MacroTeX Usage Guide
MacroTeX is a VSCode extension that helps with inserting macros in LaTeX documents.
Table of contents
Features
- Macro completion for file paths
- Auto-completion for images and various file types
- Smart path suggestions with proper relative paths
- Image preview on hover
- Preview images directly in the editor
- Bulk image insertion from explorer
- Multi-select files and insert with chosen macro
- Automatic path generation and identifier creation
- Configurable LaTeX macros
- Support for custom macro signatures
- Advanced parameter extraction modes (LaTeX notation, positional, smart)
- Smart multi-document support
- Automatic detection of main LaTeX files
- Intelligent path resolution based on document hierarchy
- File system tracking
- Automatic path updates when files are moved or renamed
- Smart commenting of references to deleted files
- Enhanced path suggestions
- Prioritized local files in suggestions
- Support for various file extensions in path suggestions
- Interactive Table Generator Sidebar
- Visual creation and editing of LaTeX tables
- Live LaTeX preview with real-time updates
- Support for multiple table environments (table, longtable, tabularx, tabulary)
- One-click insertion into documents
- CSV to LaTeX Table Conversion
- Convert CSV files directly to LaTeX tables
- Automatic insertion with proper formatting
- Macro Finder & Management
- Browse and search through all macros in your project
- Filter by macro type (newcommand, renewcommand, def)
- Save project macros to extension configuration
- Navigate to macro definitions
- Macro Expansion & Collapse
- Expand macro usage to its full definition
- Collapse expanded definitions back to macro usage
- Context menu integration in LaTeX files
Getting Started
- Install the MacroTeX extension from the VSCode marketplace
- Open your LaTeX project in VSCode
- The extension will automatically detect all main LaTeX files in your workspace
- Start using macros in any .tex file - paths will be automatically resolved to the nearest main file
Using MacroTeX
Auto-completion
- Start typing a LaTeX macro (e.g.
\fg) in your .tex file
- The extension will show available paths that match the macro's file type requirements
- Select a path to automatically insert the complete macro with proper paths
- The extension creates snippets from user-defined macros for quick insertion
Features:
- Smart path completion: Prioritizes local files and shows relative paths
- File type filtering: Only shows files matching macro's configured extensions
- Snippet generation: Automatic creation of VS Code snippets from macro signatures
- Multi-file support: Works across multiple LaTeX documents in your project
Image Preview
- Hover over an image path in your LaTeX document
- A preview of the image will be displayed in a hover tooltip
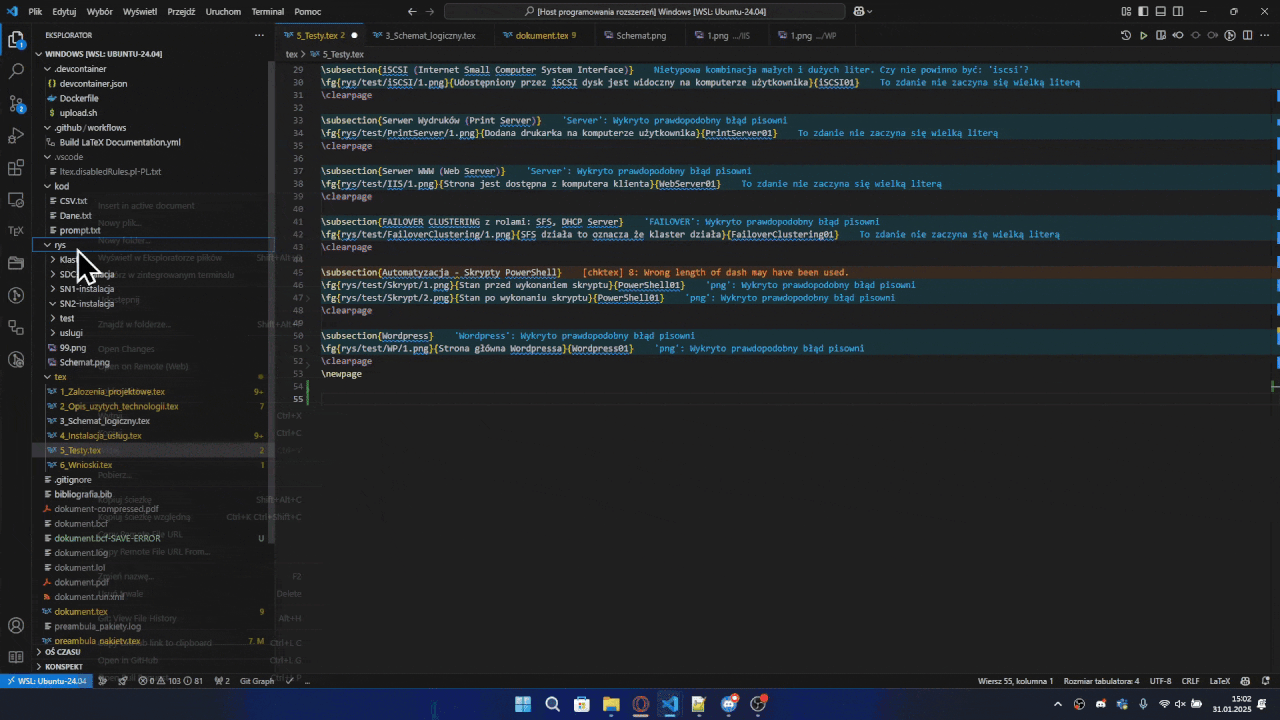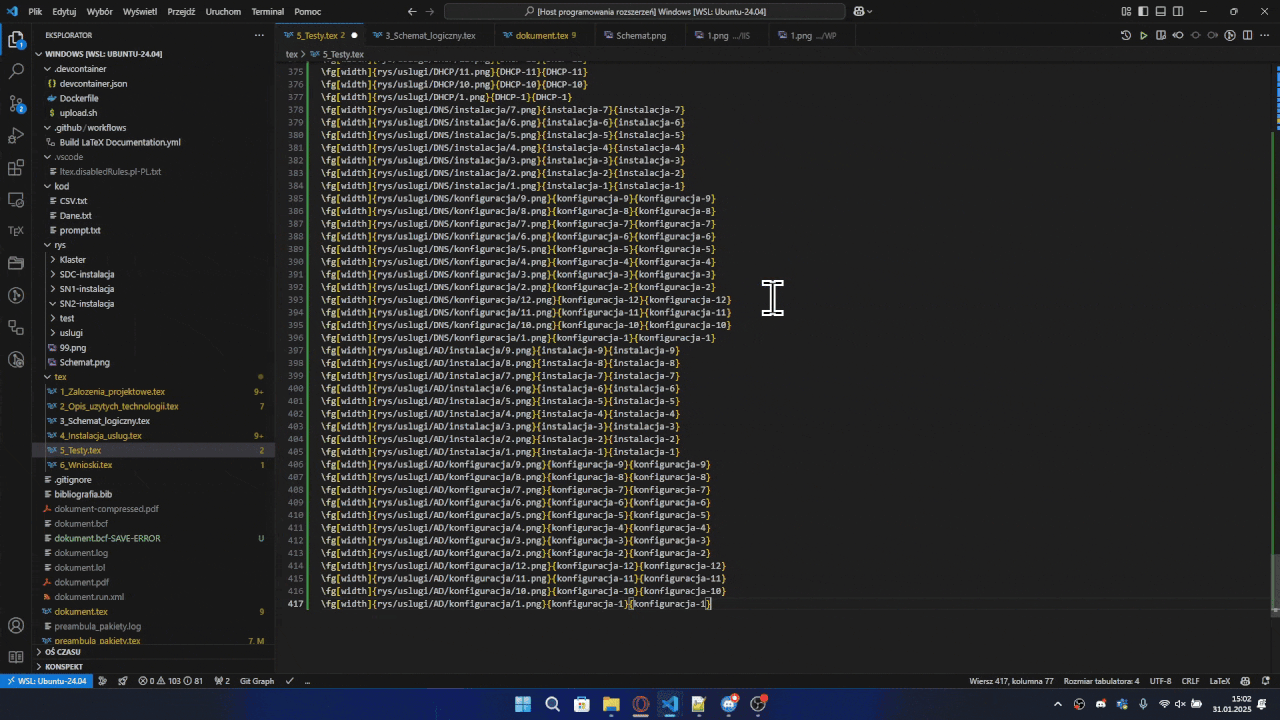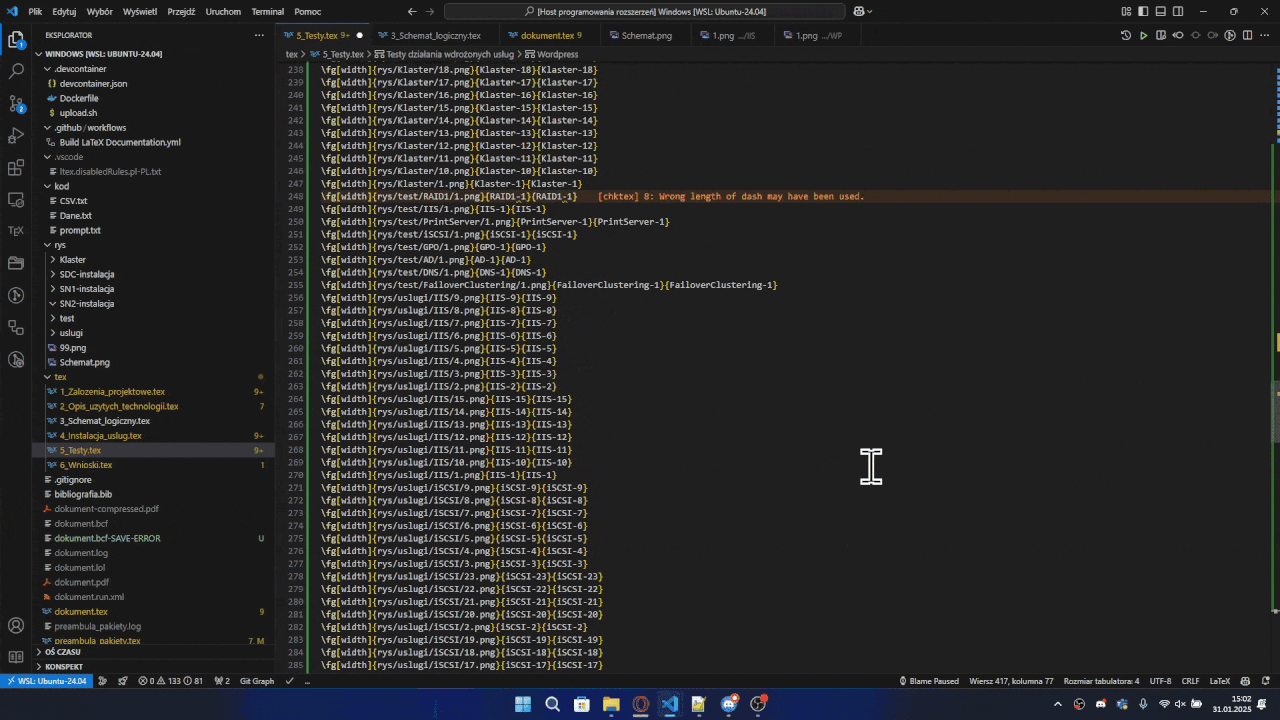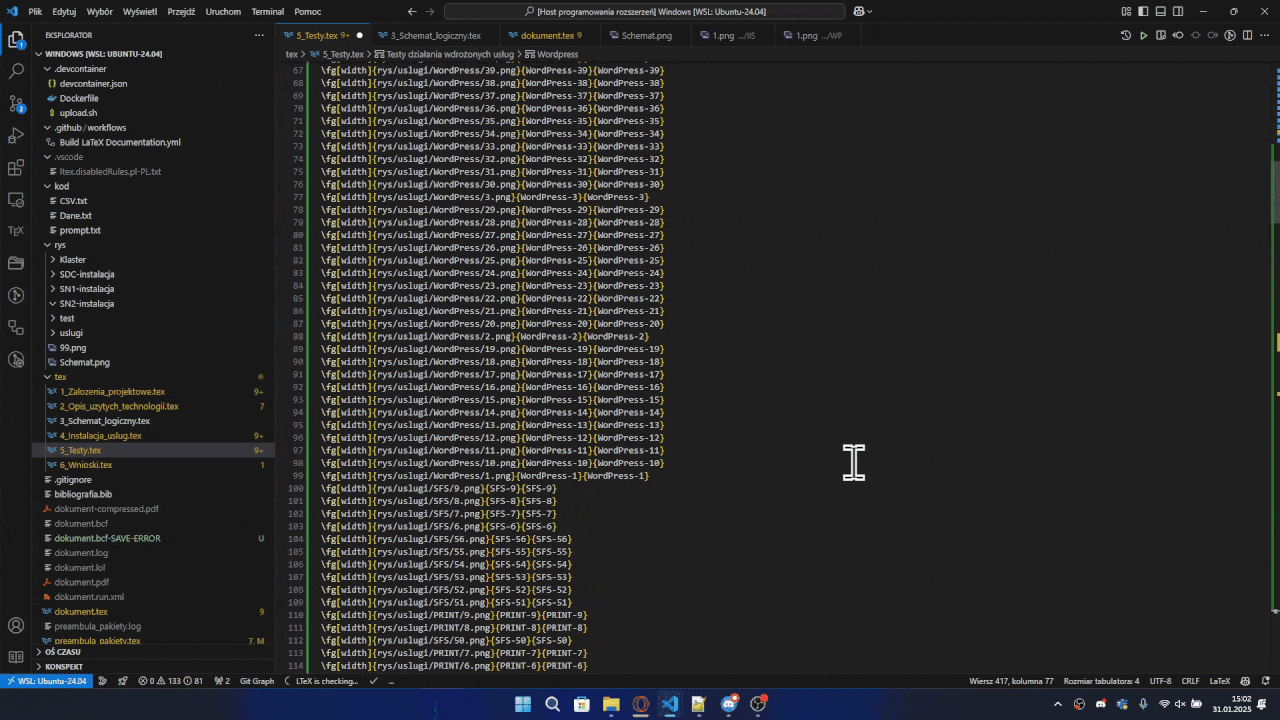
Bulk Image Insertion
- In the VSCode explorer, select one or multiple images/folders
- Right-click and select "Insert in active document"
- Choose the macro you want to use
- The extension will:
- Insert the selected images using the chosen macro
- Create proper relative paths
- Generate identifiers based on folder/file names
- Optionally insert
\clearpage after every 2 images
Example usage:
- Open the sidebar by clicking on the MacroTeX icon in the activity bar
- Use the Table Generator panel to:
- Set the number of rows and columns
- Choose table type (table, longtable, tabularx, tabulary)
- Edit table content directly in the visual editor
- Preview the generated LaTeX code in real-time
- Click "Insert LaTeX Table" to add the LaTeX table code to your active document
- The table will be inserted at the current cursor position with proper LaTeX formatting
The Table Generator features:
- Live preview: See LaTeX code update automatically as you edit
- Multiple table environments: Support for different LaTeX table types
- Interactive editing: Add/remove rows and columns dynamically
- Real-time validation: Immediate feedback on table structure
CSV to LaTeX Table Conversion
- Select a CSV file in the VSCode explorer
- Right-click and select "Insert CSV as table"
- The extension will:
- Convert the CSV data to a properly formatted LaTeX table
- Insert the table at the current cursor position in the active editor
- Maintain the structure and data from your CSV file
- Escape special LaTeX characters automatically
Use this feature to quickly import data tables from CSV files into your LaTeX documents without manual formatting.
Macro Finder
The Macro Finder is a powerful tool for managing LaTeX macros in your project:
- Open the MacroTeX sidebar and navigate to the "Macro Finder" panel
- The extension automatically scans your project for all macro definitions
- Browse through macros organized by type:
\newcommand - Standard command definitions\newcommand* - Non-long command definitions\renewcommand - Redefined commands\renewcommand* - Non-long redefined commands\def - TeX primitive definitions
Features:
- Smart filtering: Filter macros by type or search by name
- Quick navigation: Click "Go to" to jump to macro definition
- Usage examples: See how each macro should be used
- Save to configuration: Convert project macros to extension configuration for auto-completion
- Macro management: Delete or edit macro definitions directly
Macro Expansion & Collapse
Work more efficiently with LaTeX macros using expansion and collapse features:
Expanding Macros
- Select a macro usage in your LaTeX file (e.g.,
\fg{image.png}{Caption}{label})
- Right-click and select "Expand Macro to Definition" or use the command palette
- The macro usage will be replaced with its full definition
- Requires the macro to be configured in extension settings
Collapsing Definitions
- Select an expanded macro definition in your LaTeX file
- Right-click and select "Collapse Definition to Macro Usage" or use the command palette
- The full definition will be collapsed back to simple macro usage
- Automatically finds matching macro signatures from your configuration
These features help you:
- Debug macro behavior: See exactly what your macros expand to
- Clean up code: Collapse verbose definitions to concise macro calls
- Learn LaTeX: Understand how complex macros work internally
Configuration
Configure macros in VSCode settings. Example minimal setup:
"latexMacros.macrosList": [
{
"signature": "\\fg{PATH}{Caption}{Identifier}",
"extensions": ["png", "jpg"]
}
]
Path Management
- Automatic detection and handling of multiple main LaTeX files
- Smart relative path generation based on document hierarchy
- Automatic path updates when files are moved or renamed
- Intelligent handling of deleted files
- Support for nested directory structures
🎯 Best Method - LaTeX Notation (RECOMMENDED)
Use standard LaTeX notation with #1, #2, #3 - exactly as in macro definition:
{
"signature": "\\MyMacro{#1}{#2}{#3}",
"extensions": ["pdf"]
}
Example:
- Usage:
\MyMacro{dog}{cat}{bird}
- Macro definition:
\newcommand{\MyMacro}[3]{\myspecialcommand[title=#1, id=#2]{#3}}
- Expanded:
\myspecialcommand[title=dog, id=cat]{bird}
- Collapse: System finds
dog, cat, bird and returns \MyMacro{dog}{cat}{bird}
🔧 Positional Mode (only with LaTeX notation)
For LaTeX notation with positional extraction:
{
"signature": "\\MyMacro{#1}{#2}{#3}",
"extensions": ["txt", "pdf"],
"extractionMode": "positional"
}
Important: Positional mode only works with LaTeX notation (#1, #2, etc.), not with custom parameter names.
🧠 Smart Method (only for standard patterns)
System recognizes standard LaTeX patterns:
{
"signature": "\\fg{PATH}{Caption}{Identifier}",
"extensions": ["png", "jpg"]
}
📋 Configuration Examples
Macro with LaTeX notation (RECOMMENDED):
{
"signature": "\\ShowCode{#1}{#2}{#3}",
"extensions": ["py", "js", "cpp"]
}
Complex macro with many square bracket parameters:
{
"signature": "\\MyComplexMacro[#1][#2][#3]{#4}{#5}",
"extensions": ["png", "jpg"]
}
{
"signature": "\\fg{PATH}{Caption}{Identifier}",
"extensions": ["png", "jpg", "pdf"]
}
Macro with positional mode (LaTeX notation only):
{
"signature": "\\CustomMacro{#1}{#2}{#3}",
"extensions": ["tex"],
"extractionMode": "positional"
}
✅ Recommendations
- For new macros: use LaTeX notation
{#1}{#2}{#3} - simplest and most natural!
- For complex macros with multiple square brackets: use LaTeX notation
[#1,#2]{#3}{#4}
- For standard patterns (PATH, Caption, Identifier): leave default settings
- For positional extraction: only use with LaTeX notation (
#1, #2, etc.)
🔧 Complete Configuration Example
{
"latexMacros.macrosList": [
{
"signature": "\\fg{PATH}{Caption}{Identifier}",
"extensions": ["png", "jpg"]
},
{
"signature": "\\code{#1}{#2}{#3}",
"extensions": ["py", "js", "cpp"]
},
{
"signature": "\\ref{#1}{#2}",
"extensions": ["tex"]
},
{
"signature": "\\ComplexMacro[#1,#2,#3]{#4}{#5}",
"extensions": ["txt", "c", "cpp"]
}
]
}
🚀 How It Works
LaTeX Notation:
- Expand:
\MyMacro{A}{B}{C} → macro definition substitutes #1=A, #2=B, #3=C
- Collapse: System finds values in order and maps 1:1 →
\MyMacro{A}{B}{C}
Positional Mode (LaTeX notation only):
- Expand:
\MyMacro{A}{B} → \section{A}\input{B}
- Collapse: Finds all parameters → takes first two →
\MyMacro{A}{B}
Smart Mode:
- Expand:
\fg{path.png}{My Caption}{fig1} → \includegraphics{path.png}\caption{My Caption}\label{fig:fig1}
- Collapse: Recognizes patterns → PATH, Caption, Identifier →
\fg{path.png}{My Caption}{fig1}
Custom Macros
When creating custom macros, understand these placeholders:
{PATH}: Required for path autocompletion{Caption}: Optional, for image captions{Identifier}: Optional, for reference labels
Example configuration:
{
"signature": "\\fg[width]{PATH}{Caption}{Identifier}",
"extensions": ["png", "jpg"]
}
Corresponding LaTeX macro:
\newcommand*{\fg}[4][\textwidth]{
\begin{figure}[!htb]
\begin{center}
\includegraphics[width=#1]{#2}
\caption{#3}
\label{rys:#4}
\end{center}
\end{figure}
}
Troubleshooting
Common Issues
- Macro not appearing in suggestions
- Check if file extension is supported in macro configuration
- Verify macro configuration in settings (
latexMacros.macrosList)
- Ensure there is a main LaTeX file in your workspace (file with
\documentclass)
- Image preview not working
- Ensure image path is correct relative to the main LaTeX file
- Check if image format is supported (png, jpg, jpeg etc.)
- Verify the path relative to the main LaTeX file
- Path resolution issues
- Check if your document is in the same workspace as the main LaTeX file
- Verify that the file contains a
\documentclass declaration
- Ensure file paths use forward slashes (/) not backslashes ()
- Table Generator not working
- Ensure you have an active LaTeX editor open
- Check that the cursor is positioned where you want to insert the table
- Verify your VS Code version supports webview panels
- Macro Finder not showing macros
- Ensure your project contains LaTeX files with macro definitions
- Check that files are properly saved and accessible
- Try refreshing the Macro Finder panel
- Expansion/Collapse not working
- Ensure the macro is configured in extension settings
- Check that you have selected the complete macro usage or definition
- Verify you're working in a
.tex file
Support
- Report issues on GitHub repository
- Check documentation for updates
- Join community discussions


