Table of Contents
1. Introduction
Overview
Site Verifier is a robust Azure DevOps extension designed to streamline the verification of your web services and APIs, ensuring reliability and correctness throughout your development and DevOps lifecycle. Integrate it into CI/CD pipelines for proactive quality assurance.
Features
- Versatile HTTP Support: GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, PATCH methods.
- Comprehensive Verification: Checks URLs, status codes, and response content.
- Flexible Requests: Customize with headers, payloads, and authentication.
- Robust Response Handling: Filters JSON, HTML, XML, or plain text responses.
- Resilient Retries: Automatic retries for intermittent network issues.
- Customizable Content Handling: Supports various content types.
- Detailed Logging: Optional response logging for troubleshooting.
- Workflow Integration: Stores response data in variables for downstream use.
- Secure Configuration: Protects sensitive credentials with environment variables.
These features are designed to empower development and operations teams with the tools they need to ensure the robustness and reliability of their web services, making the SiteVerifier task a cornerstone of modern CI/CD practices.
2. Getting Started
Installation
To incorporate the SiteVerifier task into your Azure DevOps pipeline, follow these steps:
- Navigate to the Azure DevOps Marketplace.
- Search for "Site Verifier."
- Select the task and follow the provided instructions to install it in your organization.
Quick Start Guide
To initiate a basic verification using the SiteVerifier task, add the following step to your pipeline configuration:
steps:
- task: SiteVerifier@0
inputs:
siteUrl: 'https://example.com'
expectedStatusCode: 200
httpMethod: 'GET'
This configuration sends a GET request to https://example.com, expecting a 200 OK response. It provides a foundational demonstration of the task's core functionality, ideal for initial integration into your pipeline.
3. Configuration
Below is a comprehensive example demonstrating the SiteVerifier task's configuration with various input parameters:
steps:
- task: SiteVerifier@0
inputs:
siteUrl: 'https://example.com/api' # The fully qualified URL for the HTTP request.
expectedStatusCode: 200 # The expected HTTP status code for a successful response.
useAuthentication: true # Indicates if the request requires authentication.
authenticationMethod: 'basic' # Authentication method: 'basic' or 'header'.
requestPayload: '{"status": "ok"}' # JSON string needed for POST, PUT, or PATCH methods.
httpMethod: 'GET' # The HTTP method for the request.
contentType: 'application/json' # Content-Type header for the request.
logResponse: true # Option to log the response body for debugging.
responseOutput: 'responseContent' # Variable to store response body for further processing.
responseFilterPath: 'data.result' # Path to filter specific data from the response.
expectedPayload: '{"status": "ok"}' # Expected response payload for validation.
maxRetries: 3 # Number of retries on failure.
delayBetweenRetries: 5 # Delay in seconds between retries.
env:
SITE_USERNAME: $(Site_Username) # Environment variable for Basic Auth username.
SITE_PASSWORD: $(Site_Password) # Environment variable for Basic Auth password.
SITE_AUTH_TOKEN: $(Site_Auth_Token) # Environment variable for pre-encoded authorization header.
Task Parameters
siteUrl: Required. The target URL for verification. Must be fully qualified, including the scheme (http/https).expectedStatusCode: Optional. The expected HTTP status code from the request. Defaults to 200.useAuthentication: Optional. Indicates if authentication is required for the request.authenticationMethod: Optional. Specifies the authentication type (basic or header). Defaults to 'basic'. Only considered if useAuthentication is true.requestPayload: Optional. JSON payload for POST, PUT, or PATCH requests.httpMethod: Optional. The HTTP method to use for the request. Defaults to 'GET'.contentType: Optional. The Content-Type header for the request. Defaults to 'application/json'. Supported contentType values: application/json, text/html, application/xml, text/xml, text/plain.logResponse: Optional. Enable this option to log the response content in the build or release logs. Caution: Be mindful when enabling this feature, especially in production environments, as the response may contain sensitive information that could be exposed in log files. Review the content being logged and consider the security implications before enabling logging of response content.responseOutput: Optional. An optional task variable as an output to store the response body.responseFilterPath: Optional. JSON path expression to filter specific response data. JSON Responses: The responseFilterPath is used as a JSONPath expression, allowing precise selection within a JSON structure for validating specific parts of the response. HTML/XML Responses: With the cheerio.js library, responseFilterPath employs CSS-like selectors to pinpoint elements in HTML or XML, aiding in the extraction and validation of data from complex documents. Plain Text Responses: For plain text, responseFilterPath specifies a substring to find within the text. Existence of this substring switches a boolean value (true if found, false if not), which is then evaluated against expectedPayload for validation success.expectedPayload: Optional. The expected response payload for validation purposes. This setting is crucial for ensuring that the response from the tested endpoint matches predefined expectations, facilitating comprehensive testing across different response types. For JSON and HTML/XML: It expects the payload to match specified values or structures extracted using responseFilterPath. This could be a specific JSON object, an array, or text extracted from HTML/XML elements. Otherwise it returns null. For Plain Text: When used in conjunction with responseFilterPath, it verifies if the plain text search yields a true (presence) or false (absence) outcome, aligning this result with the expected boolean value specified in expectedPayload.maxRetries: Optional. Controls the number of retry attempts upon failure. Defaults to 3.delayBetweenRetries: Optional. The delay between retries, in seconds. Defaults to 5.environmentVariables: Optional. Additional environment variables for authentication. Use the format KEY=VALUE for each variable, separated by new lines. Accepted keys: SITE_USERNAME, SITE_PASSWORD, SITE_AUTH_TOKEN. For yaml definitions there is also another way to pass env variables, see examples.
Authentication Setup
For endpoints requiring authentication, the Site Verifier task supports two methods: Basic Authentication and custom header authentication.
Basic Authentication:
useAuthentication: true
authenticationMethod: 'basic'
env:
SITE_USERNAME: $(Site_Username) # Environment variable for Basic Auth username.
SITE_PASSWORD: $(Site_Password) # Environment variable for Basic Auth password.
Header Authentication:
useAuthentication: true
authenticationMethod: 'header'
env:
SITE_AUTH_TOKEN: $(Site_BasicAuth) # Environment variable for pre-encoded authorization header.
Configuring Retry Logic
Adjust maxRetries and delayBetweenRetries based on endpoint reliability and pipeline tolerance:
maxRetries: 3
delayBetweenRetries: 10
Payload Verification
- Defining Expected Payload: Use
expectedPayload to specify the exact expected response structure.
- Filtering Response Data: Utilize
responseFilterPath to target specific data within the response.
Environment Variables
SITE_USERNAME
- Description: Specifies the Basic Auth username.
- Required: Yes, if
useAuthentication is true and authenticationMethod is basic.
SITE_PASSWORD
- Description: Specifies the Basic Auth password.
- Required: Yes, if
useAuthentication is true and authenticationMethod is basic.
SITE_AUTH_TOKEN
- Description: Contains the pre-encoded authorization header value.
- Required: Yes, if
useAuthentication is true and authenticationMethod is header.
Security and Best Practices for Environment Variables
Securely manage environment variables to prevent unauthorized access and exposure in logs or outputs. Store sensitive information as secret variables and adhere to organizational security policies.
4. Examples
Verifying HTTP Status Code
- task: SiteVerifier@0
displayName: "Verify HTTP Status Code"
inputs:
siteUrl: "https://httpbin.org/status/200"
expectedStatusCode: 200
httpMethod: "GET"
Basic Authentication Check
- task: SiteVerifier@0
displayName: "Basic Authentication Check"
inputs:
siteUrl: "https://httpbin.org/basic-auth/user/passwd"
expectedStatusCode: 200
httpMethod: "GET"
useAuthentication: "true"
authenticationMethod: "basic"
env:
SITE_USERNAME: "user"
SITE_PASSWORD: "passwd"
- task: SiteVerifier@0
displayName: "Header Authentication Check"
inputs:
siteUrl: "https://httpbin.org/bearer"
expectedStatusCode: 200
httpMethod: "GET"
useAuthentication: "true"
authenticationMethod: "header"
env:
SITE_AUTH_TOKEN: "Bearer dXNlcjpwYXNzd2Q="
POST Request Example
- task: SiteVerifier@0
displayName: "Payload Verification with POST Request"
inputs:
siteUrl: "https://httpbin.org/post"
expectedStatusCode: 200
httpMethod: "POST"
requestPayload: '{"key": "value"}'
POST Request with Payload and Verification
- task: SiteVerifier@0
displayName: "POST Request with Body and Payload Verification"
inputs:
siteUrl: "https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts"
expectedStatusCode: 201
httpMethod: "POST"
requestPayload: '{"title": "foo", "body": "bar", "userId": 1}'
expectedPayload: '{"title": "foo", "body": "bar", "userId": 1, "id": 101}'
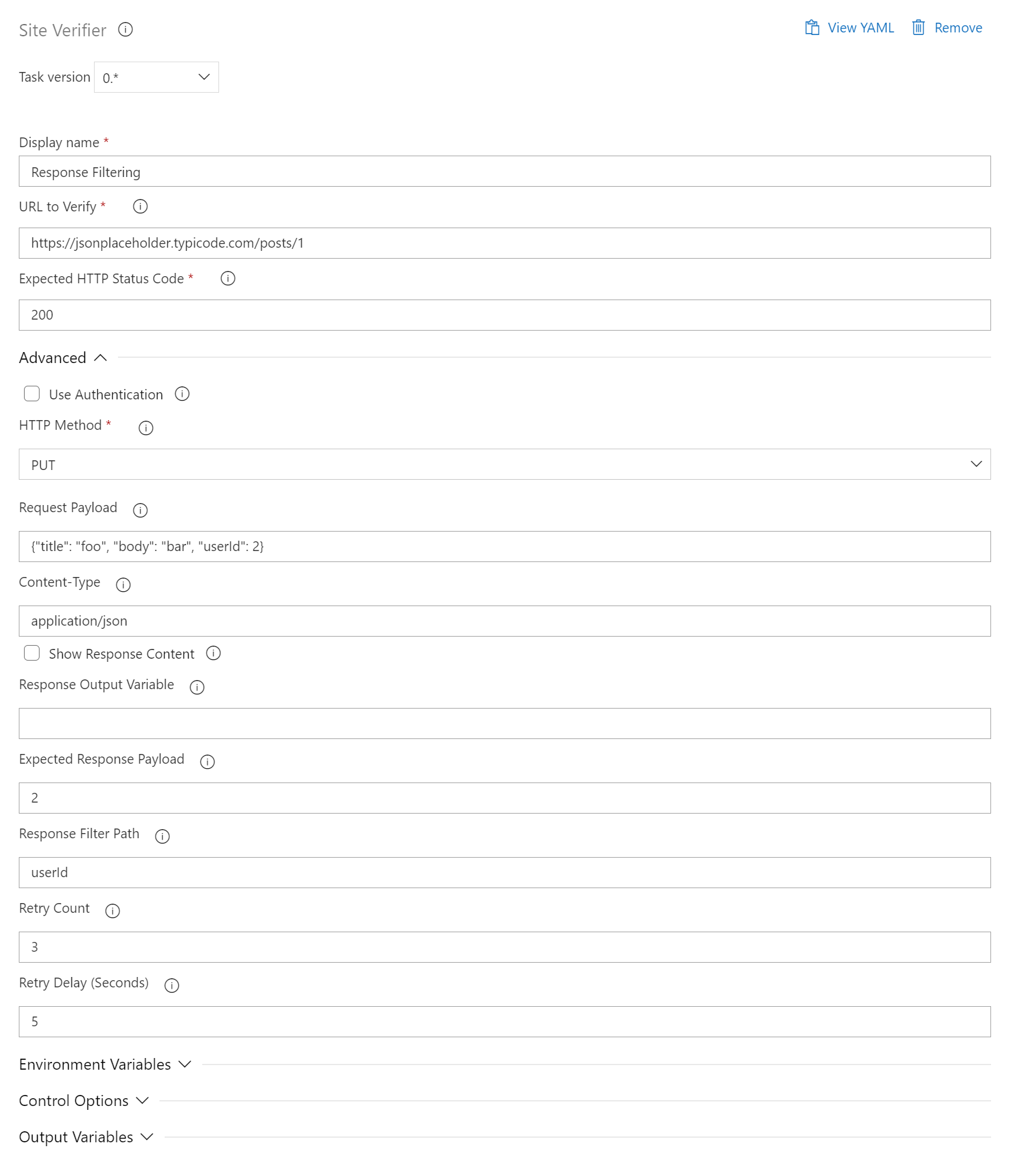
Response Filtering
- task: SiteVerifier@0
displayName: "PUT Request with Response Filtering (Non-nested)"
inputs:
siteUrl: "https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts/1"
expectedStatusCode: 200
httpMethod: "PUT"
maxRetries: 1
requestPayload: '{"title": "foo", "body": "bar", "userId": 2}'
expectedPayload: "2"
logResponse: true
responseOutput: "my_response"
responseFilterPath: "userId"
Deeply Nested Response Filtering - 1
- task: SiteVerifier@0
displayName: "GET Request with Deeply Nested Response Filtering (City)"
inputs:
siteUrl: "https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/users/1"
expectedStatusCode: 200
httpMethod: "GET"
expectedPayload: "Gwenborough"
responseFilterPath: "address.city"
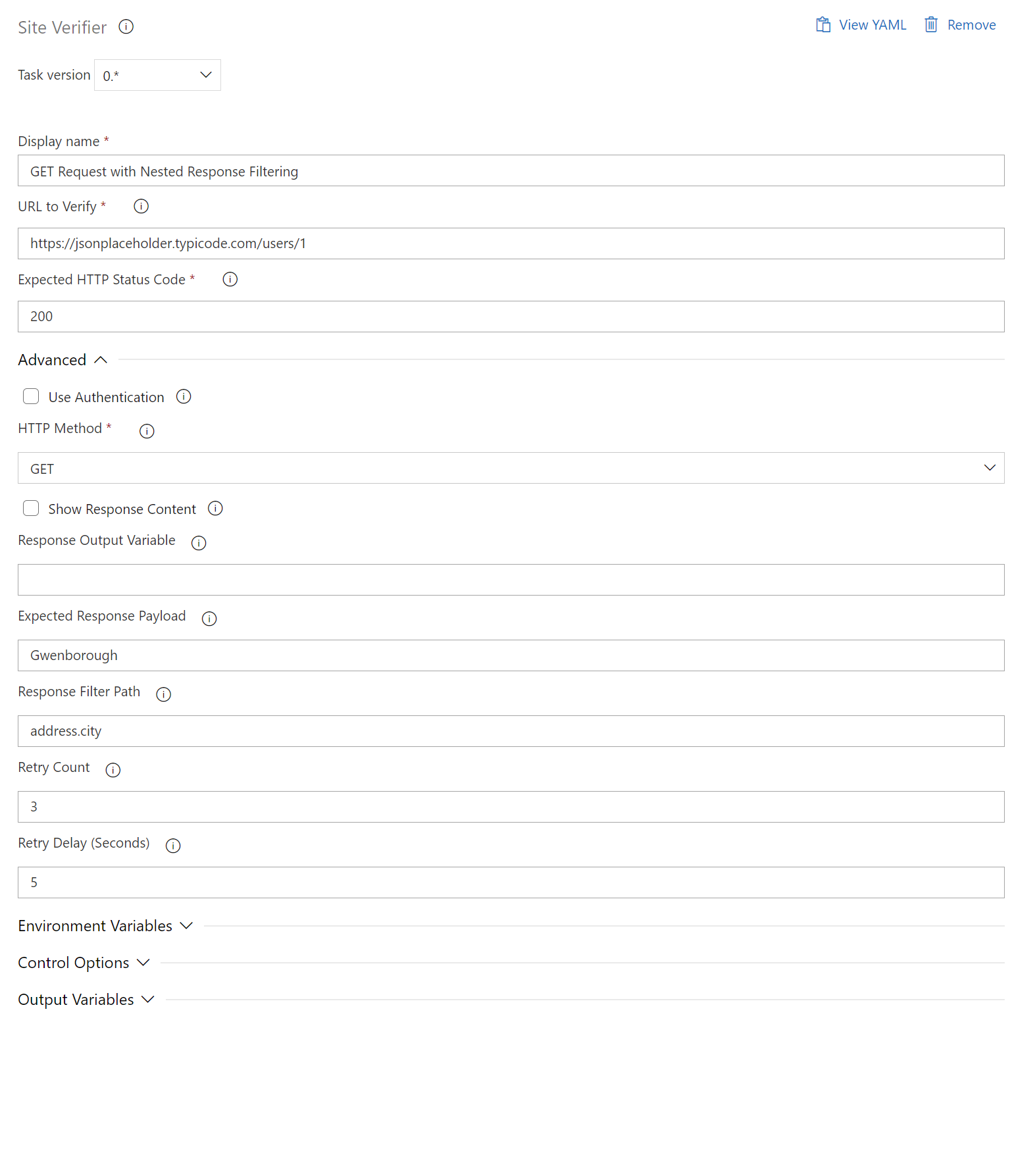
Deeply Nested Response Filtering - 2
- task: SiteVerifier@0
displayName: "GET Request with Deeply Nested Response Filtering"
inputs:
siteUrl: "https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/users/1"
expectedStatusCode: 200
httpMethod: "GET"
expectedPayload: '{ "lat": "-37.3159", "lng": "81.1496" }'
responseFilterPath: "address.geo"
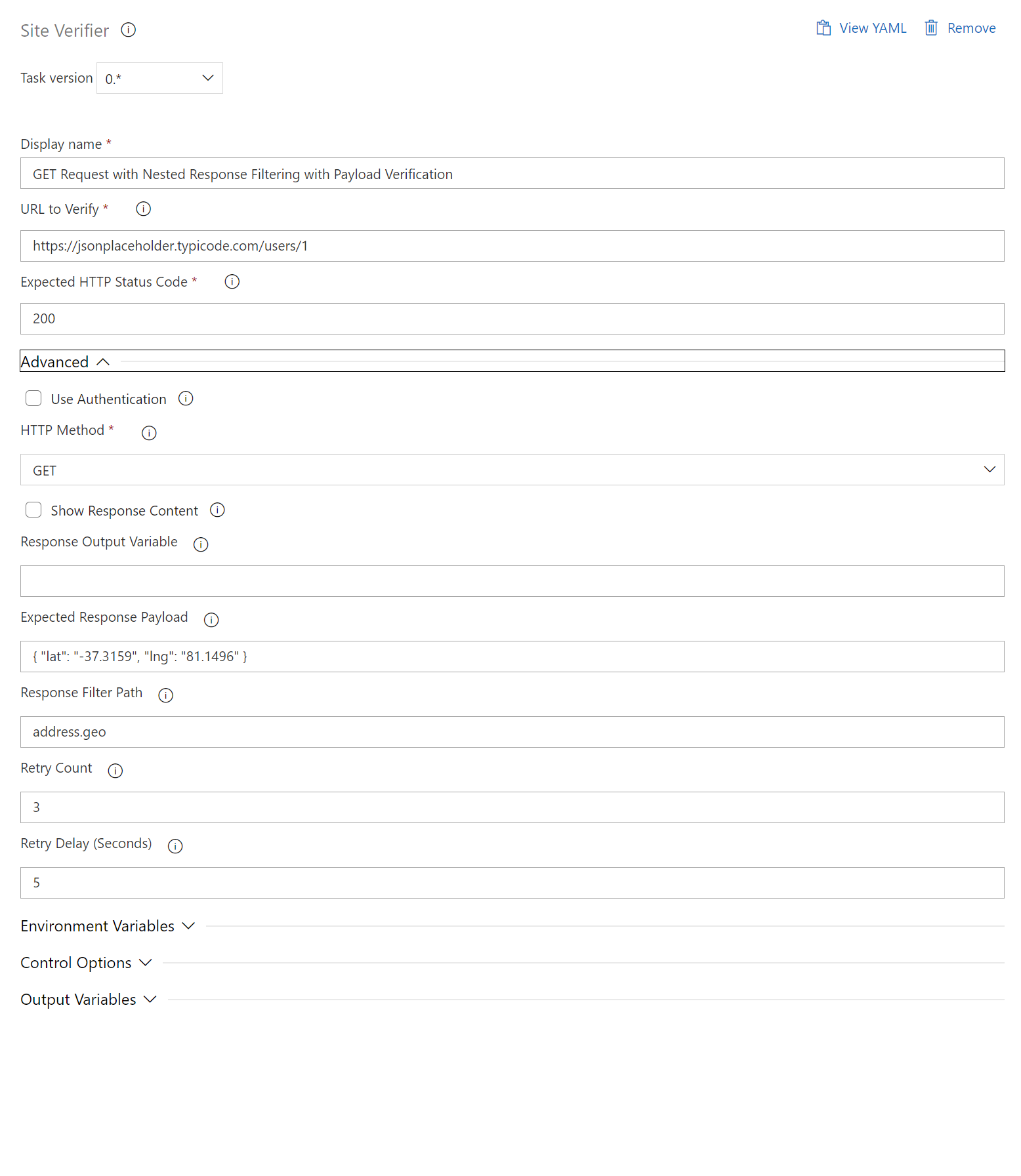
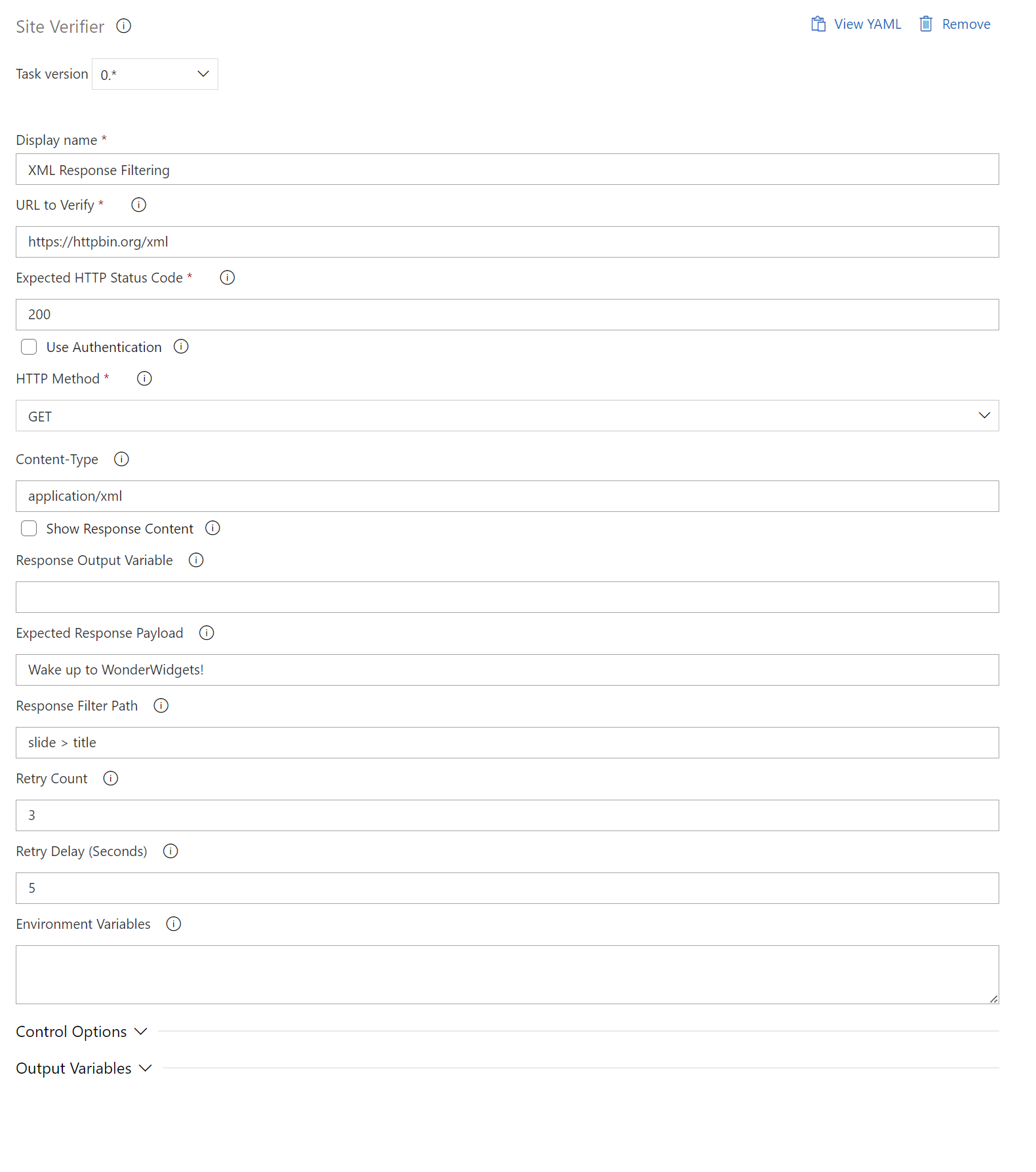
XML Response Filtering and Validation
- task: SiteVerifier@0
displayName: "Response in XML"
inputs:
siteUrl: "https://httpbin.org/xml"
expectedStatusCode: 200
httpMethod: "GET"
contentType: "application/xml"
responseFilterPath: "slide > title"
expectedPayload: "Wake up to WonderWidgets!"
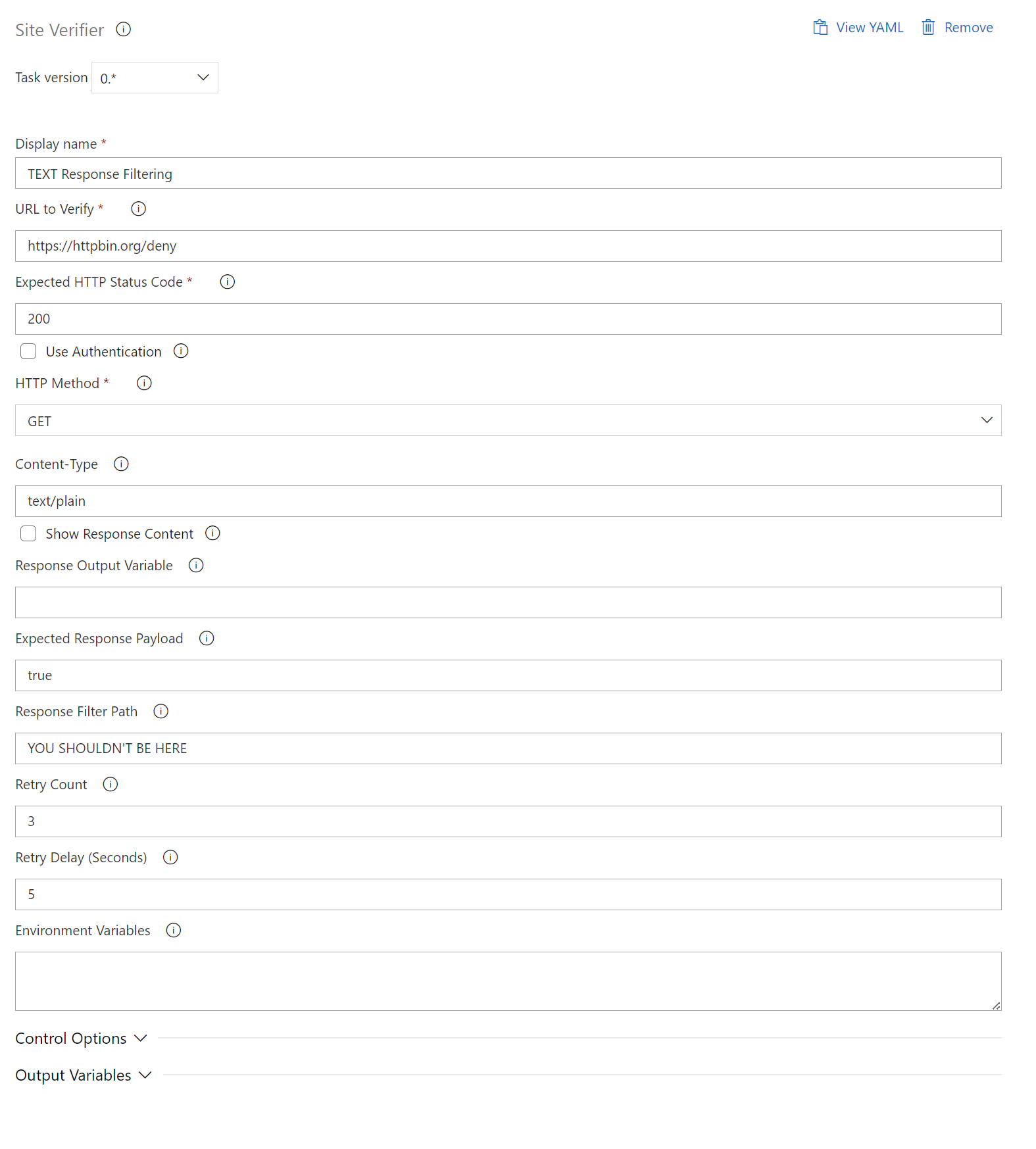
TEXT Response Filtering and Validation
- task: SiteVerifier@0
displayName: "Response in Text Plain"
inputs:
siteUrl: "https://httpbin.org/deny"
expectedStatusCode: 200
httpMethod: "GET"
contentType: "text/plain",
responseFilterPath: "YOU SHOULDN'T BE HERE"
expectedPayload: true
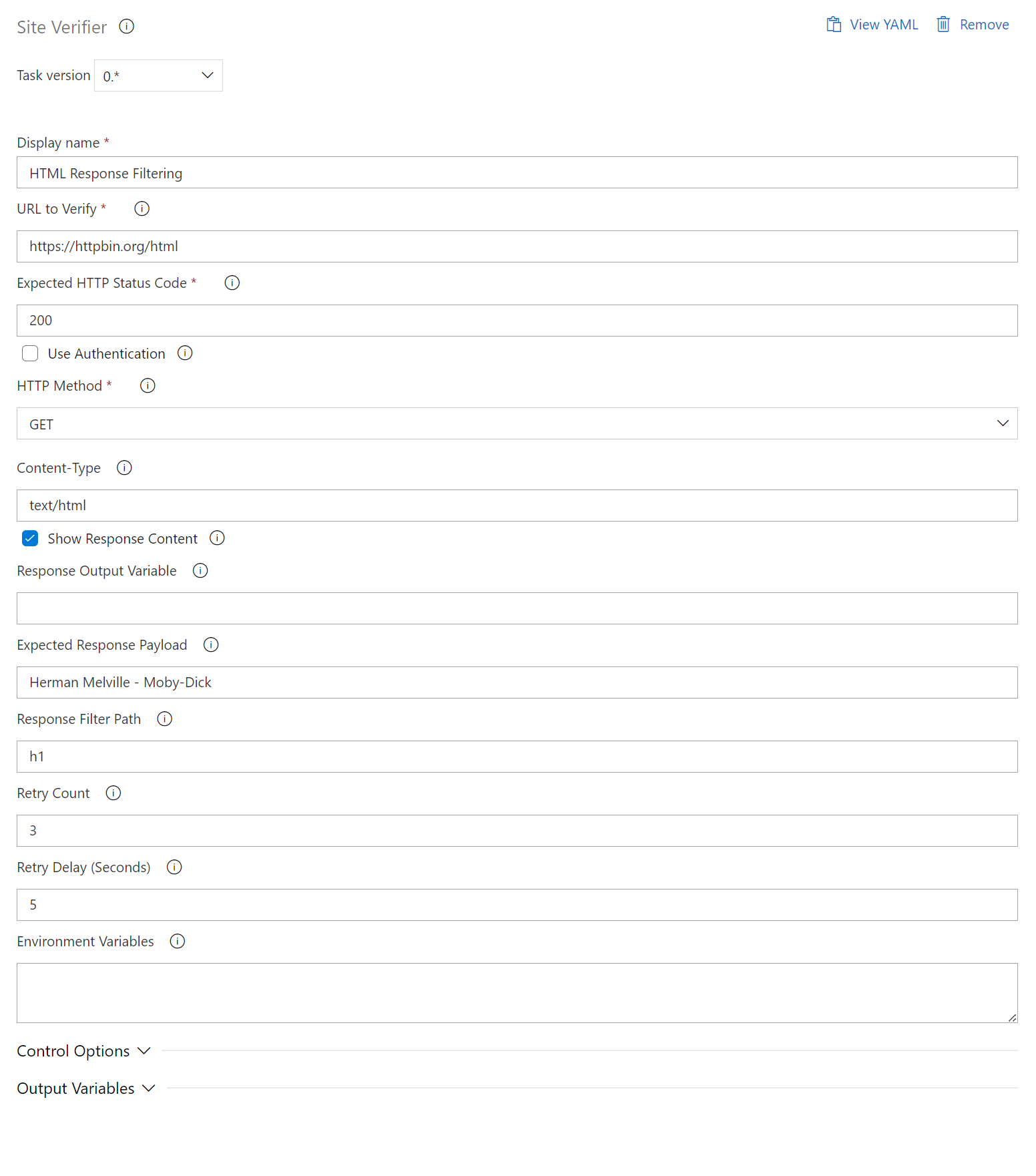
HTML Response Filtering and Validation
- task: SiteVerifier@0
displayName: "Response in HTML"
inputs:
siteUrl: "https://httpbin.org/html"
expectedStatusCode: 200
httpMethod: "GET"
contentType: "text/html"
responseFilterPath: "h1"
expectedPayload: "Herman Melville - Moby-Dick"
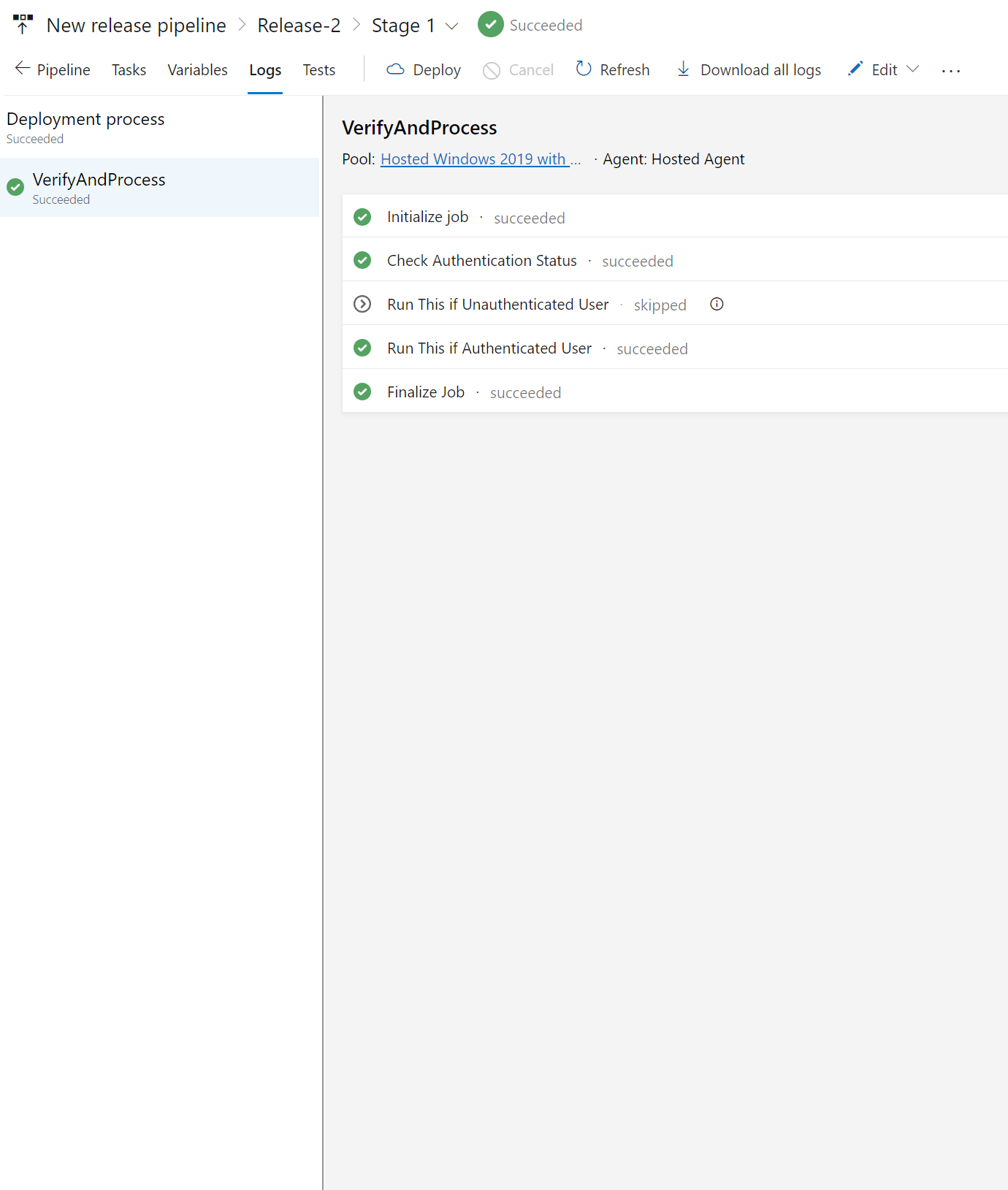
Using Response Output Variable
jobs:
- job: VerifyAndProcess
steps:
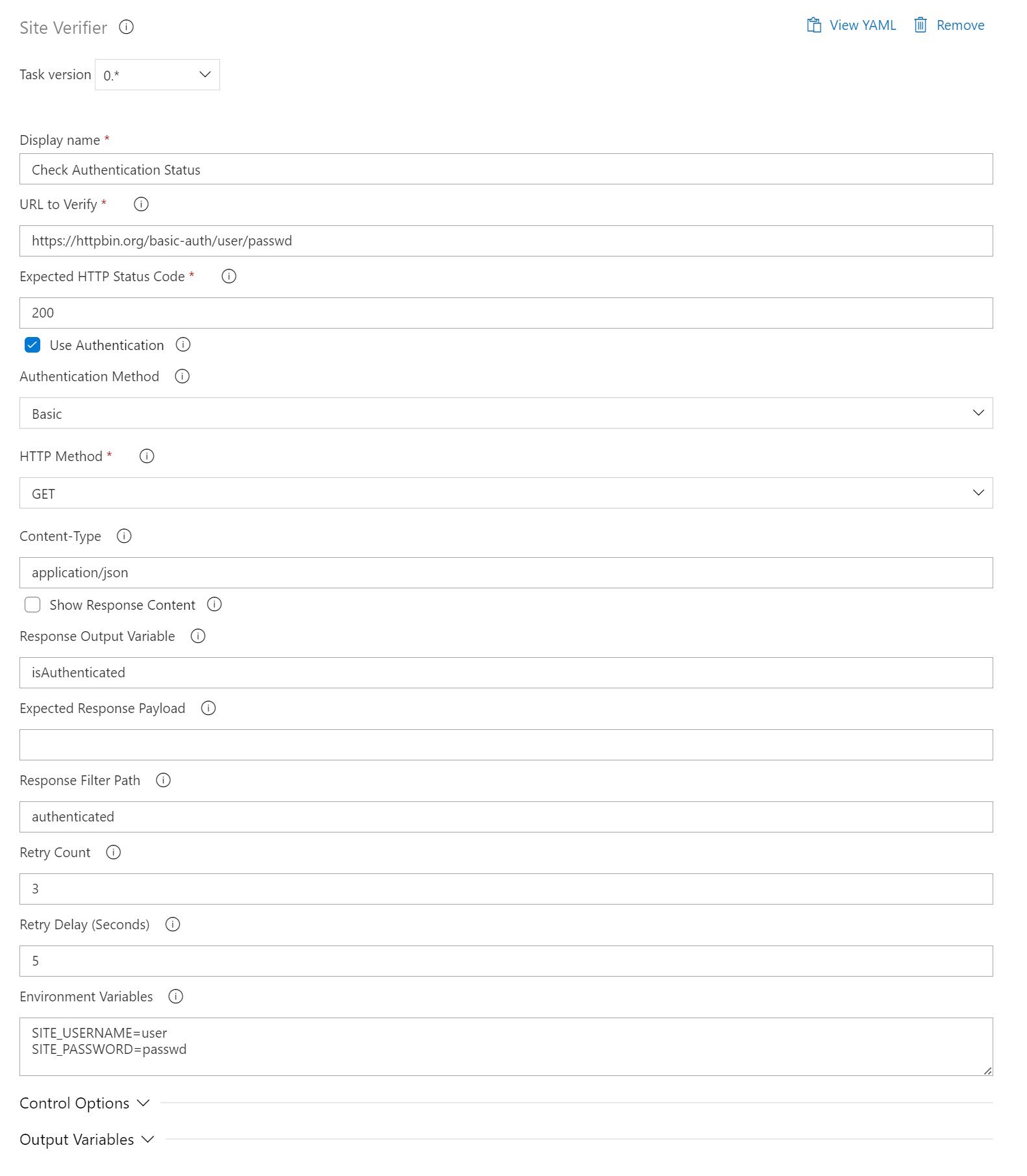
- task: SiteVerifier@0
displayName: "Check Authentication Status"
inputs:
siteUrl: "https://httpbin.org/basic-auth/user/passwd"
expectedStatusCode: 200
httpMethod: "GET"
useAuthentication: true
authenticationMethod: "basic"
responseFilterPath: "authenticated" # Filters the JSON response for the 'authenticated' property. The actual API endpoint returns a JSON object {"authenticated": true, "user": "user"}. We use this property to determine if the request was successfully authenticated.
responseOutput: "isAuthenticated" # The value of the 'authenticated' property (true or false) is stored in 'isAuthenticated'. This allows us to use the authentication status in subsequent steps.
logResponse: true
env:
SITE_USERNAME: "user"
SITE_PASSWORD: "passwd"
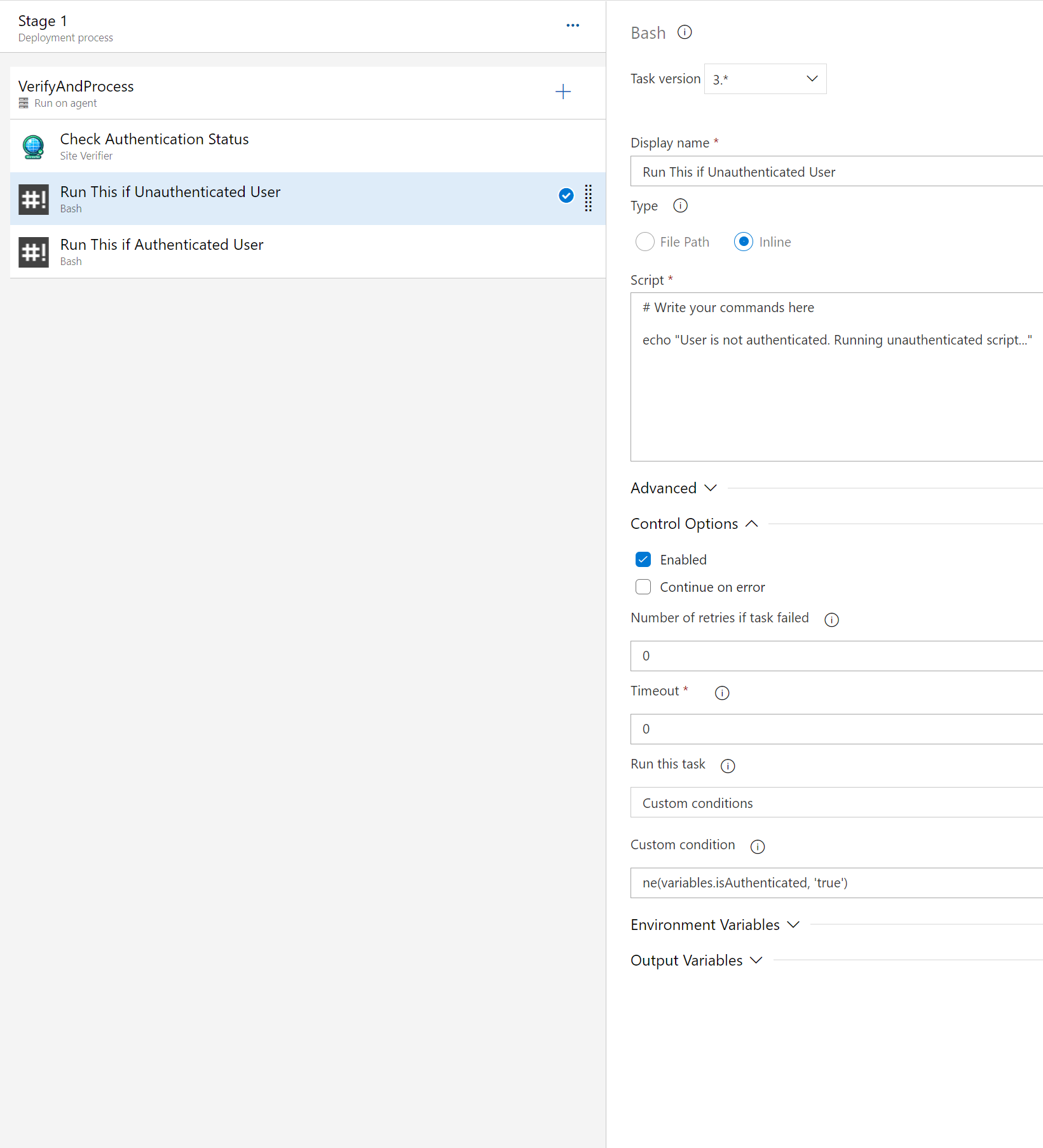
# Bash task for authenticated user
- bash: |
echo "User is authenticated. Running authenticated script..."
displayName: "Authenticated User Script"
condition: eq(variables.isAuthenticated, 'true') # This condition checks if 'isAuthenticated' equals 'true'. It confirms that the API responded with {"authenticated": true, "user": "user"}, indicating successful authentication.
# Bash task for unauthenticated user
- bash: |
echo "User is not authenticated. Running unauthenticated script..."
displayName: "Unauthenticated User Script"
condition: ne(variables.isAuthenticated, 'true') # This condition checks if 'isAuthenticated' does not equal 'true'. It indicates that the API response did not confirm authentication, either because 'authenticated' was false or the property was absent.
Using Site Verifier in Azure DevOps Release Pipelines
Introduction
The Site Verifier task integrates seamlessly into Azure DevOps Release pipelines, ensuring the availability and functionality of your web applications and APIs post-deployment. This documentation provides a comprehensive guide to configuring the Site Verifier task within a Release pipeline.
Prerequisites
Before proceeding, ensure the following prerequisites are met:
- Installation of the Site Verifier task from the Azure DevOps Marketplace.
- Adequate permissions to edit Release pipelines within your Azure DevOps project.
Configuration Steps
Follow these steps to effectively set up the Site Verifier task in your Azure DevOps Release pipeline:
1. Add the Task to Your Release Pipeline
Incorporate the Site Verifier task into your pipeline:
Tailor task parameters to your specific requirements:
URL to Verify (siteUrl): Enter the URL for verification.
Expected HTTP Status Code (expectedStatusCode): Define the expected HTTP status code.
Configure additional parameters under the Advanced section.
For sites requiring authentication:
Set up SITE_USERNAME and SITE_PASSWORD as secret variables for Basic Authentication.
Alternatively, for token-based authentication, use SITE_AUTH_TOKEN.
Ensure proper mapping and accessibility of secret variables.

Examples
Please notice the horizontal scroll to see the other use cases
Get API with Authentication
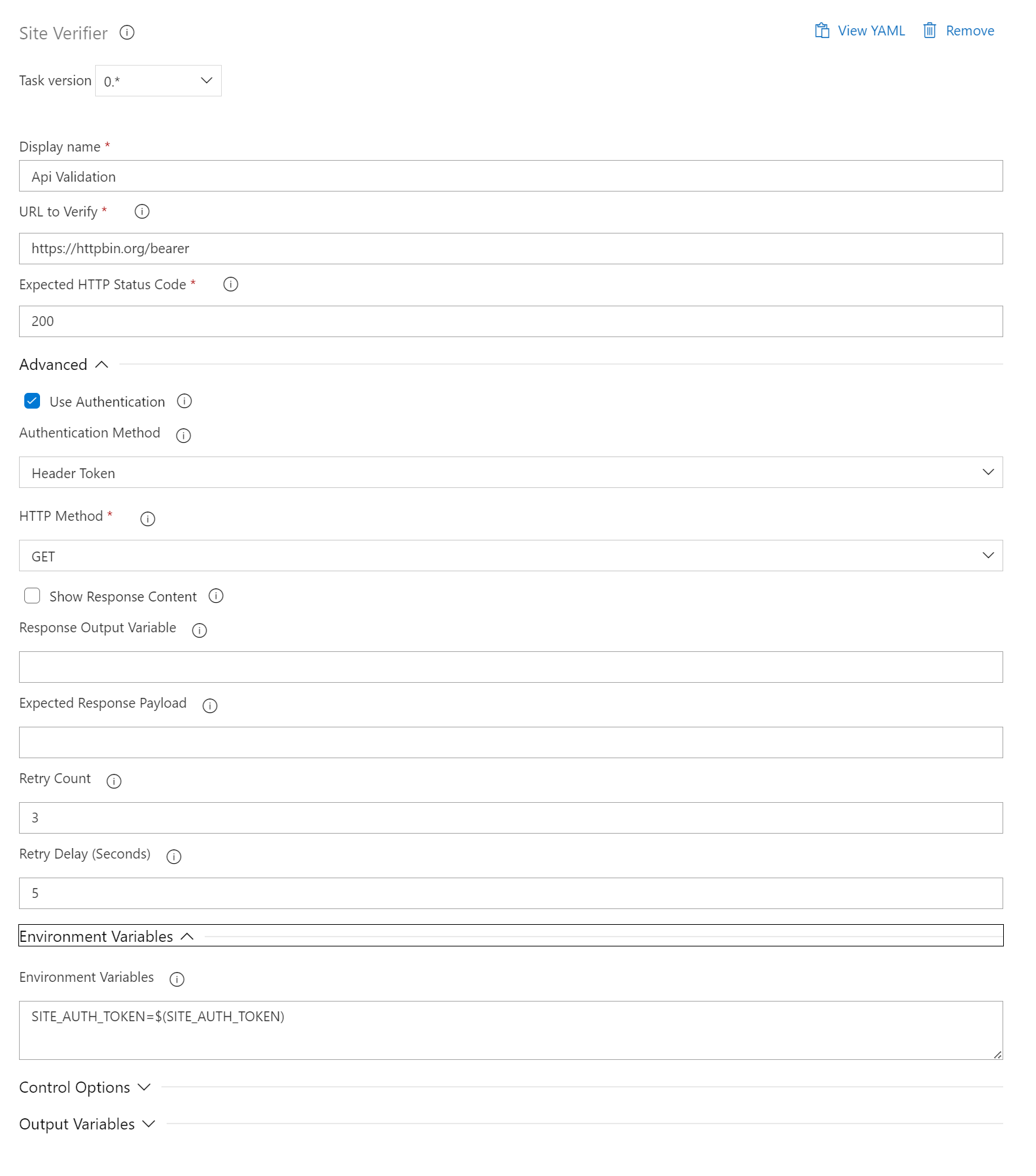
Post API with Payload Verification
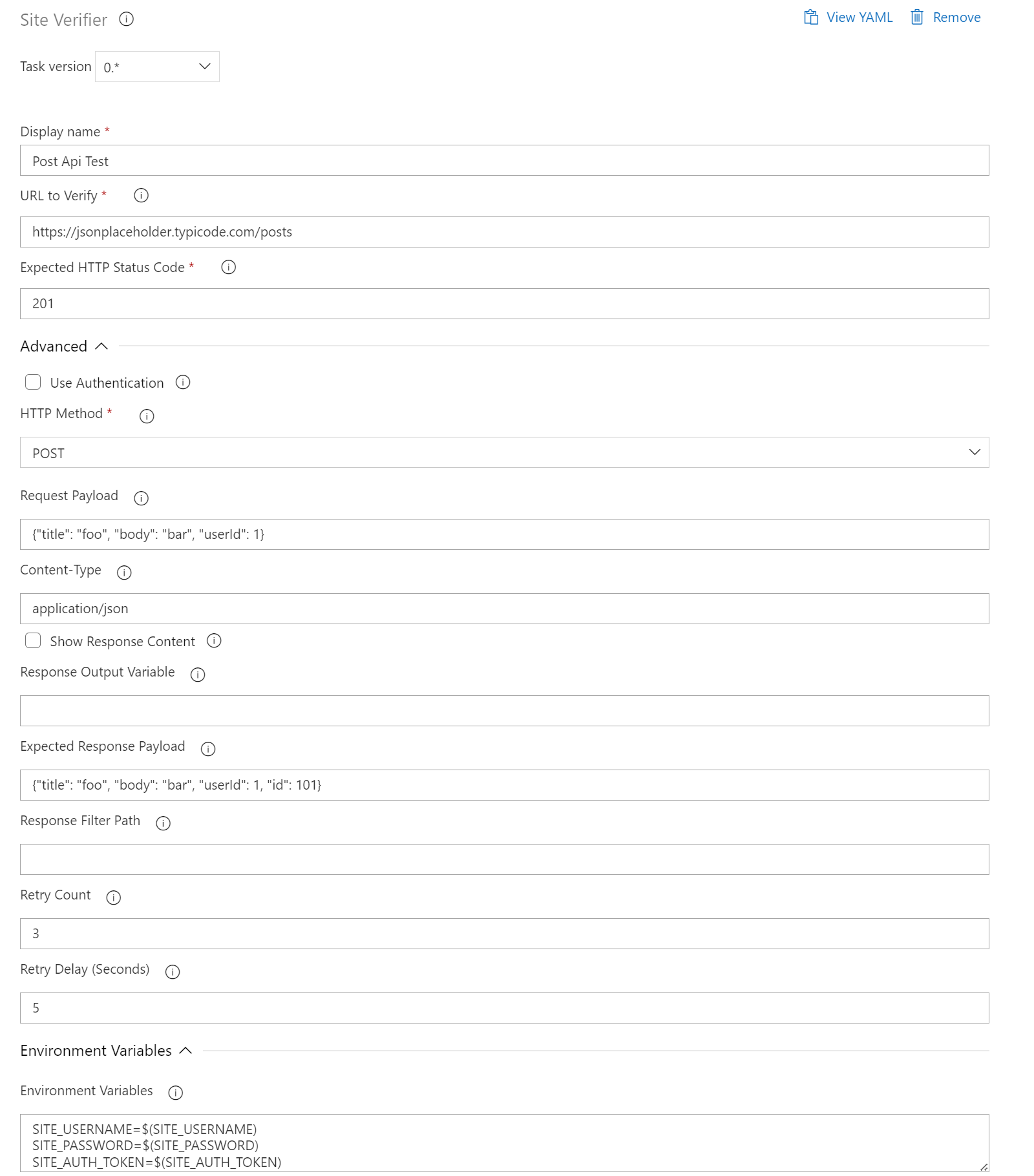
Post API
Nested Response Filter
Response Filtering Payload Verification
Response Filter (XML)
Response Filter (TXT)
Response Filter (HTML)
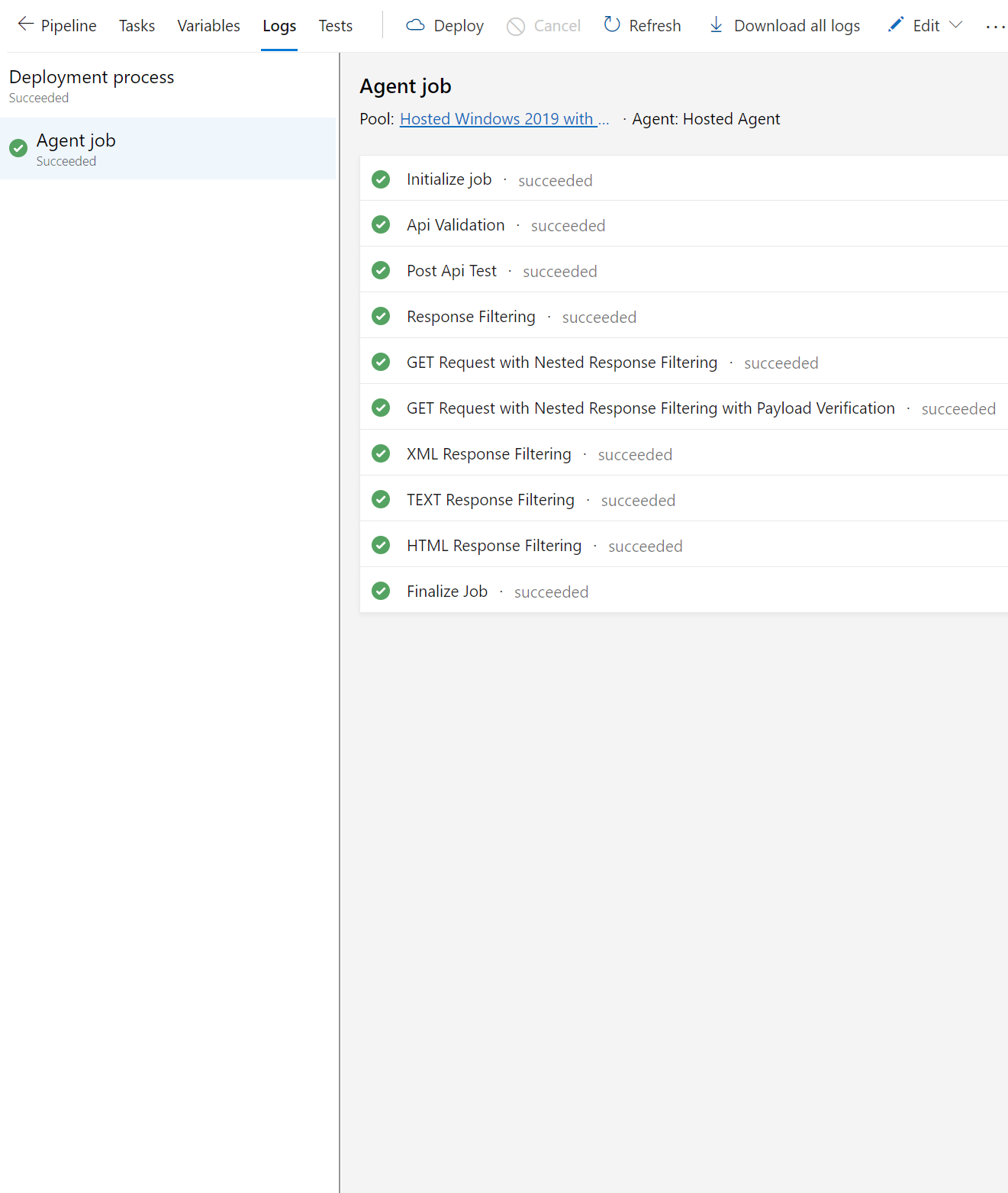
Release Tasks (Success)
Response Output
Response Output - Part 2
Response Output (Success)
Advanced Configuration (Optional)
Customize advanced parameters as needed:
- HTTP Method (httpMethod): Select the appropriate method (e.g., GET, POST).
- Use Authentication (useAuthentication): Enable if authentication is required.
- Authentication Method (authenticationMethod): Choose between Basic or Header Token.
- Request Payload (requestPayload): Provide payload for methods supporting it.
- Content-Type (contentType): Specify the Content-Type header.
- Retry Count (maxRetries) and Retry Delay (delayBetweenRetries): Configure retry settings.
- Show Response Content (logResponse): Enable logging of response content.
- Response Output Variable (responseOutput): Define variable to store response content.
- Expected Response Payload (expectedPayload) and Response Filter Path (responseFilterPath): Specify expected payload and response filter path.
- Response Filter Path (responseFilterPath): Defines JSONPath expression for JSON responses to filter data, uses CSS-like selectors with cheerio.js for HTML/XML, and specifies a substring for plain text. It aids in data validation by matching with
expectedPayload.
Execution and Results
- Save your pipeline configuration and initiate a new release for testing.
- Review logs to verify successful execution and expected site response.
Best Practices
Follow these best practices when using the Site Verifier task:
- Secure Sensitive Information: Utilize Azure DevOps secret variables for credentials.
- Optimize Retry Logic: Set appropriate retry parameters based on endpoint behavior.
- Continuous Monitoring: Regularly monitor endpoint health for timely issue detection and resolution.
Troubleshooting
Here are some tips for troubleshooting common issues:
- Authentication Failures: Verify authentication credentials and method.
- Unexpected Responses: Investigate unexpected response codes or payloads.
- Retry Issues: Adjust retry parameters and investigate endpoint stability.
- Header Configuration: Ensure correct specification of HTTP headers.
- Variable Recognition: Verify accessibility of environment variables within the pipeline context.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
- Content-Type Oversight: Ensure alignment between Content-Type header and request payload format.
- Dynamic Response Consideration: Account for dynamic elements within responses during payload expectation configuration.
Acknowledgments
















