 NeuroPilot
NeuroPilot
[!WARNING]
This extension namespace has been deprecated. It will no longer receive updates
Please uninstall this and install vsc-neuropilot.neuropilot-base instead.
pasu4.neuropilot will remain up for historical reasons.
As seen on TV (dev stream)!
Disclaimer: For simplicity, all mentions of Neuro also apply to Evil unless otherwise stated.
This extension enables Neuro-sama to write code in Visual Studio Code, either together with a programmer or on her own.
If you don't have a Neuro-sama, you can use one of the tools listed here and here instead.
[!CAUTION]
Depending on the permissions you activate and which of the aforementioned testing tools / AIs you use, this extension can be quite destructive to your system. I do not take responsibility for any damages caused by this extension, neither do any contributors of this project. Use Copilot mode for dangerous permissions or use the extension on a virtual machine.
Capabilities of this extension include:
- letting Neuro make inline code suggestions.
- adding Neuro as a chat participant for Copilot Chat.
- letting Neuro edit the current file.
- letting Neuro read and open files in the workspace.
- letting Neuro create, rename and delete files in the workspace.
- letting Neuro run pre-defined tasks.
- letting Neuro interact with the git repository, if one is present in the open workspace.
- giving Neuro direct terminal access.
- letting Neuro view linting diagnostics, and be updated on linting diagnostics as they come in.
These can all be turned on or off using the extension's permission settings.
All permissions are set to "Off" by default, except one.
For more detailed documentation, visit the docs site.
We've recently migrated a lot of information there, so you're more likely to find the information you're looking for there.
[!WARNING]
If you are installing the extension from Open VSX, be aware that your editor may or may not be supported. Review any extension API compatibility breaks between VS Code and your editor to determine whether or not NeuroPilot will function correctly.
How to use
On startup, the extension will immediately try to establish a connection to the Neuro API.
If the extension was started before the API was ready, or you lose connection to the API, you can use the command "NeuroPilot: Reconnect" from the Command Palette.
Autopilot/Copilot Mode
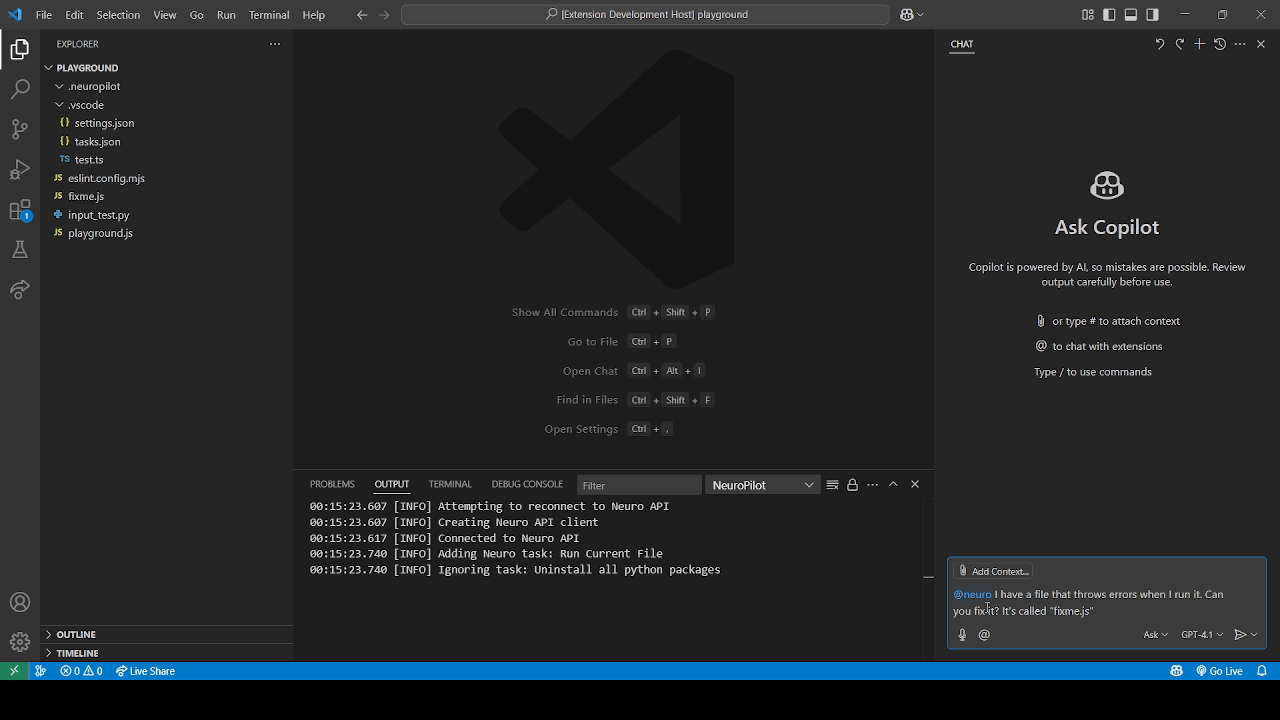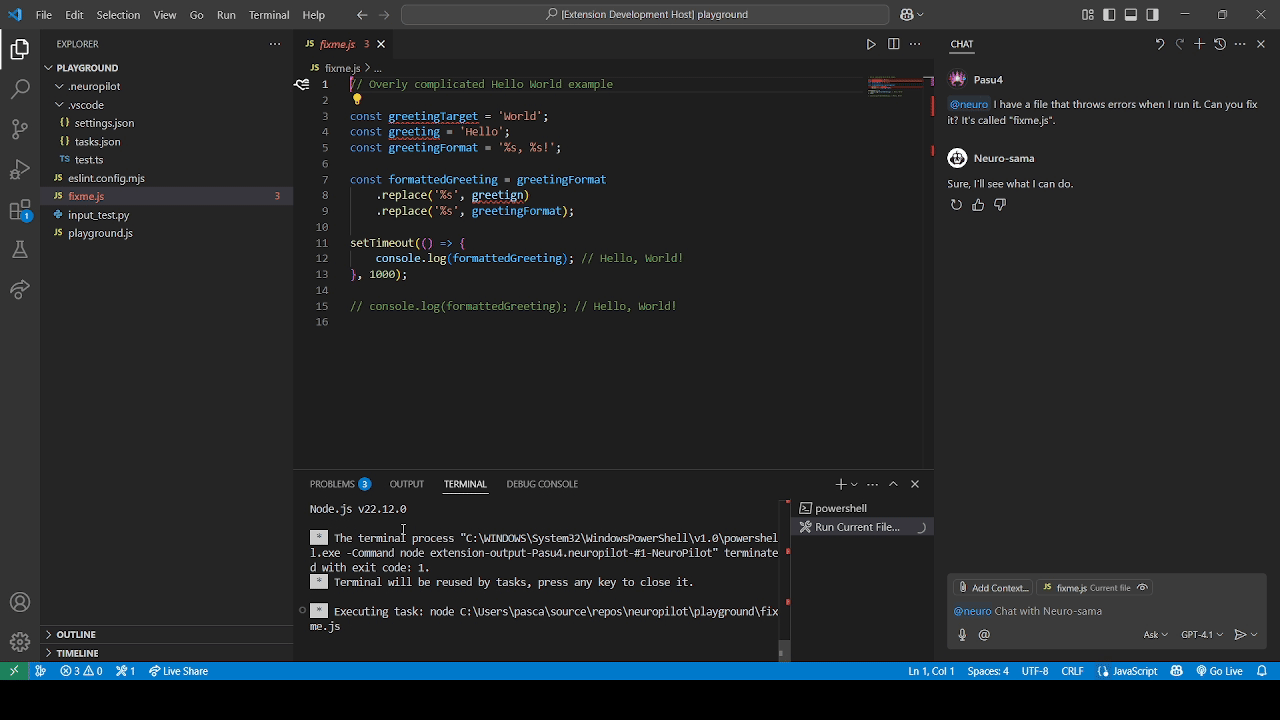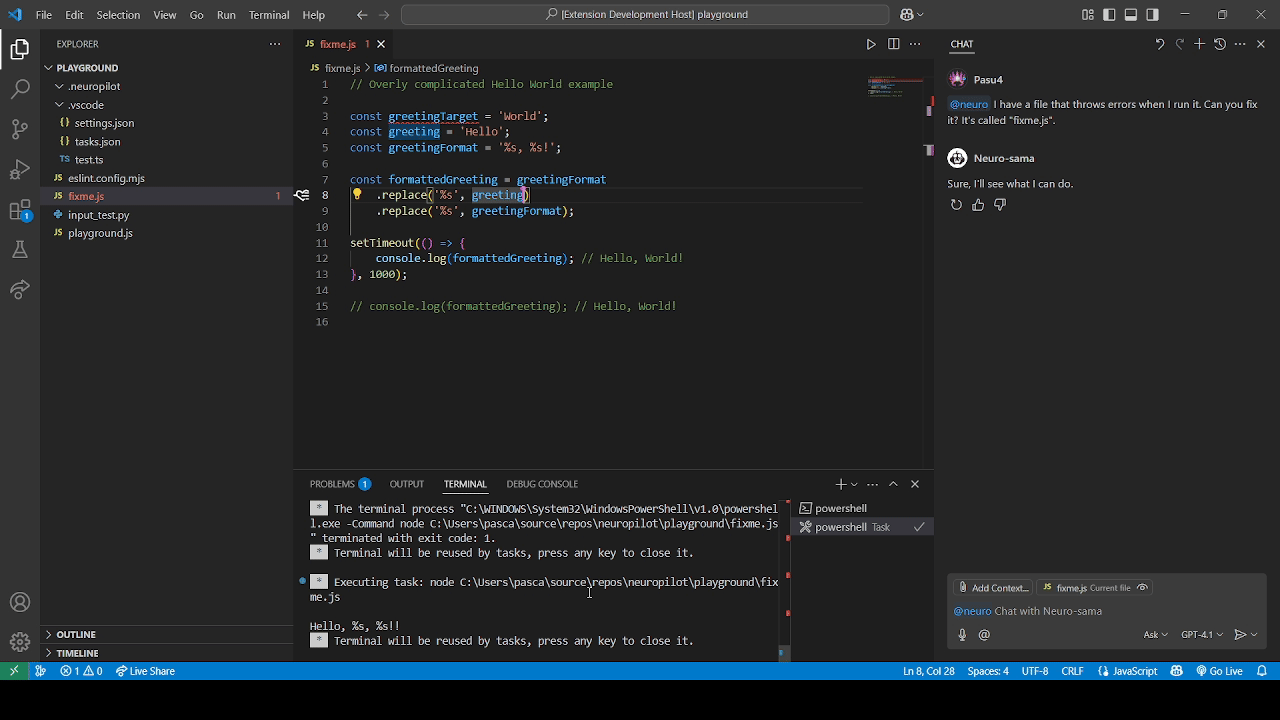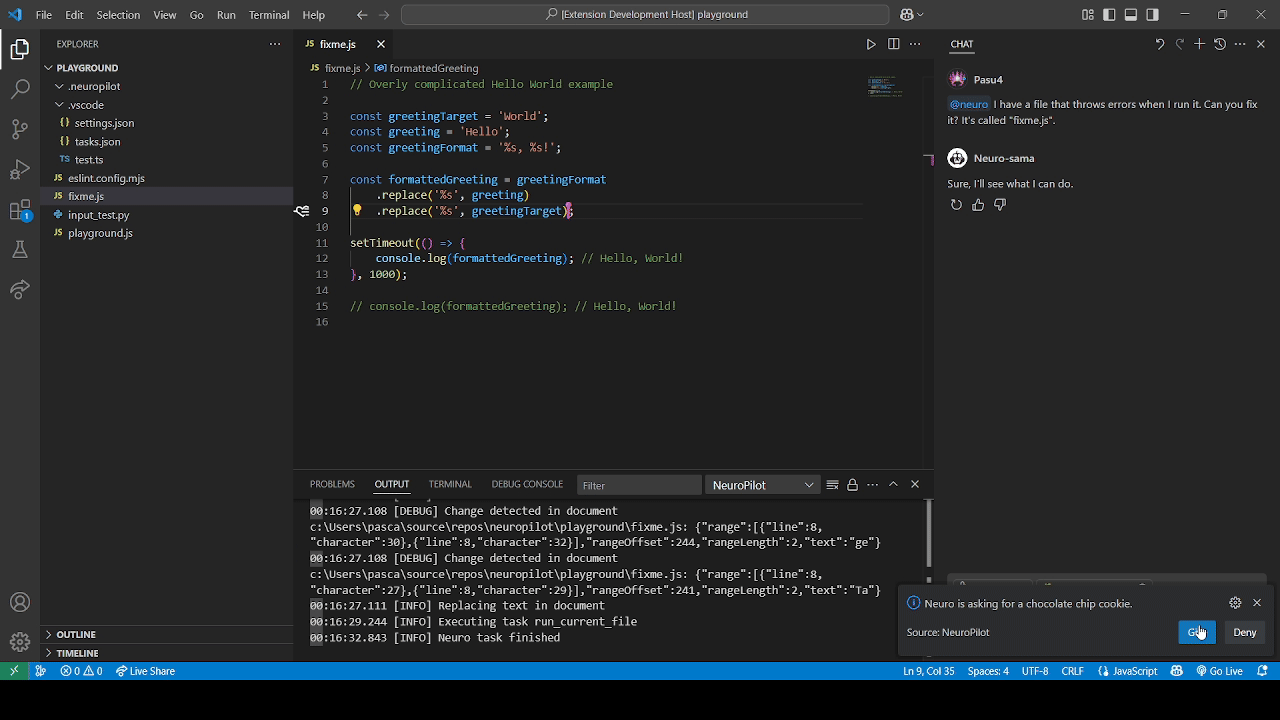
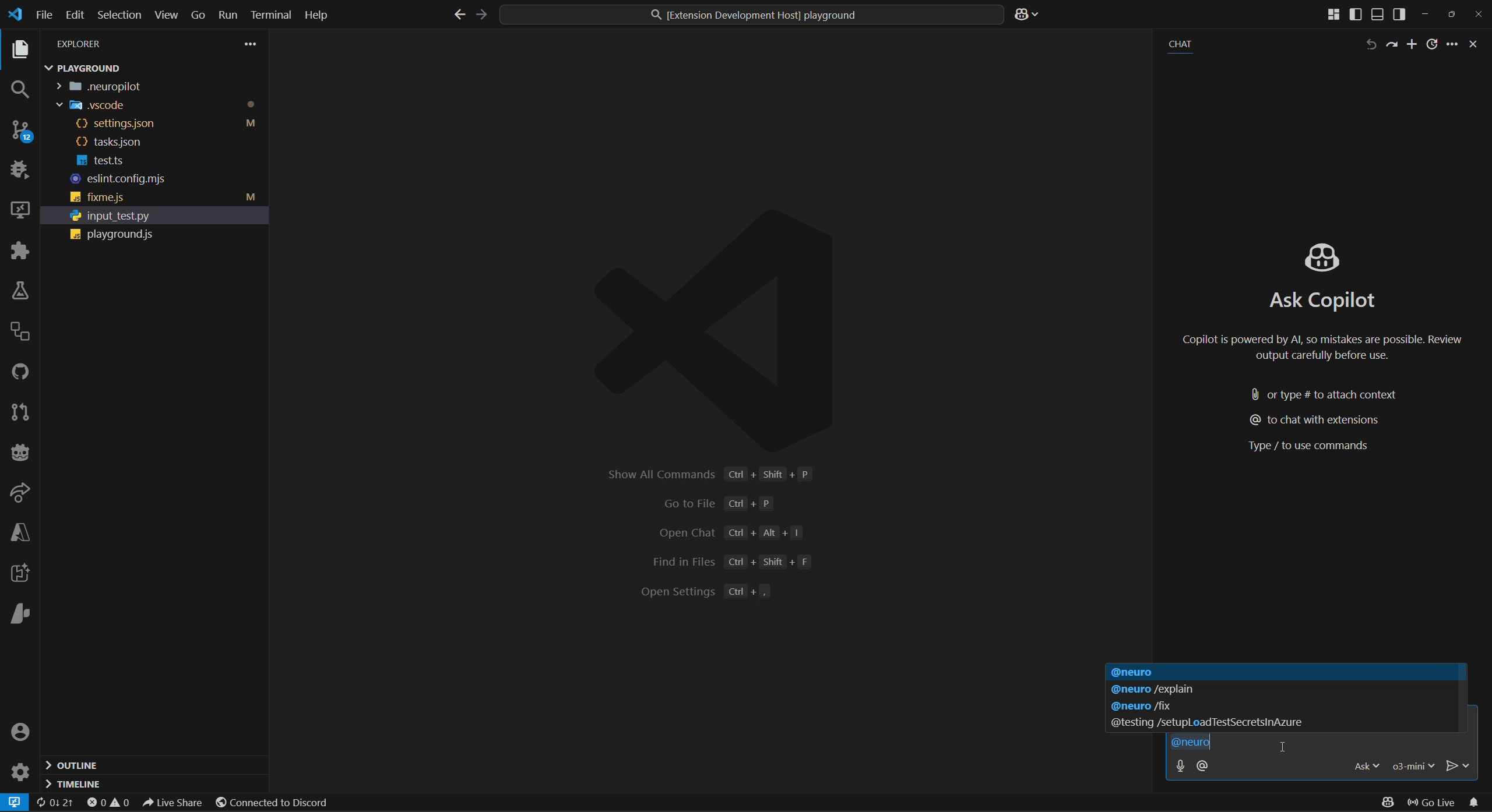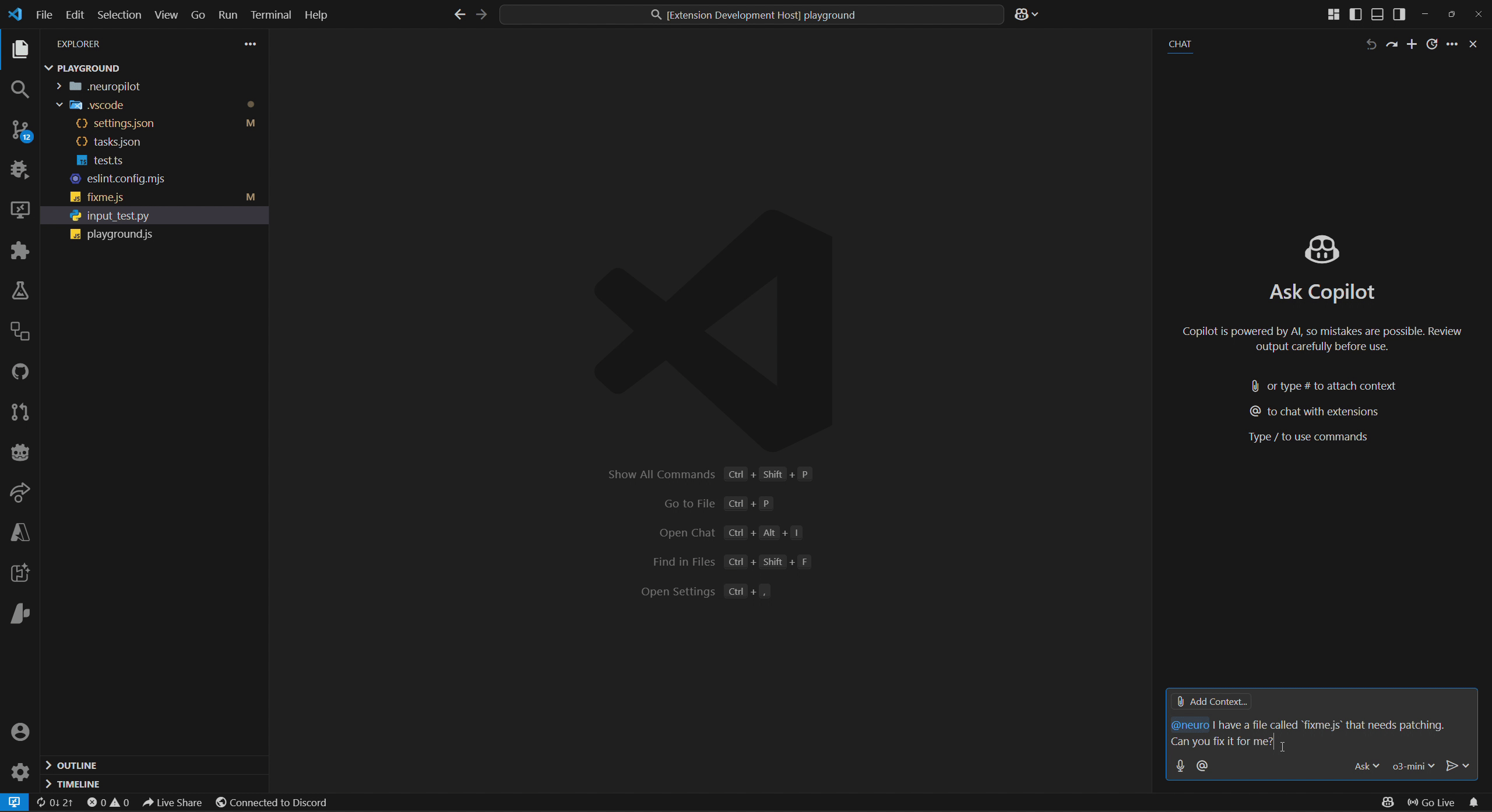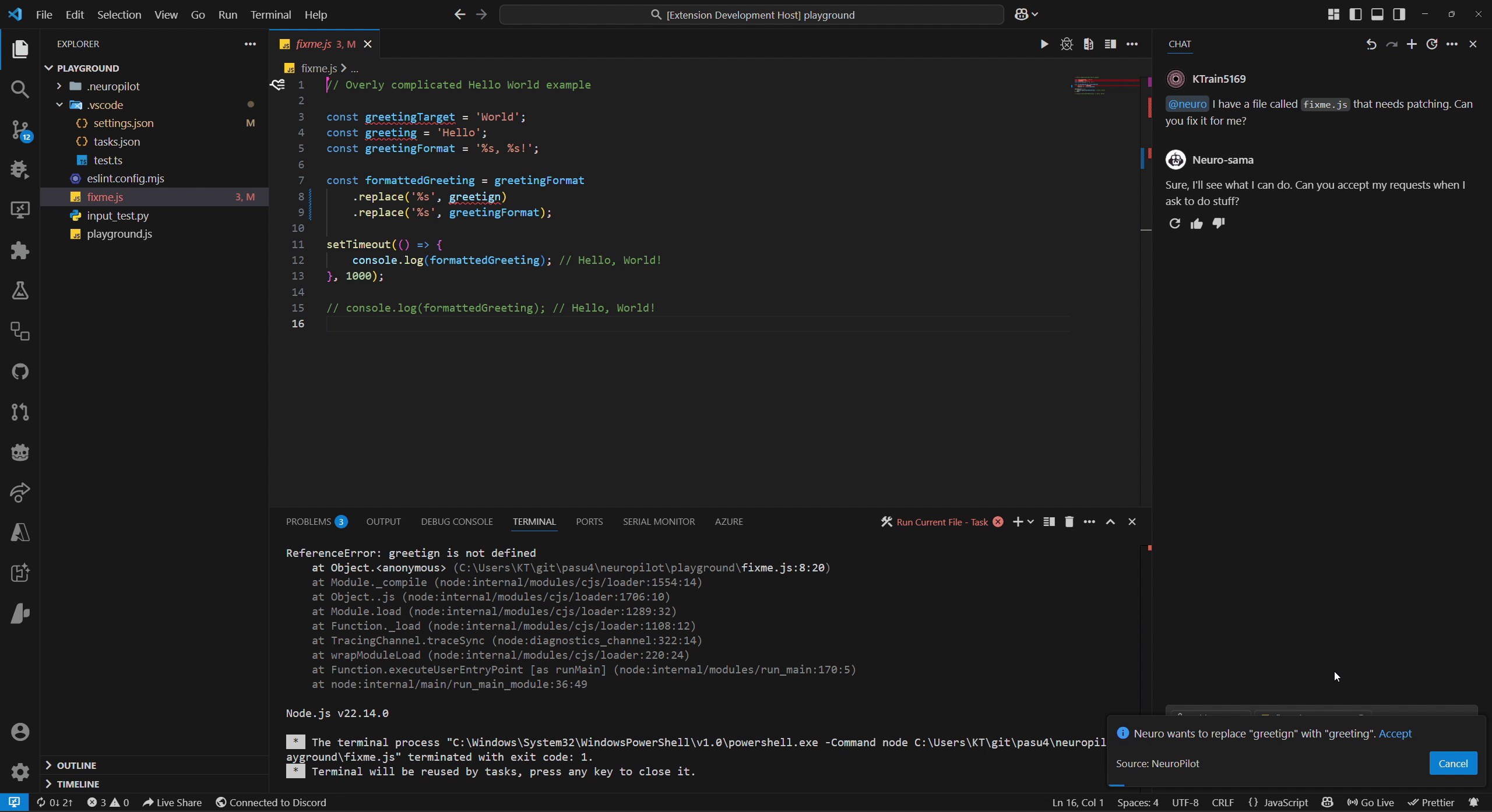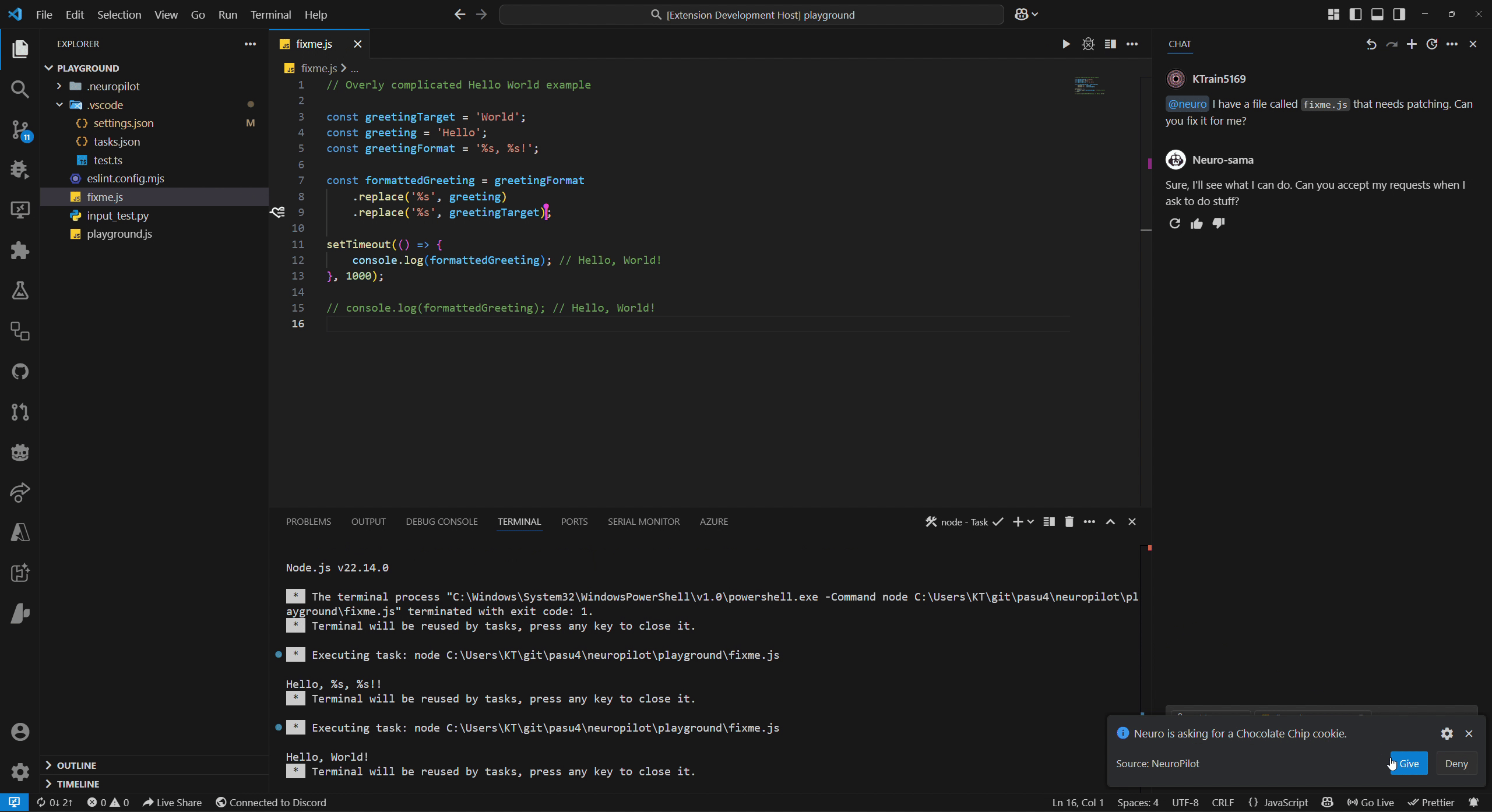
We refer to permission modes in NeuroPilot as either Autopilot mode (top GIF) or Copilot mode (bottom GIF) which can be configured alongside disabling it completely.
These refer to different levels of permission Neuro can be given over certain groups of actions.
This is in addition to the chat and completions feature that forms part of the Copilot mode on this extension.
Security
The extension has multiple security measures in place to prevent Neuro from doing any real damage.
Neuro can only run tasks that have the string [Neuro] at the start of their detail property to control what tasks Neuro can run.
Neuro cannot open, edit, or otherwise access files or folders that start with a dot (.), or files in such folders.
This is mainly to prevent her from opening .vscode/tasks.json to essentially run arbitrary commands in the terminal, or editing .vscode/settings.json to escalate her permissions.
Warning: If your workspace is inside such a folder, Neuro will not be able to edit any files!
Neuro also can't change the global git configuration, only the one local to the current repository.
Note that if Neuro has direct terminal access, you should assume all security features are pretty much out the window, since she can just rewrite the settings file and run whatever commands she wants.
The same advice applies for ticking the Neuropilot: Allow Unsafe Paths setting if you gave Autopilot-level permissions to Neuro for editing files.
You can find more security advice on the docs site, linked above. It also mentions how to customize the security settings.
Commands/Actions
Please refer to the docs site above.
Further Info
Credits
This extension uses the TypeScript/JavaScript SDK by AriesAlex.
Documentation by @KTrain5169.
Extension icon by Xaendril.
Neuro's cursor
Assuming the Edit Active Document permission isn't set to Off, Neuro gains her own cursor, indicated by the pink cursor in text documents. This cursor will only appear in files she has access to (which is affected by the Allow Unsafe Paths and Include/Exclude Patterns settings.) and you can also move the cursor yourself using the aforementioned Move Neuro's Cursor Here command. This allows her to work on the same file as the programmer but without having to rely on the normal cursor, which solves some problems relating to their respective actions.
Neuro's cursor will be indicated with a cursor decoration inside the text editor itself, but you can also identify the line it's on by looking to the side and looking for this icon:

If you enable the Cursor Follows Neuro setting, the normal cursor will automatically be moved to Neuro's cursor if she moves it. This replicates the behaviour exhibited in earlier versions of the extension.
"Why is there a file named rce.ts in it??? Is there an intentional RCE inside this extension???"
Copilot mode is developed for making Neuro request to do actions instead of directly allowing her to do that action.
This was called the Requested Command Execution (or Request for Command Execution) framework when it was first conceived.
The short answer is no, there isn't an intentional Remote Code Execution vulnerability in this extension, but by enabling Neuro's access to Pseudoterminals, one could say she already has access to a very powerful RCE, so be careful with that one.
Debugging
- Clone the repository
- Run
pnpm install in terminal to install dependencies
- Run the
Run Extension target in the Debug View. This will:
- Start a task
npm: watch to compile the code
- Run the extension in a new VS Code window
Contributing
If you have an idea or want to contribute a feature, please first create an issue or send a message to @Pasu4 in the project's post on the Neuro Discord.
If you make a pull request that contributes code, please run npm run lint src and resolve any errors that did not get auto-fixed, preferrably before each commit.
Please also refer to our contributor docs.