
Typst Sympy Calculator
About
Typst Sympy Calculator parses typst math expressions and converts it into the equivalent SymPy form. Then, calculate it and convert to typst result.
It is designed for providing people writing in typst a ability to calculate something when writing math expression. It is based on Python, Sympy and typst-sympy-calculator module.
PS: If you want to install the extension, PLEASE READ THE INSTALL DESCRIPTION!
Features
- Default Math:
- [x] Arithmetic: Add (
+), Sub (-), Dot Mul (dot), Cross Mul (times), Frac (/), Power (^), Abs (|x|), Sqrt (sqrt), etc...
- [x] Alphabet:
a - z, A - Z, alpha - omega, Subscript (x_1), Accent Bar(hat(x)), etc...
- [x] Common Functions:
gcd, lcm, floor, ceil, max, min, log, ln, exp, sin, cos, tan, csc, sec, cot, arcsin, sinh, arsinh, etc...
- [x] Funcion Symbol:
f(x), f(x-1,), g(x,y), etc...
- [x] Calculous: Limit
lim_(x -> oo) 1/x, Integration integral_1^2 x dif x, etc...
- [x] Calculous: Derivation (
dif/(dif x) (x^2 + 1) is not supported, but you can use derivative(expr, var) instead), etc...
- [x] Reduce: Sum
sum_(k=1)^oo (1/2)^k, Product product_(k=1)^oo (1/2)^k, etc...
- [x] Eval At: Evalat
x^2 bar_(x = 2), x^2 "|"_(x = 2), etc...
- [x] Linear Algebra: Matrix to raw echelon form
rref, Determinant det, Transpose ^T, Inverse ^(-1), etc...
- [x] Relations:
==, >, >=, <, <=, etc...
- [x] Solve Equation: Single Equation
x + 1 = 2, Multiple Equations cases(x + y = 1, x - y = 2), etc...
- [ ] Logical:
and, or, not, etc...
- [ ] Set Theory:
in, sect, union, subset, etc...
- [x] Other: Binomial
binom(n, k) ...
- Custom Math (in typst file):
- Typst Math Printer:
- [x] Complete
TypstMathPrinter in TypstConverter.py
- [ ] Custom Printer for
TypstCalculator.py and TypstCalculatorServer.py
- VS Code Extension:
- [x] Develop a VS Code Extension for
Typst Calculator
Install
IT IS IMPORTANT!
IT IS IMPORTANT!
IT IS IMPORTANT!
Before you use the extension, please install python and two python modules: typst-sympy-calculator and Flask.
Install Python in Python.org, and then install NECESSARY modules by running:
pip install typst-sympy-calculator
pip install Flask
Then import the typst template file typst-sympy-calculator.typ into your typst file. It will be like:
#import "typst-sympy-calculator.typ": *
This step is not necessary, but it can provide you with examples of custom functions.
Usage

Typst to Typst
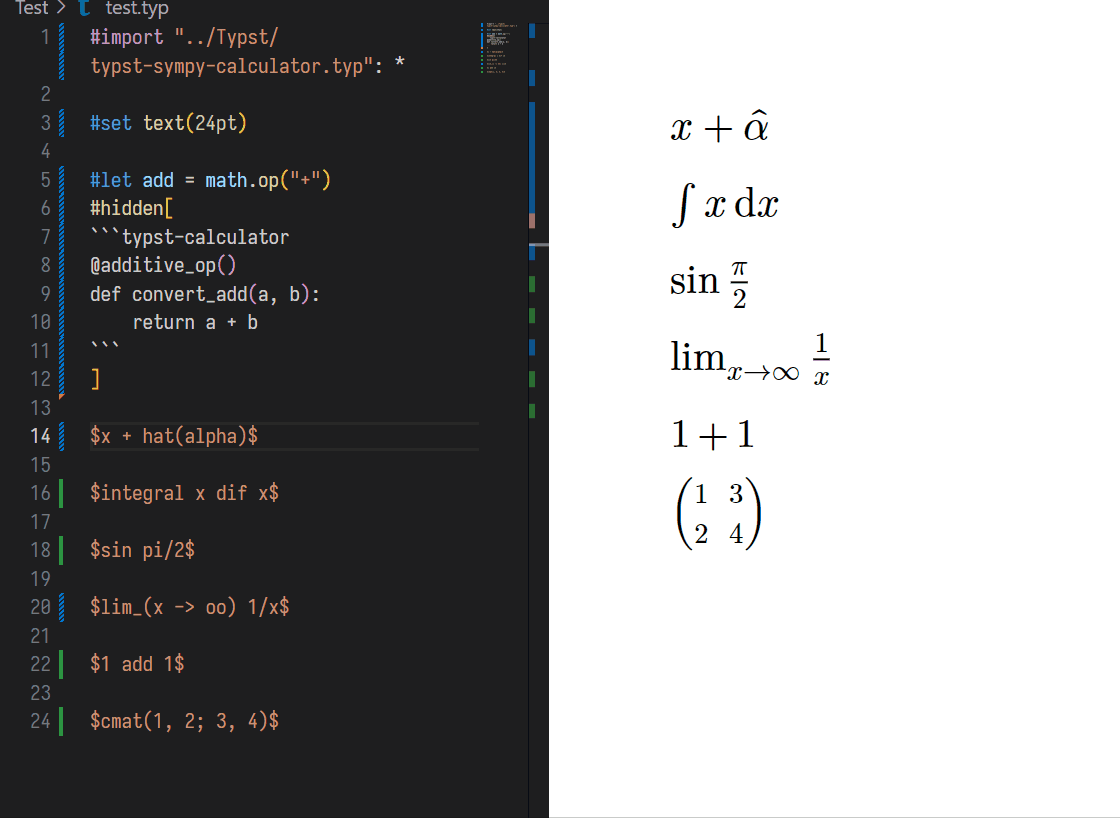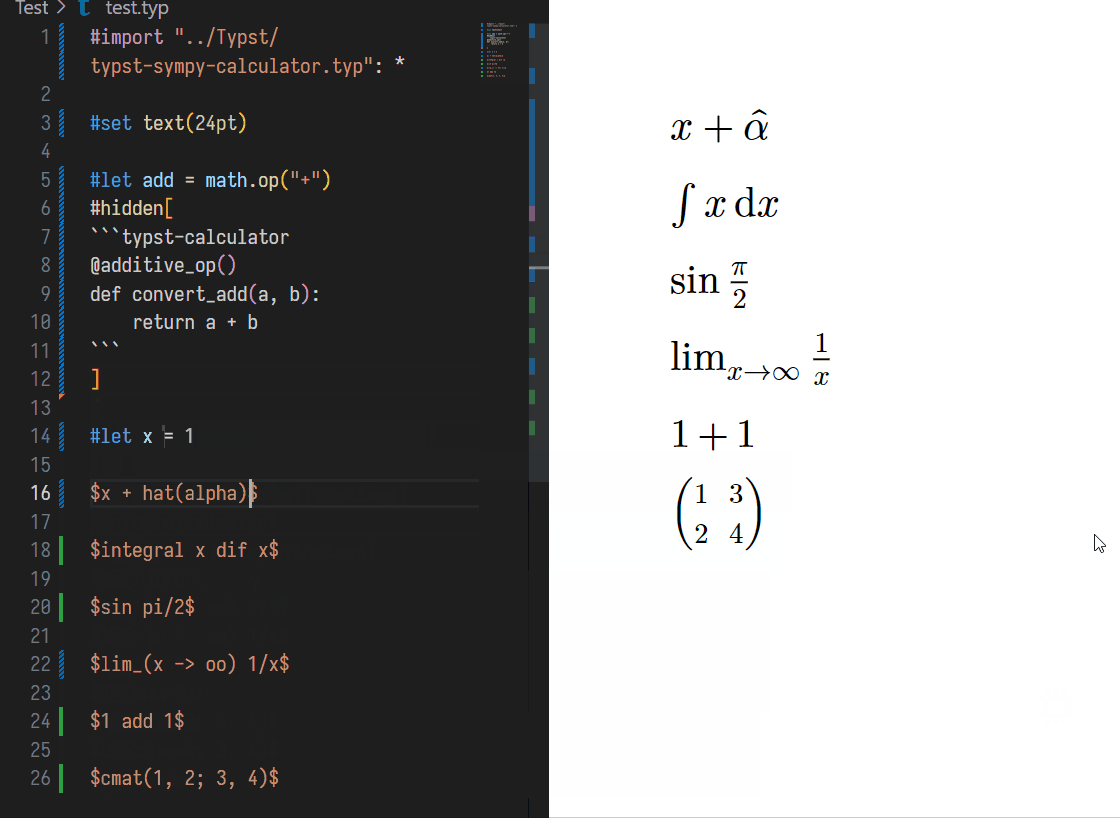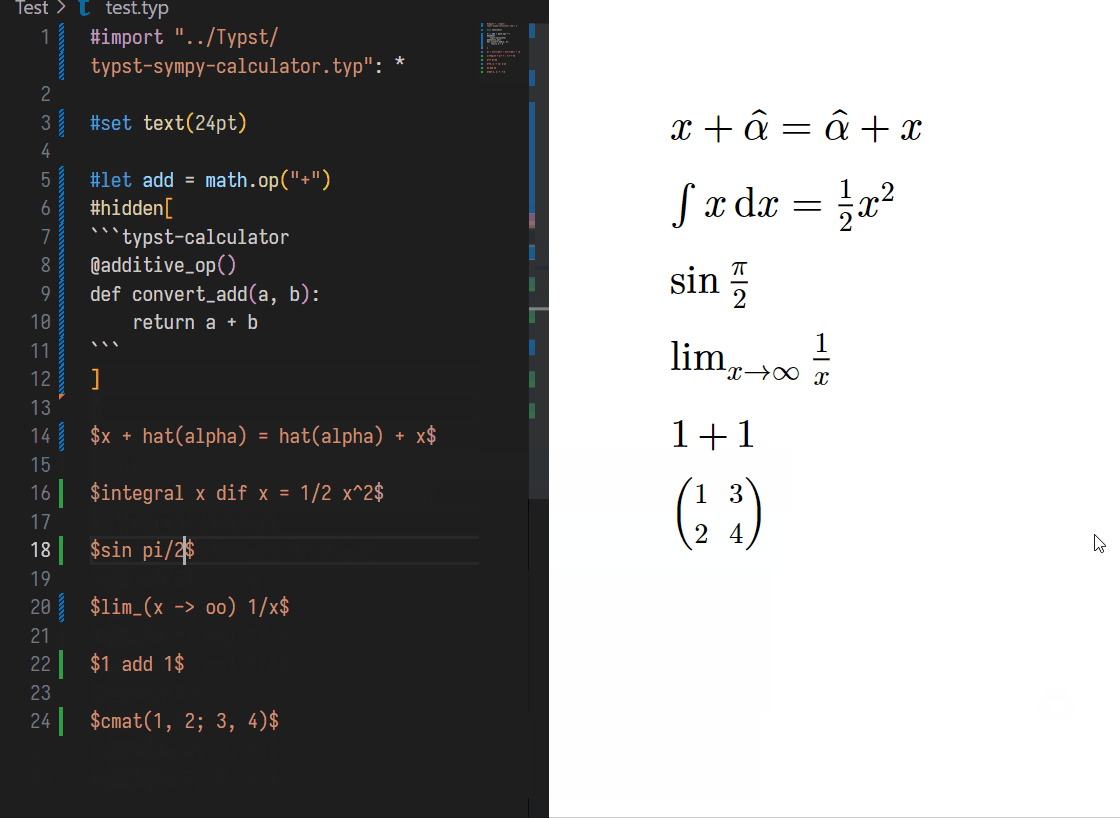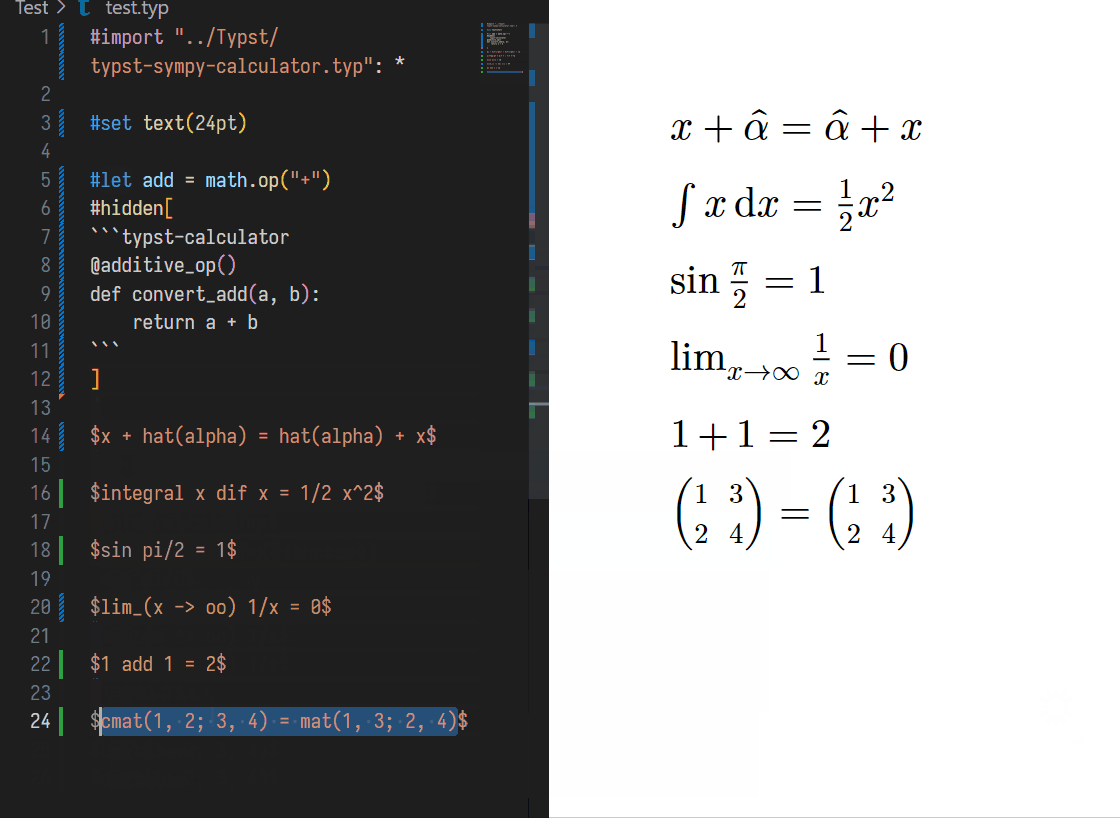
You can SELECT some text, and press Shift + Ctrl + Alt + E (equal) to get the result of the selected Typst text. It will be like:
// Before
$ integral x dif x $
// After
$ integral x dif x = 1/2 x^2 $
You can SELECT some text, and press Shift + Ctrl + Alt + R (replace) to get the result of the selected Typst text. It will be like:
// Before
$ integral x dif x $
// After
$ 1/2 x^2 $
Factor and Expand
You can SELECT some text, and press Shift + Ctrl + Alt + F (factor) to get the factor of the selected Typst text. It will be like:
// Before
$ x^2 + 2 x y + y^2 $
// After
$ (x + y)^2 $
If you are using windows, the shortcut Shift + Ctrl + Alt + F may be invalid, you can set another shortcut for it.
You can SELECT some text, and press Shift + Ctrl + Alt + X (expand) to get the expand of the selected Typst text. It will be like:
// Before
$ (x + y)^2 $
// After
$ x^2 + 2 x y + y^2 $
Typst to Numerical Result
You can SELECT some text, and press Shift + Ctrl + Alt + N (numerical) to get the numerical result of the selected Typst text. It will be like:
// Before
sqrt(2)
// After
1.41421356237310
Solve Equations and Inequations
You can SELECT some text, and press Shift + Ctrl + Alt + S (solve) to solve the equations of the selected Typst text. It will be like:
// Before
x + y = 1
// After
y = 1 - x, x = 1 - y
// Before
cases(x + y = 1, x - y = 1)
// After
cases(x = 1, y = 0)
// Before
x + 3 < 1
// After
-oo < x and x < -2
Variances
You can ASSIGN variance a value using same assignment form in typst:
#let x = 1
// Before
$ x $
// Shift + Ctrl + E
// After
$ x = 1 $
PS: You can use grammar like y == x + 1 to describe the relation of equality.
If you want to see the bonding of variances, you can press Shift + Ctrl + P, and input typst-sympy-calculator: Show Current variances, then you will get data like:
y = x + 1
z = 2 x
Functions
You can DEFINE a function using same form in typst:
#let f = math.op("f")
// Before
$ f(1) + f(1) $
// Shift + Ctrl + E
// After
$ f(1) + f(1) = 2 f(1) $
Symbols
You can DEFINE a symbol using same form in typst:
#let xy = math.italic("xy")
#let email = symbol("🖂", ("stamped", "🖃"),)
$ xy + email + email.stamped $
Accents
You can DEFINE a accent using same form in typst:
#let acc(x) = math.accent(x, math.grave)
$ acc(x) $
Decorators for Operators
You can DEFINE a operator using same form in typst:
#let add = math.op("+")
'''typst-calculator
@additive_op()
def convert_add(a, b):
return a + b
'''
// Before
$ 1 add 1 $
// Shift + Ctrl + E
// After
$ 1 add 1 = 2 $
Or just use '''typst-sympy-calculator or '''python \n # typst-calculator to define a operator.
there are some decorators you can use:
@operator(type='ADDITIVE_OP', convert_ast=convert_ast, name=name, ast=False): Define a common operator;@func(): Define a function, receive args list;@func_mat(): Define a matrix function, receive single arg matrix;@constant(): Define a constant, receive no args but only return a constant value;@relation_op(): Define a relation operator, receive args a and b;@additive_op(): Define a additive operator, receive args a and b;@mp_op(): Define a multiplicative operator, receive args a and b;@postfix_op(): Define a postfix operator, receive args a;@reduce_op(): Define a reduce operator, receive args expr and args = (symbol, sub, sup);
It is important that the function name MUST be def convert_{operator_name}, or you can use decorator arg @func(name='operator_name'), and the substring _dot_ will be replaced by ..
There are some examples (from DefaultTypstCalculator.py):
# Functions
@func()
def convert_binom(n, k):
return sympy.binomial(n, k)
# Matrix
@func_mat()
def convert_mat(mat):
return sympy.Matrix(mat)
# Constants
@constant()
def convert_oo():
return sympy.oo
# Relation Operators
@relation_op()
def convert_eq(a, b):
return sympy.Eq(a, b)
# Additive Operators
@additive_op()
def convert_plus(a, b):
return a + b
# Mp Operators
@mp_op()
def convert_times(a, b):
return a * b
# Postfix Operators
@postfix_op()
def convert_degree(expr):
return expr / 180 * sympy.pi
# Reduces
@reduce_op()
def convert_sum(expr, args):
# symbol, sub, sup = args
return sympy.Sum(expr, args)
Python
You can calculate a python expression by Shift + Ctrl + Alt + P.
You can use all sympy expression in it.
For example, you can get variances you assigned by:
# Before
typst(var['y'])
# After
typst(var['y']) = x + 1
Calculator the roots of the equation:
# Before
sympy.solve([2 * x - y - 3, 3 * x + y - 7],[x, y])
# After
sympy.solve([2 * x - y - 3, 3 * x + y - 7],[x, y]) = {x: 2, y: 1}
Thanks
License
This project is licensed under the MIT License.



