Azure Parallel Deploy
This task simplifies deploying Azure services and minimizes total time of deployment. If you have several services you want to deploy, you can use this task to do the job.
- You will have just one step in your pipeline insted of multiple Azure App Service Deploy task steps.
- All services will be deployed in parallel, hence minimizing deployment time.
The prerequisite is that there is some pattern in the name of services on both sides — the source files and Azure service names. Althoug the inconsistence in the source naming can be fixed by renaming source files in the pipeline before running this task.
This task has several limitations compared to Azure App Service Deploy task, to mention the most notable:
- The deployment is only from ZIP files.
- No support for deployment to containers.
- No file transformations and variable substitutions.
Example
Say you have three projects with services:
- Contoso.Svc1
- Contoso.Svc1
- Contoso.Svc2
These projects are built and published so there will be three source files:
- Contoso.Svc1.zip
- Contoso.Svc1.zip
- Contoso.Svc2.zip
And in the Azure portal, you have prepared three app services where you want to deploy to:
- contoso-svc1-api
- contoso-svc2-api
- contoso-svc3-api
You can easily deploy all three services with this task:
steps:
- task: AzureParallelDeploy@1
displayName: 'Deploy services'
inputs:
ConnectedServiceName: 'service connection name'
ResourceGroup: 'resource group name'
Services: 'Svc1, Svc2, Svc3'
AppNameFormat: 'contoso-{0}-api'
AppSourceFormat: 'Contoso.{0}.zip'
Usage
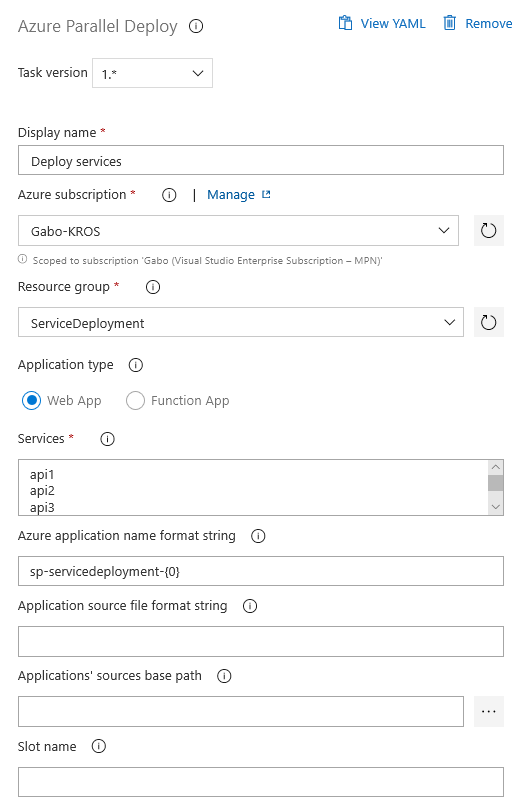
If you are using the UI, add Azure Parallel Deploy task from the Deploy category and configure it as needed:
If you are using YAML pipeline, add task with the following syntax:
steps:
- task: AzureParallelDeploy@1
displayName: 'Deploy services'
inputs:
ConnectedServiceName: 'Gabo-KROS'
ResourceGroup: 'ServiceDeployment'
Services: 'api1, api2, api3'
AppNameFormat: 'sp-servicedeployment-{0}'
This YAML syntax is for simple use, where Services input is set directly in the task. But you may want to use service names as list and not as simple string. For example when the service names are set using runtime parameter. It is convenient to have this parameter as YAML list (parameter of type object), because than it can be used in several ways, for example you can enumerate the list's values in the pipeline. But such a value cannot be directly used as input into the task, it have to be converted to string. To do that, just use join expression and make a desired string value.
parameters:
# Runtime parameter - list of values.
- name: services
type: object
default:
- api1
- api2
- api3
steps:
- task: AzureParallelDeploy@1
displayName: 'Deploy services'
inputs:
ConnectedServiceName: 'Gabo-KROS'
ResourceGroup: 'ServiceDeployment'
Services: ${{ join(',', parameters.services) }} # Convert list to string with comma delimited values.
The default value of the runtime parameter can also be written on one line:
parameters:
- name: services
type: object
default: [ api1, api2, api3 ]
Task parameters
YAML parameter name is stated in parenthesis. Parameters with asterisk are required.
Azure subscription (ConnectedServiceName) *
Azure resource manager subscription for the deployment.
Resource group (ResourceGroup) *
Resource group name in Azure Portal.
Application type (AppType)
Type of deployed applications. All deployed applications must be of the same type. The value is either WebApp or FunctionApp. If the value is not set or is invalid, WebApp is used.
Services (Services) *
Comma separated values of logical service names. These names are used for generating real service names in Azure Portal and names of source ZIP files.
Format string for app service name in Azure Portal. Format string accepts one parameter {0}, which will be replaced by the logical name of the service. For example if format string is prod-{0}-api and logical service name is forecast, the application will be deployed to prod-forecast-api app service. If the value is not set, {0} format string will be used (the name of the service in Azure Portal is the same as logical service name).
Format string for path to source ZIP files for services. Every service is deployed from single ZIP file. The format string accepts one parameter {0}, which will be replace by the logical name of the service. For example if format string is {0}-api.zip and logical service name is forecast, source file name will be forecast-api.zip. zip extension must be specified expplicitly. If the value is not set, {0}.zip format string will be used (source file name is the same as logical service name with zip extension).
Applications' sources base path (AppSourceBasePath)
Base path for services' source files. Service source zip file is searched recursively in this folder. If the value is not set, the default value is used based on the build type. If it is general build, Build.StagingDirectory value is used. If it is any other build type (release, deployment...) System.DefaultWorkingDirectory is used. Build type is determined by the System.HostType variable.
Slot name (SlotName)
The name of the slot for deployment. The same slot name is used for all deployed services.
Change Log
1.1.0
Invoke sync function triggers action after successfull deployment of Azure functions.
1.1.1
Invoke sync function triggers action must be explicitly turned on by input parameter SyncFunctionTriggers.
2.0
Add retrying.


