Dingo Language Support for VS Code
Syntax highlighting and language support for Dingo - a modern meta-language for Go with Result types, error propagation, pattern matching, and more.
Features
Language Server Protocol (LSP) Support (NEW in v0.2.0)
- Full IDE support via
dingo-lsp language server
- Autocomplete for Dingo code (powered by gopls)
- Go-to-definition (F12) - jump to type/function definitions
- Hover information - type information on hover
- Inline diagnostics - real-time error reporting
- Auto-transpile on save (configurable)
- Requires:
dingo-lsp binary and gopls installed
Syntax Highlighting
Dingo language features:
Result<T, E> and Option<T> types? error propagation operatormatch pattern matching expressions (Rust-style)- Exhaustiveness checking for match statements
- Nested pattern destructuring (
Ok(Some(value)))
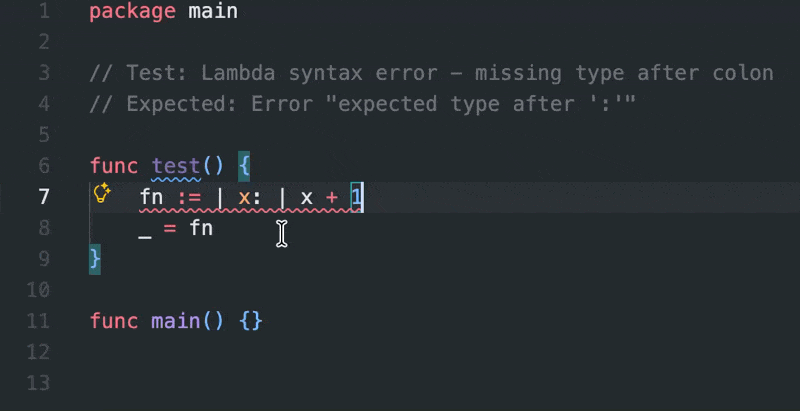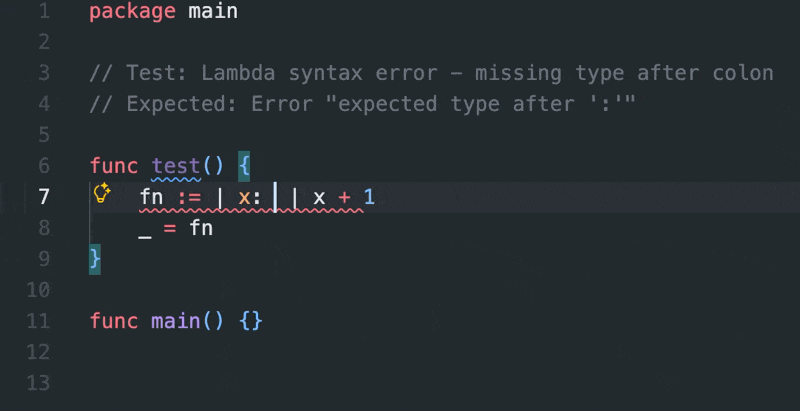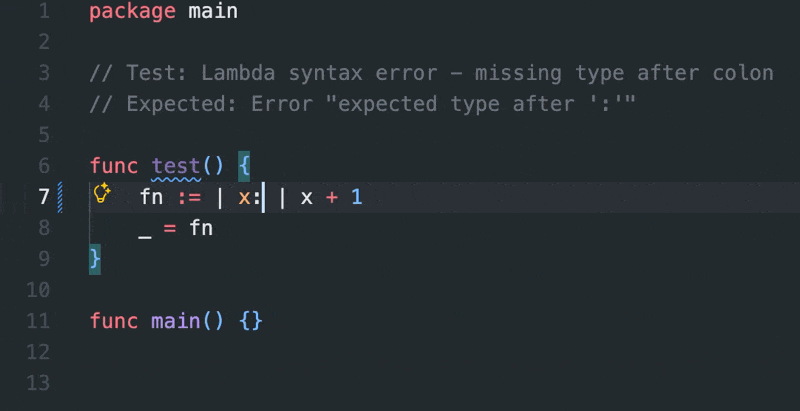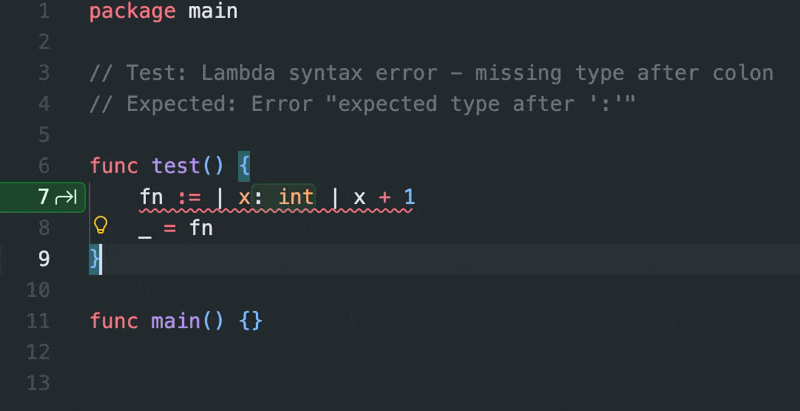
- Lambda functions with
|params| expr syntax
- Enums and sum types
- All standard Go syntax
Bracket Matching for {}, [], (), and <>
Auto-closing Pairs for brackets, quotes, and strings
Comment Support with // and /* */
Code Folding for regions and blocks
Generated Code Highlighting (NEW in v0.2.0)
- Visual highlighting of transpiler-generated code in
.go files
- Marker detection for
DINGO:GENERATED:START/END blocks
- Configurable styles:
- Subtle: Light background (default)
- Bold: Background + border
- Outline: Border only
- Disabled: No highlighting
- Theme-aware colors that work in light and dark modes
- Real-time updates with debounced performance
- Support for
.go.golden test files
Enhanced Dingo Syntax (NEW in v0.2.0)
- Error messages: Special highlighting for
expr? "custom message" syntax
- Generated variables: Muted colors for
__err0, __tmp0 variables
- Result/Option types: Improved highlighting for
Result<T,E> and Option<T>
- Constructors: Distinct colors for
Ok(), Err(), Some(), None()
- Error propagation: More visually distinct
? operator
Golden File Support (NEW in v0.2.0)
- Side-by-side comparison: Compare
.dingo files with .go.golden test files
- Keyboard shortcut:
Ctrl+Shift+D (or Cmd+Shift+D on Mac)
- Syntax highlighting:
.go.golden files get full Dingo syntax support
Commands
Dingo: Transpile Current File - Manually transpile the active .dingo fileDingo: Transpile All Files in Workspace - Transpile all .dingo filesDingo: Restart Language Server - Restart dingo-lsp (useful after updates)Dingo: Toggle Generated Code Highlighting - Quickly enable/disable highlightingDingo: Compare with Source File - Open side-by-side diff view (keyboard: Ctrl+Shift+D)
Requirements
For full LSP support (autocomplete, go-to-definition, etc.):
Dingo transpiler (dingo binary in $PATH)
gopls (Go language server)
go install golang.org/x/tools/gopls@latest
dingo-lsp (LSP server - included with Dingo)
- Automatically available after installing Dingo
Note: Syntax highlighting works without these requirements. LSP features require all three.
Installation
From .vsix Package (Recommended)
Download dingo-0.2.0.vsix from releases
Install via command line:
code --install-extension dingo-0.2.0.vsix
Or via VS Code: Extensions → ... → Install from VSIX
Reload VS Code
From Marketplace (Coming Soon)
Search for "Dingo" in the VS Code Extensions marketplace.
Manual Installation
Clone the Dingo repository:
git clone https://github.com/yourusername/dingo.git
Copy the extension to your VS Code extensions folder:
cp -r dingo/editors/vscode ~/.vscode/extensions/dingo-language
Reload VS Code
Development
To work on the extension:
Install dependencies:
cd editors/vscode
npm install
Compile TypeScript:
npm run compile
# Or for watch mode:
npm run watch
Test in VS Code:
- Open the
editors/vscode folder in VS Code
- Press
F5 to launch the Extension Development Host
- Open a
.dingo or .go file to see highlighting
Syntax Examples
Result Type
func fetchUser(id: string) -> Result<User, error> {
if id == "" {
return Err(errors.New("invalid ID"))
}
return Ok(user)
}
Error Propagation
func processUser(id: string) -> Result<User, error> {
user := fetchUser(id)? // Automatically unwrap or return error
return Ok(user)
}
Pattern Matching
match fetchUser(id) {
Ok(user) => println("Found: ${user.name}")
Err(error) => println("Error: ${error}")
}
Lambdas
numbers := []int{1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
evens := numbers.filter(|n| n % 2 == 0)
doubled := evens.map(|n| n * 2)
Configuration
The extension provides several settings to customize behavior:
LSP Settings
{
// Path to dingo-lsp binary (default: searches $PATH)
"dingo.lsp.path": "dingo-lsp",
// Automatically transpile .dingo files on save (default: true)
"dingo.transpileOnSave": true,
// Show transpilation success/failure notifications (default: false)
"dingo.showTranspileNotifications": false,
// LSP server log level: debug, info, warn, error (default: info)
"dingo.lsp.logLevel": "info"
}
Generated Code Highlighting Settings
dingo.highlightGeneratedCode
- Type: boolean
- Default:
true
- Description: Enable or disable highlighting of generated code sections
dingo.generatedCodeStyle
- Type:
"subtle" | "bold" | "outline" | "disabled"
- Default:
"subtle"
- Description: Visual style for generated code highlighting
subtle: Light background only (recommended)bold: Background color with borderoutline: Border outline onlydisabled: No highlighting
dingo.generatedCodeColor
- Type: string (hex color)
- Default:
"#3b82f620"
- Description: Background color for generated code (hex with alpha channel)
dingo.generatedCodeBorderColor
- Type: string (hex color)
- Default:
"#3b82f660"
- Description: Border color for bold/outline styles
Building from Source
cd editors/vscode
npm install
npm run compile
npm run build-grammar
npm run package
This creates a .vsix file that can be installed via:
code --install-extension dingo-0.2.0.vsix
Maintaining the Extension
When adding new Dingo language features:
- Update the grammar: Edit
syntaxes/dingo.tmLanguage.json
- Add examples: Create test files in
examples/
- Test: Use the Scope Inspector (
Developer: Inspect Editor Tokens and Scopes)
- Document: Update this README and version in
package.json
Grammar Structure
The grammar is organized into sections:
keywords: Control flow, declarations, modifiersresult-type: Result<T, E>, Ok(), Err()option-type: Option, Some(), Noneenum-variants: Pattern matching variantstypes: Built-in and user-defined typesfunctions: Function declarations and callslambdas: Lambda/arrow function syntaxoperators: All operators including ? and ??strings: String literals with interpolationnumbers: Integer, float, hex, binary, octalconstants: true, false, nil, iotaattributes: #[attribute] syntax
Adding a New Feature
Example: Adding ternary operator support
- Read
features/ternary-operator.md to understand the syntax
- Add pattern to
syntaxes/dingo.tmLanguage.json:
"ternary": {
"patterns": [
{
"name": "keyword.operator.ternary.dingo",
"match": "\\?|:"
}
]
}
- Include in main patterns:
{ "include": "#ternary" }
- Create
examples/ternary.dingo with test cases
- Test in VS Code with Scope Inspector
- Commit with descriptive message
Troubleshooting
Autocomplete not working
Ensure .dingo file is transpiled
- Manual:
dingo build file.dingo
- Or enable auto-transpile: Set
dingo.transpileOnSave: true
Check gopls is installed
gopls version
If not installed:
go install golang.org/x/tools/gopls@latest
Restart LSP
- Command Palette → "Dingo: Restart Language Server"
Check LSP logs
- Output panel → "Dingo Language Server"
- Set
dingo.lsp.logLevel: "debug" for verbose logs
Transpilation errors
- Errors appear inline as diagnostics (red squiggly lines)
- Hover over the error to see details
- Check Output panel → "Dingo Language Server" for full error messages
Extension not activating
- Ensure you're opening a
.dingo file (triggers activation)
- Check VS Code extension host logs: Developer → Show Logs → Extension Host
- Verify extension is enabled in Extensions view
dingo-lsp not found
If you see "dingo-lsp binary not found":
Ensure Dingo is installed
Add dingo-lsp to PATH
Contributing
See the main Dingo repository for contribution guidelines.
License
Same as Dingo project (see root LICENSE file).
Resources


