/codebraid-preview-vscode/issues/1)\rangle}
$\tuple{a, b, c}$
might become the commonmark_x document
$$
\newcommand{\tuple}[1]{\langle [#1](https://github.com/gpoore/codebraid-preview-vscode/issues/1)\rangle}
\global\let\tuple\tuple
$$
$\tuple{a, b, c}$
The exact details of macro definition processing will depend somewhat on how
LaTeX math is rendered and on the configuration of the renderer.
A note on filters
Scroll sync is provided for CommonMark-based formats using Pandoc's
sourcepos extension. For other formats with scroll sync, Codebraid Preview
provides an emulation of sourcepos. In either case, this inserts Div and
Span nodes into the Pandoc AST that contain information about source file
origin location in a data-pos attribute. If you use filters with your
documents and want to make sure that the preview is accurate while retaining
scroll sync capabilities, make sure that your filters skip these nodes and
only remove them if empty. For example, in a Lua filter these nodes can be
detected by checking node.attributes['data-pos'] ~= nil.
Block-level filters typically must be modified to be compatible with Pandoc's
sourcepos because it inserts many Div nodes with a data-pos attribute
into the AST. Block-level filters typically do not require modification for
Codebraid Preview's sourcepos because it only inserts Div nodes into the
AST to wrap CodeBlock and RawBlock nodes. Pandoc's sourcepos is used by
default when available (CommonMark-based formats commonmark, commonmark_x,
and gfm). To use Codebraid Preview's sourcepos instead, change the
setting codebraid.preview.pandoc.preferPandocSourcepos to false.
Custom Pandoc HTML templates
The preview is compatible with custom Pandoc HTML templates. Custom templates
should typically be based on the default Pandoc template. The default Pandoc
template can be viewed by running pandoc --print-default-template=html.
Custom templates must have this general format (case insensitive):
<!-- ... --> {optional comment(s)}
<!doctype html> {required}
<!-- ... --> {optional comment(s)}
<html {attrs}> {required; optional attributes}
<!-- ... --> {optional comment(s)}
<head> {required}
...
Currently, any optional attributes in the html tag must have names matching
the regex [a-zA-Z][a-zA-Z0-9]*(?:[:-][a-zA-Z0-9]+)* with quoted values.
Custom templates must also include CSS for the preview to display properly.
This can be done following the default Pandoc template:
$for(css)$
<link rel="stylesheet" href="$css$" />
$endfor$
The preview sets the Pandoc template variable codebraid_preview to true.
When necessary, custom templates can use this to adapt to Codebraid Preview.
For example:
$if(codebraid_preview)$
...
$else$
...
$endif$
Known limitations
Some Pandoc options have limited preview support or require special settings.
--embed-resources: Version 0.15.0 added support for --embed-resources
(and deprecated --self-contained). This option may not work when the path
to the VS Code extension installation location contains spaces. Currently,
the setting codebraid.preview.security.allowEmbeddedScripts must be
enabled for some features that rely on JavaScript, such as KaTeX math.
Note that when using --embed-resources, setting allowEmbeddedScripts to
true effectively allows all JavaScript, so this should only be used with
documents that you trust.
Extension settings
Document build and display
codebraid.preview.css.overrideDefault [true]: Whether document CSS
overrides the preview's default CSS (determines which is loaded last).
codebraid.preview.css.useDefault [true]: Whether the preview's default
CSS is used.
codebraid.preview.css.useMarkdownPreviewFontSettings [true]: Inherit
font settings (font family, font size, line height) from the built-in
Markdown preview (settings under markdown.preview), to maintain a
similar appearance.
codebraid.preview.css.useMarkdownPreviewStyles [true]: Inherit custom
styles (CSS) from the built-in Markdown preview (markdown.styles), to
maintain a similar appearance.
codebraid.preview.minBuildInterval [1000]: Minimum interval between
document builds in milliseconds. Builds only occur when there are changes.
Pandoc
codebraid.preview.pandoc.build [<default config for several formats>]:
This is where file extensions are associated with Pandoc build settings for
preview and export. For example, here is the default entry for Markdown
documents:
"*.md": {
"reader": "commonmark_x",
"preview": {"html": {"defaults": {}, "options": []}},
"export": {}
},
reader determines the input format that Pandoc uses for files with this
file extension. If a custom Lua reader is used instead of a built-in Pandoc
format, it must be quoted appropriately for usage within a shell. It will
be passed to Pandoc as a command-line option in a child process.
preview determine how the HTML preview is built. By default, there is
only a single preview build configuration for HTML. It is possible to
create multiple preview configurations. Then, when you start the preview,
you will be prompted to select the appropriate configuration. For example,
this creates an additional preview configuration with a custom highlighting
style and a table of contents:
"preview": {
"html": {"defaults": {}, "options": []},
"custom (highlight kate, table of contents)": {
"writer": "html",
"defaults": {"highlight-style": "kate"},
"options": ["--toc"]
}
}
In this case, the name of one configuration (custom ...) is not a Pandoc
writer, so the configuration must specify a writer name explicitly
("writer": "html"). The defaults values are saved in a Pandoc defaults
file and are used as fallback values. They can be overridden by options
or by values specified in user defaults files (such as
codebraid.preview.pandoc.defaultsFile). The options values are
command-line options. Each array element must be a single option, for
example, ["--filter FILTER"]. They must be quoted appropriately for being
used in a shell. Because they are command-line options that are passed to
the Pandoc executable, they override defaults and also user defaults
files.
export is similar to preview, except that it specifies build
configurations for export rather than preview. These custom export
configurations are added to the predefined export configurations that are
always available.
Within a build configuration, writer (if present) and options will be
used within a shell and must be quoted appropriately. Under Windows, a
leading unquoted ~/ or ~\ in writer or in an option value will be
expanded to the user's home directory (os.homedir()), since this is not
done by the shell.
codebraid.preview.pandoc.defaultsFile [_codebraid_preview.yaml]: Special
Pandoc defaults file in the
document directory that is used for previewing and exporting documents.
Almost all Pandoc defaults options are supported. If the defaults file
includes additional external defaults files by setting defaults, then the
following options in those additional external defaults files will be
ignored: input-files, input-file, from, reader, to, writer, and
file-scope. The preview must know the values of these options to function
correctly, and it does not attempt to replicate Pandoc's system for locating
and merging multiple defaults files.
While almost all defaults options are supported, keep in mind that some
options or option values are irrelevant or inappropriate. The preview is
HTML, so avoid options that do not affect HTML, are incompatible with HTML,
result in non-HTML output, or redirect the output.
If the defaults file is modified within VS Code, the preview will
automatically detect changes and update. If the defaults file is modified
in another editor, close and restart the preview for changes to be applied.
If the defaults file exists and it defines input-files, then the preview
will automatically work with all files in a multi-file document. If the
defaults file defines input-files (or input-file), then it will only be
applied to the specified files; it will be ignored for other files.
If the defaults file defines input-files (or input-file), all specified
files must be in the same directory with the defaults file. Document files
in subdirectories are not supported.
codebraid.preview.pandoc.extraEnv [{}]: Additional environment
variables that are set for the Pandoc subprocess used to generate the
preview and to export documents.
codebraid.preview.pandoc.executable [pandoc]: Pandoc executable. This
is used within a shell, so it must be appropriately quoted and escaped.
If this is a wrapper script for Pandoc, it must return Pandoc's version info
verbatim when called with --version.
codebraid.preview.pandoc.preferPandocSourcepos [true]: Use Pandoc's
sourcepos extension when available, instead of using Codebraid Preview's
emulation of sourcepos. Sourcepos data maps input file(s) to preview HTML
and makes possible scroll sync. Pandoc's sourcepos usually gives more
accurate scroll sync, but also typically requires block-level filters to
skip sourcepos elements with a data-pos attribute in the Pandoc AST.
Pandoc's sourcepos is only available for CommonMark-based formats
(commonmark, commonmark_x, and gfm). Codebraid Preview's emulation of
sourcepos usually gives less accurate scroll sync, but also typically
requires no modifications for block-level filters.
codebraid.preview.pandoc.showRaw [true]: Display a verbatim
representation of non-HTML raw content (Pandoc Markdown {=format}) in the
preview.
codebraid.preview.pandoc.showStderr [always]: Display a notification in
the preview when Pandoc completes without errors but its stderr is
non-empty (there are always notifications for errors). Accepted values:
never: no displaywarning: display only when stderr contains the word "warning" (case
insensitive)always: always display regardless of content
Security
The HTML preview is displayed using a webview. These settings determine which
local and remote resources, such as images and scripts, can be loaded by the
webview. These settings only determine the resources that the webview can
load. They do not affect the resources that Pandoc can access or determine
which resources Pandoc can embed in the HTML preview document (see note
below).
By default, all remote resources are disabled. By default, local resources
can only be loaded from the current workspace folders, the document directory,
and the default Pandoc user data directory (see output of pandoc --version
for location). Additional local locations can be added via
security.extraLocalResourceRoots. All types of local resources are
permitted by default except for scripts. Inline scripts are also not
permitted by default, except for those bundled as part of the extension.
Scripting capabilities should only be enabled when using documents that you
trust. Styles (CSS), particularly when combined with images/media or fonts,
can also have security implications, especially when remote resources are
involved.
Note on limitations of security settings: Many security settings
determine which resources the webview can load. However, the Pandoc option
--embed-resources uses data: URIs to incorporate the contents of linked
scripts, stylesheets, images, and videos directly into the HTML. If you
choose to use --embed-resources, be aware that this makes these security
settings irrelevant, since content is embedded in the HTML rather than being
loaded from a local or remote source. Similarly, --extract-media makes most
image and media security settings irrelevant, because it copies or downloads
all images and media to a local temp directory that is accessible by default.
--extract-media is required to preview Jupyter notebooks and is
automatically enabled only for that case.
Inline
codebraid.preview.security.allowInlineScripts [false]: Allow the
preview to use inline scripts <script>...</script>. (Scripts bundled as
part of the extension are always allowed.)
Embedded
codebraid.preview.security.allowEmbeddedFonts [true]: Allow the preview
to load fonts from data: URLs. This is helpful when using
--embed-resources (or deprecated --self-contained) to embed resources in
the preview document rather than loading them from local or remote
locations.
codebraid.preview.security.allowEmbeddedImages [true]: Allow the
preview to load images from data: URLs. This is helpful when using
--embed-resources (or deprecated --self-contained) to embed resources in
the preview document rather than loading them from local or remote
locations.
codebraid.preview.security.allowEmbeddedMedia [true]: Allow the preview
to load media from data: URLs. This is helpful when using
--embed-resources (or deprecated --self-contained) to embed resources in
the preview document rather than loading them from local or remote
locations.
codebraid.preview.security.allowEmbeddedScripts [false]: Allow the
preview to load scripts from data: URLs. This is helpful when using
--embed-resources (or deprecated --self-contained) to embed resources in
the preview document rather than loading them from local or remote
locations.
codebraid.preview.security.allowEmbeddedStyles [true]: Allow the
preview to load styles from data: URLs. This is helpful when using
--embed-resources (or deprecated --self-contained) to embed resources in
the preview document rather than loading them from local or remote
locations.
Local
codebraid.preview.security.allowLocalFonts [true]: Allow the preview to
load fonts from the current workspace folder, the document directory, the
default Pandoc user data directory (if enabled via
security.pandocDefaultDataDirIsResourceRoot), and any other locations
specified in security.extraLocalResourceRoots. (Fonts bundled as part of
the extension are always allowed.)
codebraid.preview.security.allowLocalImages [true]: Allow the preview
to load images from the current workspace folder, the document directory,
the default Pandoc user data directory (if enabled via
security.pandocDefaultDataDirIsResourceRoot), and any other locations
specified in security.extraLocalResourceRoots.
codebraid.preview.security.allowLocalMedia [true]: Allow the preview to
load media from the current workspace folder, the document directory, the
default Pandoc user data directory (if enabled via
security.pandocDefaultDataDirIsResourceRoot), and any other locations
specified in security.extraLocalResourceRoots.
codebraid.preview.security.allowLocalScripts [false]: Allow the preview
to load scripts from the current workspace folder, the document directory,
the default Pandoc user data directory (if enabled via
security.pandocDefaultDataDirIsResourceRoot), and any other locations
specified in security.extraLocalResourceRoots. (Scripts bundled as part
of the extension are always allowed.)
codebraid.preview.security.allowLocalStyles [true]: Allow the preview
to load styles from the current workspace folder, the document directory,
the default Pandoc user data directory (if enabled via
security.pandocDefaultDataDirIsResourceRoot), and any other locations
specified in security.extraLocalResourceRoots. (Styles bundled as part of
the extension are always allowed.)
Remote
codebraid.preview.security.allowRemoteFonts [false]: Allow the preview
to load fonts from remote locations via https.
codebraid.preview.security.allowRemoteImages [false]: Allow the preview
to load images from remote locations via https.
codebraid.preview.security.allowRemoteMedia [false]: Allow the preview
to load media from remote locations via https.
codebraid.preview.security.allowRemoteScripts [false]: Allow the
preview to load scripts from remote locations via https.
codebraid.preview.security.allowRemoteStyles [false]: Allow the preview
to load styles from remote locations via https.
Resource roots
codebraid.preview.security.extraLocalResourceRoots [none]: Additional
root paths from which the preview can load local (filesystem) resources,
such as images and CSS. These are in addition to the current workspace
folders, the document directory, and the default Pandoc user data directory
(if enabled via security.pandocDefaultDataDirIsResourceRoot).
Paths may be absolute or relative. In absolute paths, a leading ~/ is
expanded to the user's home directory. Relative paths are relative to the
document file; for example, ../images refers to an images directory one
level up from the document. For setting extraLocalResourceRoots paths,
either absolute or relative paths are fine. Within a document, relative
paths should be preferred because they will automatically work with the
preview's webview. If you use absolute paths, you will typically need to
build a document with --embed-resources for resources to load correctly.
codebraid.preview.security.pandocDefaultDataDirIsResourceRoot [true].
Add the default Pandoc user data directory to the root paths from which the
preview can load local (filesystem) resources, such as images and CSS. See
--data-dir in the
Pandoc documentation for
details about the data directory. See the output of pandoc --version for
the location of the data directory on your system.
Codebraid configuration
When Codebraid is used to run code, the codebraid executable is found by
searching the following locations.
If a Python interpreter is set in VS Code, the interpreter installation is
checked for a codebraid executable.
Notice that a Python interpreter can be set at the file level or workspace
level (Ctrl+Shift+P, then Python: Select Interpreter, or configure
python.defaultInterpreterPath in a workspace settings.json). A Python
interpreter can also be configured in global User Settings (File,
Preferences, Settings, Python: Default Interpreter Path). Only the first
Python interpreter that is set in the file/workspace/global sequence is
checked for a codebraid executable.
For more details about configuring Python in VS Code, see
https://code.visualstudio.com/docs/python/environments.
If a Python interpreter is not set, or its installation does not include a
codebraid executable, then the first codebraid executable on PATH is
used. There will be a warning message if a Python interpreter is set but
does not include codebraid, so that codebraid on PATH is used as a
fallback.
If the codebraid executable is part of an
Anaconda installation, it is
launched via conda run so that the relevant conda environment is activated.
For other environments and installations, the codebraid executable is run
directly.
Security
The HTML preview is displayed using a webview. A content security policy is
used to restrict what is possible in the webview. Inline styles are
permitted. Local resources associated with a document, except for scripts,
are enabled by default. All remote resources are disabled by default. To
customize webview capabilities, see settings under
codebraid.preview.security. All resources bundled with the extension
(styles, fonts, and scripts) are always allowed, to support features like
KaTeX math and scroll sync.
Code is never automatically executed with Codebraid. Code is only ever
executed when a Codebraid class is added to a code block or inline code, and
then the "Codebraid" button is clicked (or the "Run code with Codebraid"
command is invoked).
Supporting this project
Codebraid Preview is open-source software released under the BSD 3-Clause
License. If you use it regularly, please consider supporting further
development through GitHub Sponsors.
| |


