The tasks in this extension allow for running terraform cli commands from Azure Pipelines. The motivation for this extension was to provide terraform pipeline tasks that could execute on all build agent operating systems and provide guided task configuration.
Supported Commands
The Terraform CLI task supports executing the following commands
- version
- init
- validate
- plan
- apply
- destroy
- show
- refresh
- import
- output
- force-unlock
- fmt
- workspace
- state
Supported Public Cloud Providers
The Terraform CLI task supports the following Public Cloud providers
NOTE: It is possible to leverage other providers by providing configuration via environment variables using secure files or, -backend-config=key=value within commandOptions input.
Supported Backends
The Terraform CLI task supports the following terraform backends
NOTE: It is possible to leverage other backends by providing configuration via environment variables using secure files or, -backend-config=key=value within commandOptions input.
Compatibility with Build Agents
The tasks can be executed on all supported build agent operating systems including Ubuntu and MacOS.
(NEW) Task versions
All tasks supported by this extension (TerraformCLI and TerraformInstaller) support different versions. Each version will be the highest tag of that major version. There is also always one version which is higher than the highest major version tag: this version is unstable.
For example, currently TerraformCLI@0 and TerraformInstaller@0 will point to the version with the tag 0.7.11. TerraformCLI@1 and TerraformInstaller@1 will point to the version with the tag 1.1.0 and TerraformCLI@2 and TerraformInstaller@2 will point to the unstable version, basically the latest version which has been published to the main branch of the project.
The dedicated TerraformInstaller task allows for complete control over how frequently and on which agents terraform is installed. This prevents from having to install terraform before executing each terraform task. However, if necessary, this can be installed multiple times to support pipelines that span multiple build agents.
Install Latest Version
The installer task supports installing the latest terraform version by using the keyword latest as the version specified. This is the default option when the installer is added to a pipeline. Specifying latest will instruct the task to lookup and install the latest version of the terraform executable.
- task: TerraformInstaller@1
displayName: install terraform
inputs:
terraformVersion: latest
If terraformVersion not provided, task defaults to latest
- task: TerraformInstaller@1
displayName: install terraform
Install Specific Version
- task: TerraformInstaller@1
displayName: install terraform
inputs:
terraformVersion: 1.8.5
The task supports running terraform version individually. When run, if the version is out of date, the task will log a warning to the pipeline summary if there is a newer version of terraform available.
- task: TerraformCLI@1
displayName: 'check terraform version'
inputs:
command: version
When running the other commands, terraform version is also run so that the version is recorded to the build log. However, warnings regarding out of date versions will be suppressed to reduce noise.
The TerraformCLI task supports configuring the following public cloud providers. The task supports configuring multiple providers simultaneously to support multi-cloud deployments.
- Azure - Authenticates via Azure Resource Manager Service Connection included within Azure DevOps.
- AWS - Authenticates via AWS Service Connection made available via the AWS Toolkit extension.
- Google - Authenticates via service account JSON formatted key file uploaded to Azure DevOps secure files.
Azure Service Connection / Service Principal Integration
When executing commands that interact with Azure such as plan, apply, and destroy, the task will utilize an Azure Service Connection to authorize operations against the target subscription. This is specified via the environmentServiceName input
- task: TerraformCLI@1
displayName: 'terraform apply'
inputs:
command: apply
environmentServiceName: 'My Azure Service Connection'
# Subscription id for provider to target. This can be used to specify the subscription when using Management Group scoped
# Service connection or to override the subscription id defined in a Subscription scoped service connection
providerAzureRmSubscriptionId: 'my-backend-subscription-id'
Execute Azure CLI From Local-Exec Provisioner
When an Azure Service connection is provided and runAzLogin is set to true, the terraform CLI task will run az login using the service connection credentials. This is intended to enable templates to execute az cli commands from a local-exec provisioner.
Setting runAzLogin to true will indicate the task should execute az login with specified service connection.
- task: TerraformCLI@1
displayName: 'terraform apply'
inputs:
command: apply
environmentServiceName: 'My Azure Service Connection'
# indicate az login should be run as part of this command
runAzLogin: true
Setting runAzLogin to false will indicate the task should NOT execute az login with specified service connection.
- task: TerraformCLI@1
displayName: 'terraform apply'
inputs:
command: apply
environmentServiceName: 'My Azure Service Connection'
# indicate az login should NOT be run as part of this command
runAzLogin: false
runAzLogin will default to false when not specified; indicating the task should NOT run az login
- task: TerraformCLI@1
displayName: 'terraform apply'
inputs:
command: apply
environmentServiceName: 'My Azure Service Connection'
This should allow the following template configuation to be run using this task
resource "azurerm_storage_account" "st_core" {
name = "my-storage-account"
location = "eastus"
resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.rg_core.name
account_kind = "StorageV2"
account_tier = "Standard"
account_replication_type = "LRS"
# can now be run by the terraform cli task from azure pipelines
provisioner "local-exec" {
command = "az storage blob service-properties update --account-name ${azurerm_storage_account.st_core.name} --static-website --index-document index.html --404-document index.html"
}
}
Amazon Web Services (AWS) Service Connection / IAM User Integration
When executing commands that interact with AWS such as plan, apply, and destroy, the task can utilize AWS Service Connection to authorize operations. This is specified via the providerServiceAws input. The region can also be provided via providerAwsRegion input.
- task: TerraformCLI@1
displayName: 'terraform apply'
inputs:
command: apply
providerServiceAws: 'My AWS Service Connection'
providerAwsRegion: us-east-1
NOTE: This depends on the AWS Service Connection included with the [AWS Toolkit](AWS Toolkit extension.
When executing commands that interact with GCP such as plan, apply, and destroy, the task can utilize a JSON formatted key file uploaded to Azure DevOps Secure Files to authorize operations. This is specified via the providerGoogleCredentials input. This input should be the name of the secure file containing the JSON formatted key.
- task: JasonBJohnson.azure-pipelines-tasks-terraform.azure-pipelines-tasks-terraform-cli.TerraformCLI@1
displayName: 'terraform plan'
inputs:
command: plan
workingDirectory: $(test_templates_dir)
# Google Credentials (i.e. for service account) in JSON file format in Azure DevOps Secure Files
providerGoogleCredentials: gcp-service-account-key.json
# The default project name where resources are managed. Defining project on a resource takes precedence over this.
providerGoogleProject: gcs-trfrm-${{ parameters.stage }}-eus-czp
# The default region where resources are managed. Defining region on a resource takes precedence over this.
providerGoogleRegion: 'us-east-1'
Configuring Other Cloud Providers
Other cloud providers can be configured using secure env files. See aws_self_configured.yml for example.
The task currently supports the following backend configurations
- local (default for terraform) - State is stored on the agent file system.
- azurerm - State is stored in a blob container within a specified Azure Storage Account.
- aws - State is stored in a S3 bucket
- gcs - State is stored in Google Cloud Storage bucket
- self-configured - State configuration will be provided using environment variables or command options. Environment files can be provided using Secure Files Library in AzDO and specified in Secure Files configuration field. Command options such as
-backend-config= flag can be provided in the Command Options configuration field.
NOTE: self-configured can be used to execute deployments for other cloud providers. See aws_self_configured.yml for example.
AzureRM
If azurerm selected, the task will prompt for a service connection and storage account details to use for the backend. The task supports both Subscription and Management Group scoped service connections
- task: TerraformCLI@1
displayName: 'terraform init'
inputs:
command: init
backendType: azurerm
# Service connection to authorize backend access. Supports Subscription & Management Group Scope
backendServiceArm: 'My Azure Service Connection'
# Tenant id of the target backend. This can be used to override the default tenant id inherited from the service connection
backendAzureRmTenantId: 'my-tenant-id'
# Subscription id of the target backend. This can be used to specify the subscription when using Management Group scoped
# Service connection or to override the subscription id defined in a Subscription scoped service connection
backendAzureRmSubscriptionId: 'my-backend-subscription-id'
backendAzureRmResourceGroupName: 'my-backend-resource-group'
# azure location shortname of the backend resource group and storage account
backendAzureRmResourceGroupLocation: 'eastus'
backendAzureRmStorageAccountName: 'my-backend-storage-account'
# azure storage account sku, used when creating the storage account
backendAzureRmStorageAccountSku: 'Standard_RAGRS'
# azure blob container to store the state file
backendAzureRmContainerName: 'my-backend-blob-container'
# azure blob file name
backendAzureRmKey: infrax.tfstate
Automated Remote Backend Creation for Azure Storage - Deprecated
The task has deprecated support for automatically creating the resource group, storage account, and container for remote azurerm backend and will remove it in later versions. It was enabled with the ensureBackend input to true. If you need the storage account to be created before running terraform, please create steps prior to terraform init to create it.
AWS S3
If aws selected, the task allows for configuring a service connection as well as the bucket details to use for the backend.
- task: TerraformCLI@1
displayName: 'terraform init'
inputs:
command: init
workingDirectory: $(my_terraform_templates_dir)
# set to `aws` to use aws backend
backendType: aws
# service connection name, required if backendType = aws
backendServiceAws: env_test_aws
# s3 bucket's region, optional if provided elsewhere (i.e. inside terraform template or command options)
backendAwsRegion: us-east-1
# s3 bucket name, optional if provided elsewhere (i.e. inside terraform template or command options)
backendAwsBucket: s3-trfrm-dev-eus-czp
# s3 path to state file, optional if provided elsewhere (i.e. inside terraform template or command options)
backendAwsKey: 'my-env-infrax/dev-infrax'
Google Cloud Storage Bucket
If gcp selected, the task allows for defining gcs backend configuration. The authentication is done via a key in json file format provided by Google Cloud IAM. The key file can be uploaded to Secure Files in Azure DevOps and referenced from the task. The task will then use the key file for authentication.
- task: TerraformCLI@1
displayName: 'terraform init'
inputs:
command: init
workingDirectory: $(test_templates_dir)
backendType: gcs
# Google Credentials (i.e. for service account) in JSON file format in Azure DevOps Secure Files
backendGcsCredentials: gcs-backend-key.json
# GCS bucket name
backendGcsBucket: gcs-trfrm-alpha-eus-czp
# GCS Bucket path to state file
backendGcsPrefix: 'azure-pipelines-terraform/infrax'
Secure Variable Secrets
There are multiple methods to provide secrets within the vars provided to terraform commands. The commandOptions input can be used to specify individual -var inputs. When using this approach pipeline variables can be used as -var secret=$(mySecretPipelineVar). Additionally, either a terraform variables file or a env file secured in Secure Files Library of Azure DevOps pipeline can be specified. Storing sensitive var and env files in the Secure Files Library not only provides encryption at rest, it also allows the files to have different access control applied than that of the Source Repository and Build/Release Pipelines.
- task: TerraformCLI@1
displayName: 'terraform plan'
inputs:
command: plan
environmentServiceName: 'My Azure Service Connection'
# guid of the secure file to use. Can be standard terraform vars file or .env file.
secureVarsFile: 446e8878-994d-4069-ab56-5b302067a869
# specify a variable input via pipeline variable
commandOptions: '-var secret=$(mySecretPipelineVar)'
The name of the secure file can also be used.
- task: TerraformCLI@1
displayName: 'terraform plan'
inputs:
command: plan
environmentServiceName: 'My Azure Service Connection'
# name of the secure file to use. Can be standard terraform vars file or .env file.
secureVarsFile: my-secure-file.env
# specify a variable input via pipeline variable
commandOptions: '-var secret=$(mySecretPipelineVar)'
Secure Env Files
If the Secure Variables file name is *.env, it is referred as .env file. This task loads environment variables from the .env file.
.env file example
KEY1=VALUE1
KEY2=VALUE2
The TerraformCLI task supports running the Terraform output command. When this is run, pipeline variables will be created from each output variable emitted from the terraform output command. Sensitive variables will be set as secret pipeline variables and their values will not be emitted to the pipeline logs.
For example, an output variable named some_string will set a pipeline variable named TF_OUT_SOME_STRING.
This feature currently only supports primitive types string, bool, and number. Complex typed outputs such as tuple and object will be excluded from the translation.
Template has output defined
output "some_string" {
sensitive = false
value = "somestringvalue"
}
output "some_sensitive_string" {
sensitive = true
value = "some-string-value"
}
Pipeline configuration to run terraform output command
- task: TerraformCLI@1
displayName: 'terraform output'
inputs:
command: output
# ensure working directory targets same directory as apply step
# if not specified $(System.DefaultWorkingDirectory) will be used
# workingDirectory: $(my_terraform_templates_dir)
NOTE: workingDirectory must be set to the same working directory that is used to execute other operations such as apply. The default for workingDirectory is $(System.DefaultWorkingDirectory) when not specified.
Use output variables as pipeline variables
- bash: |
echo 'some_string is $(TF_OUT_SOME_STRING)'
echo 'some_sensitive_string is $(TF_OUT_SOME_SENSITIVE_STRING)'
displayName: echo tf output vars
Note that $(TF_OUT_SOME_SENSITIVE_STRING) will be redacted as *** in the pipeline logs.
The extension includes a feature to render terraform plans within the pipeline run summary. To use this feature the publishPlanResults input must be provided when running terraform plan via the TerraformCLI task. The input should be set to the name that should be assigned to the plan (however, do not use the name of a subfolder in the working directory).
Important - When enabling publishPlanResults the -detailed-exitcode option will be added when running terraform plan if it was not already provided in the commandOptions input. This will cause TERRAFORM_LAST_EXITCODE to be 2 when plan includes changes; which is a successful exitcode. Additionally, warnings will be logged to the pipeline summary when changes are present as a means to alert that changes will be made if the templates are applied.
- task: TerraformCLI@1
displayName: 'terraform plan'
inputs:
command: plan
environmentServiceName: 'My Azure Service Connection'
publishPlanResults: 'my_plan_name'
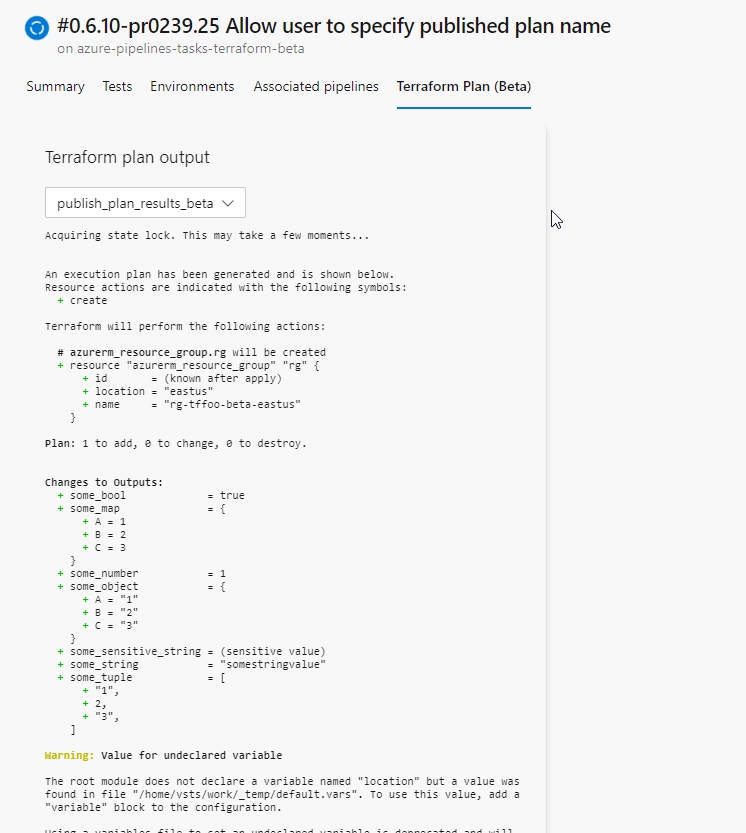
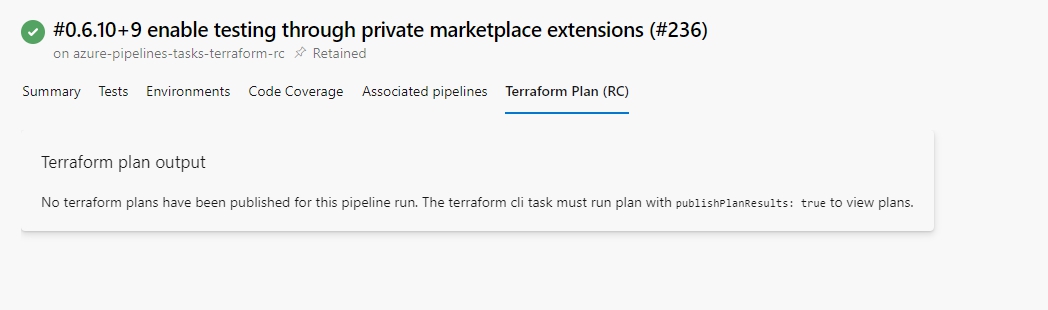
If the publishPlanResults input is not provided, then no plans will be published. In this case, the view will render empty with a message indicating no plans were found.
**Note The name set on publishPlanResults is only used for rendering in the view. It does not cause the cli to implicitly save plan output on the agent with that name.
When running terraform plan with -detailed-exitcode, a pipeline variable will be set to indicate if any changes exist in the plan. TERRAFORM_PLAN_HAS_CHANGES will be set to true if plan detected changes. Otherwise, this variable will be set to false. This can be used in conjunction with Custom Condition expression under Control Options tab of the task to skip terraform apply if no changes were detected.
- task: TerraformCLI@1
displayName: 'terraform plan'
inputs:
command: plan
environmentServiceName: 'My Azure Service Connection'
commandOptions: '-out=$(System.DefaultWorkingDirectory)/terraform.tfplan -detailed-exitcode'
Run apply only if changes are detected.
- task: TerraformCLI@1
displayName: 'terraform apply'
condition: and(succeeded(), eq(variables['TERRAFORM_PLAN_HAS_CHANGES'], 'true'))
inputs:
command: apply
environmentServiceName: 'My Azure Service Connection'
commandOptions: '$(System.DefaultWorkingDirectory)/terraform.tfplan'
The task now has the ability to set a pipeline variable TERRAFORM_PLAN_HAS_DESTROY_CHANGES if a generated plan has destroy operations. To utilize this, run terraform plan and set the -out=my-plan-file-path to write the generated plan to a file. Then run terraform show and provide the path to the generated plan file in the Target Plan or State File Path input field. If show, detects a destroy operation within the plan file, then the pipeline variable TERRAFORM_PLAN_HAS_DESTROY_CHANGES will be set to true.
- task: TerraformCLI@1
displayName: 'terraform plan'
inputs:
command: plan
environmentServiceName: 'My Azure Service Connection'
commandOptions: '-out=$(System.DefaultWorkingDirectory)/terraform.tfplan'
Run show to detect destroy operations
- task: TerraformCLI@1
displayName: 'terraform show'
inputs:
command: show
inputTargetPlanOrStateFilePath: '$(System.DefaultWorkingDirectory)/terraform.tfplan'
Skip apply if destroy operations
- task: TerraformCLI@1
displayName: 'terraform apply'
condition: and(succeeded(), eq(variables['TERRAFORM_PLAN_HAS_DESTROY_CHANGES'], 'false'))
inputs:
command: apply
environmentServiceName: 'My Azure Service Connection'
commandOptions: '$(System.DefaultWorkingDirectory)/terraform.tfplan'
Workspaces
The task supports managing workspaces within pipelines. The following workspace subcommands are supported.
Workspace Select
- task: TerraformCLI@1
displayName: select workspace foo
inputs:
workingDirectory: $(terraform_templates_dir)
command: workspace
workspaceSubCommand: select
workspaceName: foo
Workspace New
- task: TerraformCLI@1
displayName: select workspace foo
inputs:
workingDirectory: $(terraform_templates_dir)
command: workspace
workspaceSubCommand: new
workspaceName: foo
Importing resources
The task supports importing existing resources.
Import
- task: TerraformCLI@1
displayName: 'terraform import env'
inputs:
command: import
workingDirectory: $(terraform_templates_dir)
resourceAddress: azurerm_resource_group.myrg # The resource type and name in your .tf file
resourceId: "/subscriptions/000-...-0000/resourceGroups/MyRG" # The Azure object id for the Resource Group (see with `az group list` in Powershell)
State Management
The task supports managing state within pipelines. The following state subcommands are supported.
State List
- task: TerraformCLI@1
diplayName: 'terraform state list'
inputs:
command: state
workingDirectory: $(terraform_templates_dir)
stateSubCommand: list
stateSubCommandAddresses: module.my_module
State Move
- task: TerraformCLI@1
diplayName: 'terraform state mv'
inputs:
command: state
workingDirectory: $(terraform_templates_dir)
stateSubCommand: mv
stateMoveSource: azurerm_resource_group.myrg
State Remove
- task: TerraformCLI@1
diplayName: 'terraform state rm'
inputs:
command: state
workingDirectory: $(terraform_templates_dir)
stateSubCommand: rm
stateSubCommandAddresses: azurerm_resource_group.myrg,azurerm_resource_group.yourrg
Force Unlock
- task: TerraformCLI@
displayName: 'terraform force-unlock'
inputs:
command: forceunlock
lockID: '6b49ea93-d4bb-6d06-4a88-63189f162bf7'




